Ms. Liedman · Web viewSurface Area: The sum of the areas of all the faces (lateral and bases)....
Transcript of Ms. Liedman · Web viewSurface Area: The sum of the areas of all the faces (lateral and bases)....

11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections
Polyhedron: A 3-dimensional figure whose surfaces are polygons.
Faces: Each polygon surface.
Edge: The segment formed by the intersection of the faces.
Vertex: The point where edges intersect.
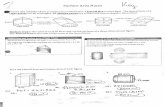
Ex: How many vertices, edges, and faces? List them.
Vertices: 6 (R,S,T,U,V,W)
Edges: 9 (RS, RV, SW, VW, UV,TW, UT, RU, ST)
Faces: 5 (ΔRUV, ΔSTW, STUR, SRVW, UTWV)
F + 20 = 30 + 2 20 + 12 = E + 2
F = 12 30 = E
Net: A 2-dimensional drawing that you can fold and make a 3-D figure.

Draw a net for the pyramid.
Cross Section: The intersection of a solid and a plane. (A slice of the solid)
Ex: What are the cross sections of the cones?
Triangle Circle

11.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders
Prism: A polyhedron with two congruent and parallel faces (bases)
-Name prisms using the shape of the base.
-Lateral Faces: The non parallel faces
Lateral Area: The sum of the areas of all the lateral faces.
Surface Area: The sum of the areas of all the faces (lateral and bases).

Find the surface area.
1. Lateral Area: (LA = ph)
= (4+4+3+3) (5) = 70
2. Area of base: 4(3) = 12
3. Surface Area: LA + 2(Area of Base)
= 70 + 2(12) = 94 cm²
1. Find 3rd side of the triangular base:
3² + 4² = x²
X = 5
2. Lateral Area (LA = ph)
LA = (3 + 4 + 5)(6) = 72
3. Area of base: ½(3)(4) = 6
4. Surface Area: LA + 2(Area of Base)
= 72 + 2(6) = 84 cm²

Find the surface area.
LA = 2πrh = 2π(2)(10) = 40π
Area of base: 2²π = 4π
Surface Area: LA + 2Area of Base
= 40π + 2(4π) = 48π m²
LA = 2π(5)(30) = 75π
Area of base: 5² π = 25π
SA = 75π + 2(25π) = 125π cm²

11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones
Height: The altitude of the whole pyramid.
Slant height: Height of the lateral face
Find the surface area.
LA= ½ pl
= ½(52)(8) = 208
Area of base = 169
SA = LA + Area of base
= 208 + 169 = 377 m²
Area of base = 100
Slant height: 5² + 12² = c²
169 = c²
C = 13
LA = ½(40)(13) = 260
SA = 260 + 100 = 360 m²

Find the surface area. Leave in terms of π.
LA = πrl
= 6(12)π = 72π
Area of base = 6²π = 36π
SA = LA + Area of base
= 72π + 36π = 108π in²
Find the surface area. Round to the nearest tenth.
Slant height = 8² + 14² = c²
260 = c²
C = 16.1
LA = 8(16.1)π = 404.6
Area of the base: 8²π = 201.1
SA = 404.6 + 201.1 = 605.7 in²

11.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
Volume: The space that a figure occupies.
Ex: Find the volume of the prism.
V = 5(3)(4) = 60 ft³ V = ½(10)(6)(5) = 150 m³

Ex. Find the volume. Leave in terms of π.
V = 2²π(10) = 40π m³

11.5 Volumes of Pyramids and Cones
Ex: Find the volume.
V = 1/3(10)(10)(9) = 300 in³
Height: x² + 5² = 12²
x² = 119
x = 10.9
V = 1/3(10)(10)(10.9) = 363.3 m³

Ex. Find the volume.
V= 1/3(64π)(14) = 298.7π in³
Height: h² + 6²= 12²
h = 10.4
V = 1/3(36π)(10.4) = 124.8π in³

11.6 Surface Area and Volumes of Spheres
Ex: Find the surface area.
SA = 4(5²)π = 100π m² SA = 4(6²)π = 144π cm²
Ex: Find the surface area given the circumference.
A grapefruit with C = 14 cm
π d = 14
d = 14/π = 4.5 (r = 2.25)
SA = 4(2.25²)π = 63.6

Ex. Find the volume.
V = 4/3(5³)π = 4/3(25π) = 100π/3 V = 4/3(6³)π = 4/3(216π) = 288π
Ex. A sphere has a volume of 900 in³. What is the surface area?
4/3 r³π = 900
r³π = 675
r³ = 214.9
r = 6.0
SA = 4(6²)π = 144π in²

11.7 Areas and Volumes of Similar Solids
Similar solids: Solids with the same shape and proportional dimensions.
Ex:
Yes 6/5
Ex. Compare the first figure to the second.
Scale Factor: ½
Area scale factor: ¼
Volume scale factor: 1/8
Ex. Each pair of figures is similar. Find the scale factor of the smaller figure to the bigger figure.
250π/432π
Simplify to get 125/216
Cube root to get 5/6

18/32
Simplify to 9/16
Square root to get ¾