Mitosis
-
Upload
white-tiger -
Category
Science
-
view
188 -
download
1
Transcript of Mitosis

CELL CYCLE AND DIVISON
MITOSIS IN HUMAN CELLS

What Are Cells?• Cells are the structural and functional unit of life• They house many organelles, each with a specific task.• Cells vary in in size and shape depending on their specific functions.
Example: RBCs are disc shaped to easily flow in blood and don’t have nucleus to increase the surface area to carry oxygen and can squeeze through the tiniest capillaries• The three basic features of a cell are:
I. Plasma MembraneII. NucleusIII. Cytoplasm

The Nucleus-Brain of the cell• It’s the control centre of the cell• It houses a nucleolus (centre of RNA synthesis), and
chromatin material and enclosed by a nuclear membrane• The chromatin material contains DNA, which says who
you are.

There are two types of Cell Division• Mitosis: A complete set of DNA is replicated (all 23 pairs in case
of human cells). The genetic material of the daughter cells are exactly same as that of the parent cell.
Example: replication of epithelial tissues• Meiosis: Half of the complete set of DNA is replicated (exactly 23
in case of human cells). Only half of the genetic material is replicated and therefore the daughter cell cannot replicate unless another set of genetic material doesn’t fuse with the existing set.
Example: creation of an ova or a sperm cell

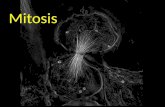
MITOSISTHIS .PPT EXPLAINS THE PROCESS OF MITOSIS IN EUKARYOTIC ANIMAL
CELLS ONLY

Preview Of Cell Cycle • INTERPHASE
I. G1- Gap1/Growth1II. S- Synthesis Of Chromatin MaterialIII. G2- Gap2/Growth2
• M- PHASEI. Mitosis- occurs in
a) Prophaseb) Metaphasec) Anaphased) Telophase
II. Cytokenesis

The Cell Cycle

INTERPHASE

The G1 Stage• More Cytoplasm and Organelles and synthesized • The cell grows larger• Functions normally
S stage• Synthesis Stage• The DNA is replicated

The G2 Stage
• The cell is ready for division •Organelles required for division are ready•Organelles and proteins are synthesized• Interphase completes after this stage

MITOTIC (M) PHASE

• MITOSIS

Prophase• Chromatin condenses into
Chromosomes which consists of two chromatids connected by the centromere
• Centrosome splits into two centrioles which move to opposite poles of the cell
• The centrioles fix themselves firmly to their respective poles through a kind of microtubule called Asters
• The Nuclear Membrane and the Nucleolus of the Nucleus Dissolve .
• Spindle fibres or Kinetochore (another type of microtubule) produced by the centrioles attach to the centromere of each chromosomes.

Metaphase• Centrioles pull chromosomes to the equator of the cell• An imaginary line passes through the equator of the cell called
Metaphase Plate

Anaphase• Occurs rapidly• Sister chromatids are pulled apart -in a chromosome a single chromatid
contains one set of DNA (23 pairs in case of humans)

Telophase• Chromatids reach to pole of the cell and decondense• Nuclear membrane and Nucleolus reform• Kinetochores and Asters dissolve
NEW ORGANELLES, NUCLEUS ETC. COME
TO ONE SIDE
OLD ORGANELLES AND GENETIC
MATERIAL COME TO THE OTHER SIDE

• CYTOKENESIS

CYTOKENESIS• Cytoplasm divides• Cleavage furrow forms in the cell membrane
CLEAVAGE FURROW

Picture Gallery

THANK YOU .PPTs EXPLAINING THE MEIOSIS AND CELL DIVISION IN PLANTS WILL BE
RELEASED SOON
-By Aryaman