Mitosis and Meiosis Summary
-
Upload
carlos-rocha -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Mitosis and Meiosis Summary
-
8/12/2019 Mitosis and Meiosis Summary
1/1
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS SUMMARY
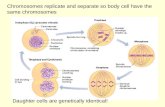
INTERPHASE: It is not a stage in mitosis, is a preparation phase. It is the busiest phase ofthe cell cycle.
a) Cell grows in size and protein production is high. (G1)b) Cell copies the chromosomes and form chromatids.(S)c) Mitochondrion and other organelles for reproduction are manufactured.(G1)d) Cell prepares for mitosis. (G2)
MITOSIS STAGES
1. Prophase: The nucleus begins to disappear and the nucleolus disintegrate, thechromosomes appear clearly. Structures are completely absent, centrioles begin tomigrate to opposite ends of the cell. The spindle appears and the chromosomesbegin to line up in the middle of it.
2. Metaphase: In this stage chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers bytheir centromeres. This arrangement is important because it ensures that each newcell receives an identical and complete set of chromosomes.
3. Anaphase: Separation of chromatids begin and are pulled apart by the shorteningspindle fibers. Cell cleavage begins.
4. Telophase: Final stage that begins as the chromatids reach the opposite poles ofthe cell. All organelles and structures begin to appear as the new cells prepare fortheir own independent existence. The chromosomes leave the spindle and nucleusis formed.
MITOSIS IMPORTANCE
Mitosis guarantees genetic continuity, resulting two new cells that carry out the samecellular processes and functions as the parent. This is the way tissues and organs growexcept for neurons.
MEIOSIS 1 STAGES
1. Prophase 1: As chromosomes line up the cross over or recombination is takingplace to mix the characteristics.
2. Metaphase 1: Centromere attaches to spindle so homologous chromosomes arelined up side by side.
3. Anaphase 1: Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends ofthe cell.
4. Telophase 1: spindle break down chromosomes and cytoplasm divides to give 2daughters with double number of chromosomes (diploid).
MEIOSIS 2 STAGES
1. Prophase 2 JUST AS IN MITOSIS EXCEPT FOR REPLICATION
2. Metaphase 2 OF CHROMOSOMES GIVING 4 HAPLOID = GAMETES3. Anaphase 24. Telophase 2
MEIOSIS IMPORTANCE
Cells formed by mitosis are identical to each other and to the parent cell. Recombination orcrossing over during meiosis 1 provides a way to rearrange the genetic information andgive genetic variation to the daughter cells.The behavior of chromosomes in meiosis provides the physical basis for explainingMendels results in genetics.