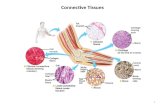
Microbial Challenge Host Immuno- inflammatory response Connective tissue and bone metabolism...
-
Upload
corey-french -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
1
Transcript of Microbial Challenge Host Immuno- inflammatory response Connective tissue and bone metabolism...

Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Connective tissue and bone metabolism
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Environmental and acquired risk factors
Genetic risk factors
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Pathogenesis of Periodontitis

Pathogenesis of Periodontitis
Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Bacteria attacking the body• Antigens• Lipopolysaccharides• Other virulence factors

Pathogenesis of Periodontitis
Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Bacteria attacking the body• Antigens• Lipopolysaccharides• Other virulence factors
The body defense:• Antibodies• Neutrophils

Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Connective tissue and bone metabolism
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Inflammatory response releases:• Cytokines• Prostanoids• Matrix Metalloproteinases
Pathogenesis of Periodontitis

In Patient A, who is NOT susceptible to periodontitis:
Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Connective tissue and bone metabolism
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Tissue and bone repair/healing

In Patient B, who is susceptible to periodontitis:
Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Connective tissue and bone metabolism
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Tissue destruction and bone loss

Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Connective tissue and bone metabolism
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Deepening of periodontal pockets, furcation involvement, contaminated cementum…
In Patient B, who is susceptible to periodontitis:

Microbial Challenge
Host Immuno-inflammatory response
Connective tissue and bone metabolism
Clinical signs of disease initiation and progression
Environmental and acquired risk factors
Genetic risk factors
Page, Ann Periodontol 1998
Pathogenesis of Periodontitis

In periodontitis, what is actually occurring in a periodontal pocket…

Periodontal Pathogens has invaded:
• Periodontal pocket• Cementum• Gingival tissue
In a patient susceptible to periodontitis, how does the body react?

1. Epithelial Cells produce IL-8 and ICAM-1 in response to bacteria & antigens
IL-8/ICAM-1

2. IL-8 and ICAM-1 are chemotactic signals for neutrophils, which are recruited to the sulcus
Neutrophils
Bacteria/Antigens

3. Neutrophils control bacterial assault by phagocytosis but also secrete matrix metalloproteinases or collagenases (MMP-8) which results in collagen degradation
MMP-8

4. Interaction of antigens with B cells lead to production of antibodies and complements, which contribute to phagocytosis
B-cell
Plasma Cell
T-cell

5. In response to bacterial LPS, various cells produce IL-1, TNF-, and PGE2
Activated B-Cell
LPSMacrophage
Fibroblast
IL-1TNF-
PGE2

Activated B-Cell
Macrophage
Fibroblast
IL-1TNF-
Osteoclast activation
PGE2
6. Production of IL-1, TNF-, and PGE2 leads to osteoclast activation, proliferation and differentiation

Higher amounts of IL-1, TNF-, PGE2, MMPs
Disease Health
Lower amounts of IL-10, TGF-, IL-
1ra, TIMPs
Major Mediators
• Proinflammatory• Destructive

Lower amounts of IL-1, TNF-, PGE2, MMPs
Disease Health
Higher amounts of IL-10, TGF-, IL-
1ra, TIMPs
• Anti-inflammatory• Protective