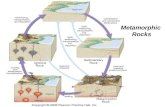
Metamorphic rocks. Metamorphism Factor and limits of metamorphism Factor of metamorphism include...
-
Upload
malcolm-snow -
Category
Documents
-
view
254 -
download
1
Transcript of Metamorphic rocks. Metamorphism Factor and limits of metamorphism Factor of metamorphism include...

Metamorphic rocksMetamorphic rocks

MetamorphismMetamorphism (Meta=change, Morph=form or character). So, metamorphism means to change form or character).
It is define as a subsolidus process leading to change in mineralogy, structures (textures) and/or chemical composition of an igneous, sedimentary, or prior metamorphic rocks. These changes were made due to subjection of these rocks to physicochemical conditions (P, T, active chemical fluids) higher than those occurring in the zone of weathering, cementation and diagenesis
Features of Metamorphism
- It principally formed in solid state and before melting,
- Metamorphism can be considered to be isochemical, except perhaps for removal or addition of volatiles (H2O, CO2),
- The process of extensive chemical changes during transformation is known as metasomatism.

Factor and limits of metamorphismFactor of metamorphism include three variables:Factor of metamorphism include three variables:
Temperature Temperature Pressure Pressure chemical active fluids chemical active fluids
1- Temperatures: 1- Temperatures: (leads to increase in grain size)(leads to increase in grain size)
-Limits of temperaturesLimits of temperatures
- Limits of Temperature- Limits of Temperature lower limit (150±50 °C)lower limit (150±50 °C)
higher limit (beginning of higher limit (beginning of melting, 650-1100 °C)melting, 650-1100 °C)
- Low limit depend on the original protolith - Low limit depend on the original protolith lower T (shale, organic matters)lower T (shale, organic matters)
higher T (Igneous rocks and carbonates)higher T (Igneous rocks and carbonates) - Beginning of melting depend on: Beginning of melting depend on:
protolith compositionprotolith composition the presence of aqueous fluidsthe presence of aqueous fluids

Example: Example: - - At 5 kbar and presence of aqueous fluidAt 5 kbar and presence of aqueous fluid - granites begin to melt at ~ 660 °C - granites begin to melt at ~ 660 °C
- basalts begin to melt at ~800 - basalts begin to melt at ~800 - A- At 5 kbar and dry conditions - t 5 kbar and dry conditions - granites begin to melt at ~ 1000 °Cgranites begin to melt at ~ 1000 °C
- basalts begin to melt at ~1120 °C - basalts begin to melt at ~1120 °C
Source of Temperature for metamorphism:Source of Temperature for metamorphism:- heat flowing into the base of the crust from the mantle- heat flowing into the base of the crust from the mantle- heat brought into the crust by rising magma bodies - heat brought into the crust by rising magma bodies - heat generated from radioactive decay- heat generated from radioactive decay- the effect of rapid uplift and erosion - the effect of rapid uplift and erosion - heat related to burial effect and geothermal gradient- heat related to burial effect and geothermal gradient
Geothermal gradient:Geothermal gradient: (rate of increasing temperature with depth, mean = 25 (rate of increasing temperature with depth, mean = 25 °C/km)°C/km) - Subduction zone- Subduction zone (10 °C/km) (10 °C/km) - Precambrian Shields - Precambrian Shields (12-20 °C/km) (12-20 °C/km) - Collisionl orogens (25-30 °C/km) - Collisionl orogens (25-30 °C/km) - Active arc-margin (30-35 °C/km) - Active arc-margin (30-35 °C/km) - Extensional orogens (40-50 °C/km) - Extensional orogens (40-50 °C/km) - Mid-ocean ridges (~ 60 °C/km) - Mid-ocean ridges (~ 60 °C/km)

2- Pressures:2- Pressures: (leads to reducing grain size and deformation)(leads to reducing grain size and deformation) - -
----- Pressure is define as force/unit area- Pressure is define as force/unit area
- Unit of pressure (bar, kbar), 1 bar = 0.987 atmosphere = 14.5 pound/inch- Unit of pressure (bar, kbar), 1 bar = 0.987 atmosphere = 14.5 pound/inch22
- pressures types - pressures types confining pressure confining pressure or lithostatic pressure (Por lithostatic pressure (P lithlith))
directive or deviatoric pressuredirective or deviatoric pressure
fluid pressure (Pfluid pressure (Pfluidfluid))
effective pressure (Peffective pressure (Pee))
PPee = P = Plithlith – P – Pfluidfluid

Pressures:Pressures:
- - Limits of pressureLimits of pressure
lower limit (a few of bars, at Earth’s surface)lower limit (a few of bars, at Earth’s surface)
Higher limits (30-40 in the collisional orogen or up to 100 kbar Higher limits (30-40 in the collisional orogen or up to 100 kbar
in the ultrahigh pressure metamorphism)in the ultrahigh pressure metamorphism)
- - Source of pressure Source of pressure
burial influence of an overlying rock columnburial influence of an overlying rock column
Plate tectonic and movement of plate segmentsPlate tectonic and movement of plate segments
- - Geobaric gradientGeobaric gradient (change of pressure with depth ) (change of pressure with depth )
average = 0.285 kbar/km or ~1kbar/3kmaverage = 0.285 kbar/km or ~1kbar/3km

Pressure and fabric changesPressure and fabric changes
►►LithostaticLithostatic pressurepressure = uniform stress (hydrostatic) = uniform stress (hydrostatic)
► ► DeviatoricDeviatoric stressstress = unequal pressure in different directions. = unequal pressure in different directions.
Deviatoric stress can be resolved into three mutually Deviatoric stress can be resolved into three mutually
perpendicular stress (perpendicular stress () components:) components:
i) i) 11 is the maximum principal stress is the maximum principal stress
ii) ii) 22 is an intermediate principal stress is an intermediate principal stress
iii) iii) 33 is the minimum principal stress is the minimum principal stress
In hydrostatic situations all three are equalIn hydrostatic situations all three are equal

Pressure and fabric changes, ContPressure and fabric changes, Cont . .
► ► StressStress is an applied force acting on a rock (over a particular is an applied force acting on a rock (over a particular
cross-sectional area)cross-sectional area)
► ► StrainStrain is the response of the rock to an applied stress (= is the response of the rock to an applied stress (=
yielding or deformation)yielding or deformation)
► ► Deviatoric stressDeviatoric stress affects the textures and structures, but not affects the textures and structures, but not
the equilibrium mineral assemblagethe equilibrium mineral assemblage
► ► StrainStrain energyenergy may overcome kinetic barriers to reactions may overcome kinetic barriers to reactions
Deviatoric stresses come in three principal types: Deviatoric stresses come in three principal types:
– TensionTension
– CompressionCompression
– ShearShear

TensionTension: : 3 is negative, and the resulting strain is extension, or pulling 3 is negative, and the resulting strain is extension, or pulling
apart. Tension fractures may open normal to the extension direction and apart. Tension fractures may open normal to the extension direction and
become filled with mineral precipitates.become filled with mineral precipitates.
original shapeoriginal shape strain strain ellipsoidellipsoid
1
3

CompressionCompression: : 1 is dominant; therefore, folding or more homogenous 1 is dominant; therefore, folding or more homogenous
flattening are caused. flattening are caused.
1
3

ShearShear motion occurs along planes at an angle to motion occurs along planes at an angle to 1 and causing slip along 1 and causing slip along
parallel planes and rotation.parallel planes and rotation.
1

Foliation is a common result, which allows us to estimate the Foliation is a common result, which allows us to estimate the orientation of orientation of 1 1
- - 1 > 1 > 2 = 2 = 3 3 foliation and no lineation foliation and no lineation
- - 1 = 1 = 2 > 2 > s3 s3 lineation and no foliation lineation and no foliation
- - 1 > 1 > 2 > 2 > 3 3 both foliation and lineation both foliation and lineation
1

3- Metamorphic fluids3- Metamorphic fluids (leads to chemical changes)(leads to chemical changes)
mostley are Hmostley are H22O and COO and CO22 types types
- include- include Ascending fluids from Magma chamber Ascending fluids from Magma chamber Descending fluids of the meteoric water Descending fluids of the meteoric water
- - Proofs of importance of fluids in metamorphismProofs of importance of fluids in metamorphism
most metamorphic minerals are hydrous, so water most metamorphic minerals are hydrous, so water
should be present should be present
most of metamorphic reactions involves dehydration of most of metamorphic reactions involves dehydration of
decarbonation decarbonation
ms + chl ms + chl bt + grt + qtz + H bt + grt + qtz + H22O O
CaCOCaCO33 + SiO + SiO22 CaSiO CaSiO33 + CO + CO22 Fluids could preserved as inclusion in neoblasts in Fluids could preserved as inclusion in neoblasts in
metamorphic rocks. metamorphic rocks.