MTE119 - Solution Problem 4.3
description
Transcript of MTE119 - Solution Problem 4.3
-
Mechatronics Engineering
NAME & ID DATE MTE 119 STATICS EXAMPLE PROBLEM
CHAPTER 4
PAGE
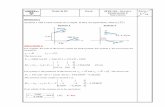
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 4.3: (REFER TO P.4-96 TEXTBOOK)
Goal:
Determine the resultant couple moment of the two couples that act on the pipe assembly.
Given:
The distance from A to B is 400d mm= . Express the result as a
Cartesian vector.
SOLUTION:
Plan:
Find the position vector for both couples (draw FBD if diagram above is not enough)
Define the force vectors Calculate the couple moments and find the resultant by adding them both
Execute:
First, let us verify equilibrium
( )0 : 50 50 0xF = + = 0yF = ( )0 : 35 35 0zF = + =
Position Vector:
The position vector from A to B is:
( ) ( ) ( ) 0.35 0.35 0.4cos30 0 0.4sin 30 0ABr i j k= + + D DJJG m 0.3464 0.2ABr j k= +
JJGm
Force Vectors:
1 35F k=JG N 2 50F i= JG N
12
-
Mechatronics Engineering
NAME & ID DATE MTE 119 STATICS EXAMPLE PROBLEM
CHAPTER 4
PAGE
Couple Moments:
The respective couple moments are given by:
( ) 11C ABM r F= JJG JJG
( )
10 0.3464 0.20 12.20 0 35
C
i j kM i= =
N-m
and,
( ) 22C ABM r F= JJG JJG
( )
1
0 0.3464 0.20 10.0 17.350 0 0
C
i j kM j k= =
N-m
Then, the resultant couple moment is:
( ) ( ) ( )1 2
R C CM r F M M= = +JJG G JG JJG JJG 12.2 10.0 17.3RM i j k= JJG N-m
VERY IMPORTANT:
Note that the moment RMJJG
must be reacted at some point in the structure for it to be in equilibrium. This will occur at the point in where the structure is built-in or fixed to the wall (i.e. the origin of coordinates in this case).
2