METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI proizvodnja – … · The precipitation kinetics of rapidly...
Transcript of METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI proizvodnja – … · The precipitation kinetics of rapidly...
Univerzitet u Zenici University of Zenica
Bosnia and Herzegovina FAKULTET ZA METALURGIJU I MATERIJALE
FACULTY OF METALLURGY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozijum sa međunarodnim učešćem
8th Scientific/Research Symposium
with International Participation
METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI proizvodnja – osobine – primjena
METALLIC AND NONMETALLIC MATERIALS
production – properties – application
KNJIGA ABSTRAKTA sa elektronskim izdanjem Zbornika radova BOOK OF ABSTRACTS with electronic edition of Proceedings
Zenica, April 2010.
UREDNIK/EDITOR Dr Sulejman Muhamedagić IZDAVAČ/PUBLISHER Univerzitet u Zenici Organizaciona jedinica Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale Travnička cesta 1, 72000 Zenica Tel: ++ 387 401 831, 402 832, Fax: ++ 387 406 903 KOMPJUTERSKA OBRADA TEKSTA TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND DTP Diana Ćubela Almaida Gigović-Gekić Hasan Avdušinović Adnan Mujkanović ŠTAMPA/PRINTED BY EURO COPY M.S. Serdarevića 27, Zenica TIRAŽ/ISSUE: 120 primjeraka/copies
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozijum sa međunarodnim učešćem „Metalni i nemetalni materijali“, Zenica, BiH, 27. – 28. april 2010.
ORGANIZACIONI ODBOR / ORGANIZING COMMITTEE
Dr Sulejman Muhamedagić, President
Dr Hasan Avdušinović, secretary Mr Almaida Gigović-Gekić, technical secretary
Mr Adnan Mujkanović, technical secretary Dr Fuad Begovac
Dr Jusuf Duraković Dr Diana Ćubela
Dr Marina Jovanović Dr Ilhan Bušatlić Larisa Omerović
NAUČNI ODBOR
INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC/RESEARCH COMMITTEE
Dr Anžel Ivan, SI Dr Begovac Fuad, BA Dr Beroš Ana, BA Dr Bikić Suada, BA Dr Bikić Farzet, BA Dr Bizjak Milan, SI Dr Brdarević Safet, BA Dr Burzić Zijah, SP Dr Bušatlić Ilhan, BA Dr Chumbley Scot, US Dr Ćubela Diana, BA Dr Delijić Kemal, CG Dr Dolinšek Slavko, SI Dr Drljević Sulejman, BA Dr Duraković Jusuf, BA Dr Durman Mehmed, TR Dr Džonlagić Nusreta, BA Dr Ekinović Sabahudin, BA Dr Fidančevska Emilija, MK Dr Gojić Mirko, HR Dr Hessling Goetz, DE, Dr Hodolič Janko, SP
Dr Holger Frenz, DE Dr Ibrahimefendić Salih, BA Dr Ivanković Hrvoje, HR Dr Jovanović Marina, BA Dr Kosec Borut, SI Dr Kurtović Azra, BA Dr Lamut Jakob, SI Dr Lazić Dragica, BA Dr Mahmutović Aida, BA Dr Mirjanić Dragoljub, BA Dr Mamuzić Ilija, HR Dr Muhamedagić Sulejman, BA Dr Mujezinović Aziz, BA Dr Oruč Mirsada, BA Dr Ostojić Milinko, BA Dr Pašalić Zakir, BA Dr Pašić Sead, BA Dr Pašić Zijad, BA Dr Petković Darko, BA Dr Petrovski Petar, BA Dr Ranogajec Jonjaua, SP Dr Rizvanović Mirsada, BA
Dr Rusell Alen, US Dr Salihović Senaid, BA Dr Senk Dieter, DE Dr Spužić Sead, AU Dr Sredojević Jovan, BA Dr Stanojlović Rodoljub, SP Dr Subašić Kemal, BA Dr Šestić Mediha, BA Dr Šetrajčić Jovan, BA Dr Tomašević Sreto, BA Dr Uzunović Faik, BA Dr Vitez Ivan, HR Dr Volkov-Husović Tatjana, SP Dr Vukojević Dušan, BA Dr Yalcin Senay, TR Dr Zelić Jelica, HR Dr Zlokolica Miodrag, SP Dr Žigić Izet, BA Dr Živković Dragana, BA Dr Živković Živan, BA
i
VIII Naučno stručni simpozijum sa međunarodnim učešćem „Metalni i nemetalni materijali“, Zenica, BiH, 27. – 28. april 2010.
SADRŽAJ/CONTENTS
stranica/page
UVODNA PREDAVANJA/KEYNOTES PAPERS 1. Metal expansion penetration on casting components of grey cast iron
Izudin Dugić, Attila Diószegi, Ingvar L Svensson ...................................................... 3
2. Porous ceramic materials Emilija Fidančevska................................................................................................. 13
SEKCIJA METALNI MATERIJALI/SESSION METALLIC MATERIALS 1. Prednost proizvodnje visokokvalitetnih bakrenaca u topionicama koje prerađuju
sulfidne koncentrate bakra Lj. Misic, T. Apostolovski-Trujic, S. Ivanovic.......................................................... 23
2. Review of thermodynamic simulation models in copper matte production -The impurities behaviour analysis E. D. Požega, L. D, Gomidželović, D. T. Živković, V. K. Trujić .............................. 24
3. Dobijanje srebra i bakra visoke čistoće iz istrošene posrebrene bakarne žice S. Dimitrijević, S. Dragulović, S. Ivanović, D. Marković, R. Todorović ................ 25
4. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic predicting of phase equilibria in Ga-GeSb0.855 system A. Kostov, D. Živković, D. Manasijević, D. Minić, Ž. Živković ............................... 26
5. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic calculation in Pb-Zn-Ag system D. Živković, D. Minić, D. Manasijević, A. Mitovski, Lj. Balanović, Ž. Živković ..... 27
6. Thermal analysis of the ternary system Bi-Cu-Sn D. Manasijević, D. Minić, D. Živković, N. Talijan, A. Grujić, S. Marjanović......... 28
7. Numerical study of the chill wheel cooling during continuous free jet melt-spinning B. Karpe, B. Kosec, M. Bizjak, T. Kolenko .............................................................. 29
8. The precipitation kinetics of rapidly solidified Al based alloys M. Bizjak, G. Dražič, L. Kosec, B. Karpe ................................................................ 30
9. Microstructure and characterisation of rapidly solidified Au-La ribbons T. Zupančič Hartner, R. Rudolf, B. Kušić, K. Mahrabi, I. Anžel ............................ 31
10. Uticaj sadržaja δ-ferita na mehanička svojstva austenitnog nehrđajućeg čelika A. Gigović-Gekić, M. Oruč ...................................................................................... 32
11. Faktori koji utiču na toplootpornost legure na bazi nikla – IN.100 R. Todorović, A. Kostov, Lj. Todorović ................................................................... 33
12. Mikrostruktura, mehaničke i električne osobine legura ternarnog Bi-Cu-In sistema A Aljilji, D. Minić, V. Čosović, M.Kolarević, D. Manasijević, D. Živković............. 34
13. Mikrostruktura, mehaničke i električne osobine legura ternarnog Cu-In-Sb sistema D. Minić, A. Aljilji, J. Stajić-Trošić, D. Manasijević, D. Živković .......................... 35
14. Uticaj aluminija i titana na temperaturu rekristalizacije Superlegure Nimonic 80A O. Beganović,B. Muminović, B.Fakić, F. Uzunović ................................................ 36
15. Recrystallization temperatures of cold deformed Au- 0,5La alloy B. Kušić, T. Zupančič Hartner, I. Anžel................................................................... 37
16. Uticaj vremena izotermalnog poboljšanja na mikrostrukturne karakteristike uzoraka od austemperovanog nodularnog liva H. Avdušinoviæ, S. Tomašević. F. Begovac.............................................................. 38
17. Inductive heating and quenching of planetary shafts for the automotive industry B. Kosec, B. Karpe, A. Nagode, M. Ličen, G. Kosec ............................................... 39
18. Eksperimentalna ispitivanja tvrdoće zavarenog spoja čelika Fadil Islamović, Fatka Kulenović, Dženana Gačo, Esad Bajramović .................... 40
19. Procena preostalog veka trajanja materijala bubnja kotla sa aspekta mikrostrukture Z. Karastojković, R. Popović, Z. Kovačević, Z. Janjušević .................................... 41
20. Kontrola atmosfere u pećima za termičku obradu J. Duraković, D. Ćubela, A. Gigović-Gekić............................................................. 42
21. Modifikovani bakar: ekološka alternativa za Cu-Cd leguru A. Ivanovic, S. Dimitrijevic, V. Marjanovic, V. Cvetković - Stamenkovic ............... 43
22. Uticaj indijuma na osobine nekih bezolovnih lemnih legura A. Milosavljević, D. Živković, N. Talijan, A. Grujić ................................................ 44
23. Korozija hirurških instrumenata u dezinfekcionim sredstvima M. Cacan, S. Islamović, S. Gojak, S. Gutić.............................................................. 45
24. Uticaj polianilinske prevlake na korozione karakteristike visokolegiranog nehrđajućeg čelika M. Cacan, F. Lutvić, S. Gutić, S. Islamović, S. Gojak ............................................. 46
ii
25. Uticaj koncentracije 1-fenil 5-merkapto tetrazola na elektrohemijsko ponašanje mesinga u rastvoru boraksa Z. Ljubomirović, M. Antonijević, M. Petrović, M. Radovanović ............................. 47
26. Plemeniti metali kao materijali za električne kontakte V. Marjanović, V. Cvetković-Stamenković, A. Ivanović........................................... 48
27. Čelici za poboljšavanje prema europskim standardima I. Vitez, V. Marušić, D. Krumes, A. Milinović ......................................................... 49
28. Savremeni trendovi u proizvodnji nehrđajućih čelika Š. Žuna ..................................................................................................................... 50
29. Prilog strategiji razvoja novih materijala u BiH M. Oruč, M. Rimac, N. Šehić-Mušić ........................................................................ 51
SEKCIJA NEMETALNI MATERIJALI /SESSION NONMETALLIC MATERIALS 1. Uloga karakteristika stijenskih materijala u metodološkim tokovima izbora
drobilica i mlinova I. Šišić, N. Alić ......................................................................................................... 55
2. Ispitivanje i karakterizacija glina Srednje Bosne M. Jovanović, J. Zelić .............................................................................................. 56
3. Ispitivanje kvaliteta gline i mogućnosti njene eksploatacije sa lokaliteta „Ulice“ D.Lazić, J.Penavin-Škundrić, S.Sladojević, Lj.Vasiljević, R. Smiljanić, D.Kešelj, D. Smiljanić.............................................................................................................. 57
4. Potencijalnost ležišta dolomita „Tunel“ kod Konjica i mogućnosti njihove primjene M. Operta, N. Škripić, S. Salihović .......................................................................... 58
5. Keramičko-tehnološke osobine opekarske gline „Čavka“ A. Šeper, A. Kobilica, M. Jovanović ........................................................................ 59
6. Mineraloško-petrografska i tehnološka svojstva gline ležišta „Golo brdo“ kod Visokog A. Hamzabegović, M. Stević, Dž. Alijagić ............................................................... 60
7. Geološka građa, potencijalnost i kvalitativne odlike glina ležišta “Kečkovac” po bušotini B-9 A. Baraković, P. C. Katanić, D. Baraković.............................................................. 61
8. Activated sintering of magnesium oxide from seawater with TiO2 addition V. Martinac, T. Maleš, M. Labor ............................................................................. 62
iii
9. Promjena energetskih karakteristika aktivne mase olovnih baterija dodatkom H3PO4 u elektroit N. Avdić .................................................................................................................... 63
10. Kemijska reaktivnost i vezivanje hidrauličnog vapna praćeni procesima njegove hidratacije P. Krolo, T. Kosor, P. Dabić.................................................................................... 64
11. Optimizacija klasiranja dekompozirane suspenzije natrijum aluminatnog rastvora R. Smiljanić, D. Lazić, D. Smiljanić, Ž. Živković..................................................... 65
12. Ispitivanje adsorpcionih mogućnosti CaFeO3 perovskita S. Sladojević, J. Penavin-Škundrić, D. Lazić, B. Škundrić, D. Bodroža, S.Zeljković66
13. Uticaj površinski aktivne materije – PAM na adsorpcione osobine Mordenita Z. Levi, D. Bodroža, S. Sladojević, D. Lazić, J. Penavin-Škundrić, P. Dugić ......... 67
14. The effect of MgO addition on the synthesis of mullite from rice husk ash and technical alumina R. Adziski, E. Fidancevska, D.Milovski ................................................................... 68
15. Fabrication of magnezite-chromite refractory using different binders D. Milovski, V. Jovanov, R. Adziski, E. Fidancevska............................................... 69
16. Primjena ekspandiranog polistirena za proizvodnju izolacionih i ambalažnih materijala i upravljanje nastalim otpadom P. Dugić, Z. Petrović, V. Aleksić, V. Mićić, M. Perušić .......................................... 70
17. Internal stresses in polymeric materials based on aminoplast N. Vukas, I.Horman ................................................................................................. 71
18. Ispitivanje uticaja koncentracije SiO2 i temperature precipitacije na deaglomerabilnost precipitiranog SiO2 metodom raspršavanja laserske svjetlosti A. Mujkanović, P. Petrovski, Lj. Vasiljević, G. Ostojić ........................................... 72
19. Ispitivanje uticaja dodatka elektrofilterskog pepela na proces hidratacije mjerenjem specifične električne provodnosti cementnih pasti I. Bušatlić, P. Dabić , M. Rizvanović, N. Bušatlić .................................................. 73
20. Geopolymeric binders prepared by using the Croatian coal-fly ash J. Zelić , D. Jozić, M. Nikola Mužek , D. Krpan-Lisica ........................................... 74
21. Kinetika hidratacije PC i svojstva nastalog cementnog kompozita uz dodatak zeolitnog otpada koji sadrži Zn2+-ione P. Krolo, R. Bulat, P. Dabić .................................................................................... 75
22. Crveni mulj kao baza za sintezu željezovitih cemenata J. Mikić, M. Sudar.................................................................................................... 76
iv
23. Uticaj silicijske prašine na osobine cementa tipa Cem II/B – W 42,5N u Tvornici cementa Kakanj N. Merdic, Z. Pašić, N.Haračić, I. Bušatlić ............................................................. 77
24. Korištenje pećne prašine za proizvodnju cementa u Tvornici cementa Kakanj N. Merdic, Z. Pašić, N. Haračić, I. Bušatlić ............................................................ 78
25. Karakterizacija EFP iz TE Gacko i mogućnosti njegove primjene P.Petrovski, I.Bušatlić , S.Govedarica i D.Miloševic, N.Bušatlić .......................... 79
26. Uticaj agregata, za proizvodnju asfalta, na hrapavost kolovoznih konstrukcija E. Softić, N. Alić, A. Softić ..................................................................................... 80
27. Primjena DPV i DPASV metoda kod određivanja cinka F. Bikić, M. Rizvanović ............................................................................................ 81
28. Kvalitativna analiza motornog ulja FT-IR spektrofotometrijom F. Bikić ..................................................................................................................... 82
29. Konduktometrijska metoda određivanja prihvatljivog dodatka otpadnog mulja i zasićenog zeolita iz pogona pocinčavanja u cementu P. Dabić, P. Krolo, D. Barbir, M. Maretić ............................................................. 83
30. Primjena kalibracionih etalona u XRF (x-ray fluorescence) spektrometrijskoj analizi N.Haračić, P. Petrovski, M. Rizvanović, N. Merdić, I. Bušatlić ............................. 84
31. On-line kontrola kvaliteta pomoću PGNAA analizatora i XRF spektrometra N.Haračić, P. Petrovski, M. Rizvanović, N. Merdić, I. Bušatlić ............................. 85
32. Implementation of image analysis of surface on thermal shock and cavitation resistance testing of low cement high alumina castable S. Martinovic, M. Dojcinovic, J. Majstorovic, T. Volkov-Husovic .......................... 86
33. Stanja elementarnih pobuđenja u superrešetkama kristalnih organskih materijala S.M.Vučenović, S.Pelemiš, B.Škipina, J.P.Šetrajčić ................................................ 87
34. Uticaj mehaničkih karakteristika materijala na stabilnost i sigurnost konstrukcije zidanih sakralnih tornjeva A. Čaušević .............................................................................................................. 88
35. Vakumirana ostakljenja A. Salihbegović ........................................................................................................ 89
36. Energetska učinkovitost u zgradarstvu uz primjenu domaćih materijala N. Rustempašić......................................................................................................... 90
v
SEKCIJA ZAŠTITA RADNE I ŽIVOTNE SREDINE I ODRŽIVI RAZVOJ /SESSION ENVIROMENT PROTECTION AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT 1. Tehnologija prerade čeličanske troske u ArcelorMittal Zenica
S. Muhamedagić, Ć.Talam, ..................................................................................... 93
2. Menadžment recikliranja u procesu proizvodnje gvožđa i čelika A. Mahmutović, L. Torlaković, S. Vilić, F. Vardo, A. Jusufović, E. Merdić, S. Omić94
3. Japanski model održivog razvoja D. Ćubela ................................................................................................................. 95
4. Korišćenje sirovog drvnog otpada kao goriva u tehnološke svrhe V. Đukić.................................................................................................................... 96
5. The GAP analysis of the wood processing sector in Bosnia and Herzegovina I. Alagić.................................................................................................................... 97
6. Rješavanje okolinskih problema u eksploataciji i pripremi stijenskih masa dijabaza na površinskim kopovima D. Vejzović, N.Vejzović, A. Mahmutović, ............................................................... 98
7. Upravljanje građevinskim otpadom u skladu sa EU standardima N. Rustempašić......................................................................................................... 99
8. Environmental labeling of products with eco-labels type I I. Budak, B. Kosec, M. Soković, J. Hodolič, Š. Goletić.......................................... 100
9. Štetni efekti saobraćaja na životnu sredinu V. Đukić.................................................................................................................. 101
vi
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
EKSPANZIJSKA PENETRACIJA METALA NA ODLIVCIMA OD SIVOG LIJEVA
METAL EXPANSION PENETRATION ON CASTING COMPONENTS
OF GREY CAST IRON
Izudin Dugic*, Linnaeus University, School of Engineering, Växjö, Sweden, Attila Diószegi and Ingvar L Svensson, Jönköping University, School of
Engineering/Component Technology and Casting, Jönköping
*Corresponding author: [email protected] Key words: Grey cast iron, solidification, graphite expansion, casting simulation, inoculation, metal expansion penetration, eutectic cell size, primary austenite. ABSTRACT Cast irons are a family of sophisticated design materials with precise engineering properties.
In some grey cast iron components which are cast in sand moulds, the metal sometimes penetrates into
the mould producing defects which cause difficulty when cleaning the components. Metal penetration
is a casting surface condition resulting from either physical, mechanical and/or thermo chemical
reactions or a combination of these at the mould–metal interface.
The present work will summarize research efforts to understand the mechanisms of metal expansion
penetration performed in collaboration with Swedish foundries. The main parts of the experimental
works are based on some casting components.
1. INTRODUCTION One of the most important factors in the production of cast iron is the production of cast components without any defects. In some grey cast iron components which are cast in sand moulds, the metal sometimes penetrates into the mould producing difficulties in cleaning the components. Penetration is often so severe that castings are beyond the point of economical rework and must be scrapped. Machining of castings that exhibit this defect is often difficult and may result in excessive tool wear. Metal penetration is a casting surface condition resulting from various physical, mechanical and/or thermo–chemical reactions either singly or in combination at the mould–metal interface. The metal penetrates into the voids between the sand grains to various depths without displacing the grains, thus yielding a phase of sand grains surrounded by metal and frequently by mould-metal reaction products. The general definition for metal penetration, accepted by the foundry industry, as proposed by Draper and Gaindar [1], is the condition in which cast metals has entered the inter–granular space of the moulding material, up to and beyond the first layer of sand grains. In the published literature, numerous names have been given to the various types of penetration. During eutectic solidification, cast iron solidifying with an austenite–graphite eutectic has been demonstrated to expand, significantly. The expanding metal exerts a significant pressure on the mould walls. If the mould is rigid, and if the metal cannot be pushed back in the riser or the gates because they have solidified, this pressure results in metal penetration, called expansion penetration. This type of penetration was first identified by Levelink and Julien [2] who called it exudation penetration. They indicated that expansion occurring during eutectic solidification may result in exudation of eutectic in locations where a solidifying metal shell does not obstruct it. This is especially so at “hot spots”, such as “L”, “T” and “Y”, where the metal is still liquid at the time expansion occurs due to eutectic solidification. Eutectic exudation penetration appears to occur mostly in grey cast iron and very seldom in ductile iron. Expansion penetration depends upon the metallurgical characteristics of the solidifying metals and alloys. Metal penetrations have been discussed by many authors [3,4,5,8] and lot of works have been done in the industries to understand how to avoid metal penetration. To give an increased knowledge of the metal penetration mechanism and the influence from different factors, a series of test castings was performed at the different foundries. 2. INFLUENCE OF CHEMICAL COMPOSITION The influence of chemical composition has been discussed by many authors [6] and suggestions for improvements have been made. In order to analyze how the chemical composition of the casting iron have an influence on metal expansion penetration, a series of test castings were made on casting components in a production scale. The experiments work was carried out at the foundry of ITT Flygt AB with a Seiatsu production line. The casting component studied was “Styrklo” (figure 1a) and eight castings were mounted on the pattern plate (figure 1b). The weight of each “Styrklo” is 7.8 kg and the total casting weight is 78 kg. The castings were made in green sand moulds with a typical moulding hardness of 80 to 85 GF. Melting was done in a high frequency furnace with a charge composition of 40 % recycled metal, 20 % pig iron and 40 % steel. After melting, the melt is transported in a 1 ton pouring
ladle to a production line. The casting temperature was 1430 °C with a variation of ±10 °C. The chemical composition of the base melt for each casting experiment is shown in table 1. Table 1. The chemical composition of the base melts. Cequ = % C + % Si / 4.
Element in wt % Experi-ment C Si Mn P S Cr Cu Cequ A 3.45 1.78 0.66 0.082 0.091 0.05 0.24 3.895 B 3.41 1.88 0.64 0.084 0.092 0.05 0.24 3.880 C 3.33 2.02 0.62 0.075 0.089 0.04 0.25 3.835 D 3.27 1.99 0.62 0.123 0.087 0.05 0.21 3.767 E 3.30 2.04 0.60 0.102 0.074 0.07 0.26 3.810
The inoculant used in these experiments was of a ferro-silicon-strontium type. The inoculant had a particle size between 1.0 and 6.0 mm and inoculation was made in the stream when pouring the melt from the high frequency furnace to the pouring ladle. The amount of inoculant added was 0.15 % for all experiments, and the time between inoculation and casting in the mould flasks was 2 minutes. After blasting, all casting components were documented by an ocular inspection. The metal penetration often occurs in two places on this casting. These are shown in figure 1a and the places are called “side” and “beneath” respectively. On most castings, other types of surface defects had also formed; e.g. scabs and surface shrinkage. The following parameters have been calculated for each chemical composition: percentage of castings having metal penetration defects and percentage of castings having scab defects. These results are shown in table 2.
Figure 1a. The casting component Figure 1a. The geometry of the casting “Styrklo”. The circles show the areas components – upper part. where surface defects usually occur. The microstructures close to the penetration areas were analysed in an optical microscope. Etching was performed in the following etching solution: 10 g NaOH, 40 g KOH, 10 g C6H3N3O7 and 50 ml H2O. The etching time was 5 minutes at a temperature of 80 °C. In figures 2a and 2b, micrographs are shown of the some microstructures (before and after etching) close to the metal penetration areas.
Table 2. Statistical listing of different surface defects found on the castings.
Experiment Casting defect A B C D E
Metal penetration (%) 100 91.0 16.0 0.0 0.0 Scab (%) 0.0 0.0 50.0 100 85.0
Figure 2a. Experiment A, microstructure Figure 2b. Experiment A, microstructure before etching, (magnification 150 X). after etching, (magnification 150 X). 3. INFLUENCE OF THE INOCULATION AND CASTING TEMPERATURE The primary reason to inoculate [7,9] cast iron is to improve the mechanical properties and machinability of iron castings. It is carried out by adding a material called an inoculant to molten iron for the purpose of establishing nucleation centres (sites) for the precipitation (formation) of graphite. Inoculation in grey cast irons results in an increase in the temperature where the eustenite-flake graphite eutectic forms, most often associated with an increase in the number of nucleation sites for this eutectic. The aims of the experiments were to investigate the effect of inoculants, inoculant amount and casting temperature on the metal expansion penetration in grey cast iron using a same commercial casting component and at the same foundry (ITT Flygt AB). Two series of experiments were done. In the first experimental series, five different inoculants were investigated. The inoculant which gave the best results with regards to (minimum) metal penetration in an earlier investigation was chosen for this study: inoculant H, containing silicon, aluminium and zirconium. The inoculation was made in the stream during pouring the melt from the holding furnace to the pouring ladle. The amounts of inoculant added were 0.05 %, 0.15 % and 0.30 %. The results from an ocular inspection of the castings are summarised in Table 3. Table 3. The chemical composition of the inoculants. Inoculant % Si % Ca % Al % Zr % Mn % Ba % Sr % Ti A 72-78 max 0.1 max 0.5 - - - 0.6-1.0 - B 73-78 0.09 0.48 - - - 0.6-1.0 - D 59-65 1.5-3.0 1.0-1.5 - 9.0-11.0 4.0-6.0 - - E 51-55 1.0 1.0-1.3 - - - - 9.0-11.0H 44-50 2.5-3.5 1.0 1.5-2.0 - - -
After sand blasting, the penetration severity in all castings was investigated by an ocular inspection. The results are given in tables 4 and 5. Table 4. The average casting defects calculated for the first experimental series.
Inoculants A B D E H
Metal penetration in mm2 45.30 97.93 86.08 112.23 22.18 Metal penetration in % 46.03 76.78 59.57 64.58 34.09 Shrinkage in % 3.17 8.93 12.77 4.16 13.63 Table 5. The average casting defects calculated for the second experimental series.
The amount of inoculant and casting temperature 0.05 % 0.15 % 0.30 %
Casting defects 1440°C 1410°C 1390°C 1420°C 1390°C 1370°C 1420°C 1400°C 1370°C Metal pene-tration (mm2)
0 0 0.81 23.16 5.50 1.16 81.12 4.40 0
Metal pene-tration (%)
0 0 3.25 34.37 10.00 3.22 75.00 6.67 0
Bulb (mm2) 0 0 9.84 9.06 12.50 8.06 6.25 22.50 11.72 Bulb (%) 0 0 35.48 31.25 46.66 32.26 25.00 66.67 40.62 Shrinkage (%) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 The penetration areas were analysed metallographically in an optical microscope. Etching was performed in “Steads etching solution” (10 g copper chloride, 40 g magnesium chloride, 20 ml hydrochloric acid dissolved in 1000 ml 95 % ethyl alcohol). The etching time was 5 min at room temperature. After etching, the samples were rinsed in ammonium hydroxide to remove the precipitated copper. In figures 3a and 3b, micrographs are shown of the microstructure and eutectic cell size close to the metal penetration using inoculants H and E.
Figure 3a. The microstructure close to the Figure 3b. The microstructure close to the metal metal penetration area, the best case of metal penetration area, the worst case of metal penetration, using inoculant (H). penetration, using inoculant (E).
0.5 mm 0.5 mm
4. SIMULATION OF THE SOLIDIFICATION OF GREY CAST IRON COMPONENTS A series of simulations were performed with the casting simulation program MAGMASOFT® using the add-on module MAGMAiron®, especially developed for cast iron simulation. MAGMASOFT® is designed to simulate heat and fluid flow and optionally simulate stress/strain and microstructure formation phenomena in the casting process. Cast iron simulations require an accurate consideration of the microscopic phase separation, of the melt analysis, and other information such as the type and effect of melt inoculation. The MAGMAiron® module utilises a microscopic kinetic growth model to predict the solidification sequence of cast iron alloys. Before any pattern was built, a simulation of mould filling and solidification supplied basic information for the comprehensive optimisation of casting design and parameters. A series of simulations were performed for a commercial casting component with its gating system. The mould filling sequence and the solidification were considered in the simulations. During the solidification simulation, MAGMASOFT® calculated the heat flow in the casting and the mould and took the effect of feeding and casting shrinkage into account. Some results from the simulation are shown in Figures 4a and 4b. These pictures show the location of the pores. The geometry is clipped in the z- and y-directions. It is relevant to note that the predicted porous areas perfectly match the areas where surface defects occurred in the experiments.
Figure 4a. 3-D result from the simulation Figure 4b. 3-D result from the simulation showing the location of pores. The geometry showing the location of pores. The geometry is clipped in the z-direction. is clipped in the y-direction.
Figure 5a. Results from 3-D simulation of Figure 5b. Results from the 3-D simulation, the liquid fraction, when 5 % liquid in total showing the location of the pores. The geometry remains. The x-ray option is used is clipped in the z-direction.
No. 5 No. 5
A complete mould with 8 components and associated gating system was modelled. In the simulation, the mould filling sequence and the solidification process were considered. In Figure 5a the last areas to solidify are shown using the x-ray option when 5 % liquid remains. In Figure 5b the location of the pores is shown. The geometry is clipped in the z-direction. These areas perfectly match the defect areas found experimentally. 5. THE MECHANISMS OF METAL EXPANSION PENETRATION A cylindrical test cup with an internal core has been designed and optimized to obtain a hot spot at the metal-mould interface, see figure 6a and figure 6b. For optimisation of the test cup geometry the MAGMASOFT® simulation program was used. The diameter of the test cup is 80 mm, and the height is 80 mm. The internal core diameter is 30 mm, and is rounded at the end in contact with the bulk metal with a radius of 15 mm. The experiments were carried out at the Volvo Foundry in Skövde. The melt was poured from a holding furnace to a small ladle holding approximately 30 kg metal. Inoculants were added in the bottom of the ladle before pouring. The liquid metal was immediately poured into the test cup after which the cover containing the thermocouple was placed on top of the cup. Two test cups were poured from each charge. One sample was allowed to cool under normal conditions (as cast) and the other was DAAS-treated. The direct austempering after solidification (DAAS) technique was introduced by Sikora [10] to investigate the macrostructure of grey cast iron. The principle of the DAAS method is that using a special thermal process the austenite phase is retained and keeps the crystalline orientation defined during solidification. This method is very suitable for examination of the macrostructure of austenite grains. The procedure involves shaking out the casting at approximate 950 ºC, transferring the casting into a furnace held at 900 ºC, holding for 30min, quenching in a molten salt bath held at 360 ºC, and holding there for 90min before finally air-cooling to room temperature.
Figure 6a. Test cup for investigation of metal expansion penetration mechanism.
Figure 6b. Solidification time of the test cup.
It has been demonstrated that expansion penetration appears both before and after the columnar to equiaxed transition.The penetration phenomenon before columnar to equiaxed transition is shown in Figure 7a. The investigated microstructure at the metallic interface for this type of penetration is presented in Figure 7b.
Figure 7a. The metallic interface and Figure 7b. Microstructure of the penetrated penetrated metallic strip. strip containing exclusively eutectic phase The penetration phenomenon after columnar to equiaxed transition presents the largest amount of adhered sand grains, Figure 8a. The microstructure at the metallic interface for this type of penetration is presented in Figure 8b.
Figure 8a. Distorted metallic interface Figure 8b. Microstructure of the distorted and penetrated metallic strip. metallic interface. To compare the observations that expansion penetration appears both before and after the columnar to equiaxed transition a series of experiments were done on cylinder head cast in grey cast iron. The cylinder heads, see Figure 9a, studied were prepared on a standard moulding line using green sand as moulding material at the Skövde Foundry of Volvo Truck Component Corporation. The specimens for study were cut out from the areas where metal penetration had occurred. Some of these specimens are shown in figures 9b. The specimens were ground and polished in order to investigate the graphite morphology by optical microscopy. After a first inspection the specimens were he etched in a picric acid-based reagent at 110 ºC in order to investigate the primary austenite and eutectic cells. The microstructure of the casting surface in connection with the penetrated particles for the metal expansion penetration before the columnar to equiaxed transition (Figure 10a) consists of a eutectic strip with graphite lamellas oriented mainly perpendicularly to the mould
surface. This combination of microstructure in the penetrated and the casting surface is identical to that observed by earlier experiments.
Figure 9a. A sectioned cylinder head. Figure 9b. The investigated specimens showing metal expansion penetration. Behind the penetrated areas of eutectic composition there was observed a second type of microstructure in connection to the mould surfaces. This type of microstructure indicates a normal fraction of primary phase behind the casting surface (Figure 10b) and a much less dense primary phase in connection with the casting surface. The normal fraction of primary phases refers to the chemical composition.
Figure 10a. Microstructure of the first Figure 10b. Microstructure at metal-mould group of expansion penetration. interface with sparse fraction primary phase austenite and an anomalous interdendritic phase. 6. CONCLUSIONS These experiments on the castings components showed that carbon and phosphorus levels had an important influence on metal penetration and shrinkage behaviour. Metal penetration decreases when decreasing the carbon content and increasing the phosphorus content. The experiments with different inoculants show that the type and amount of inoculation of grey cast iron will influence the tendency towards metal penetration in areas with late solidification times and where the melt is in contact with the sand mould.
Experiments using different inoculants show that the best results regarding reduced metal penetration have been obtained when using an inoculant which contains silicon, aluminium and zirconium. For this inoculant, the average penetration area was only about 20 % of that which was found using the worst inoculant. The worst cases of metal penetration were obtained using an inoculant containing titanium. A large number of small eutectic cells and a high volume of the small cells were observed, which leads to severe metal penetration. By simulation it is possible to detect the areas where porosities are likely to be formed. Simulation results show that expansion penetration generally occurs in the same regions as shrinkage depending on the freezing rate if the area is close to a surface. The freezing parameters will give a change in the excess or deficiency of the metal versus the precipitation of the graphite, giving rise to either expansion or shrinkage. Cylinder heads have an extremely complex shape with large areas of concave casting surfaces. Investigation of cylinder heads cast under industrial production conditions reveal the same mode of expansion penetration mechanisms as found an experimental test cups cast at the same foundry and under same metallurgical conditions. The metal expansion penetration before and after columnar to equaixed transition is observed to dominate. 7. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study is based on experimental work performed in collaboration between Jönköping University, Linnaeus University in Växjö, ITT Flygt AB Foundry and Volvo Powertrain Foundry in Skövde. Both the Universities and the Foundries are warmly acknowledged. 8. REFERENCES
1. A. B. Draper and J. L. Gaindhar, ”Metal penetration–a critical literature review,” AFS Transactions, vol. 85, pp. 163–199, 1977.
2. H. G. Levelink and F. P. M. A. Julien, “Penetration and shrinkage by interaction of solidifying cast iron and casting mould–Part 2”, AFS Cast Metals Research Journal, vol. 9 (2), pp 105-109, 1973.
3. P. J. Thorpe, “Avoidance of metal penetration and sand burn–on in iron castings,” Brit. Foundryman, vol. 64, pp. 38–396, 1971.
4. Kagawa, A; Kiguchi, S; Osada, M, “Volumetric change in freezing cast irons”, Transactions of the Japan Foundrymen's Society. Vol. 14, pp. 18-23. Dec. 1995
5. D.M. Stefanescu, T.S. Piwonka, S. Giese, and A. Lane, “Cast Iron Penetration in Sand Moulds, Part I: Physics of Penetration Defects and Penetration Model”, AFS Transactions, vol. 104, (1996), pp 1233-1248.
6. Srivatsan, T S; Sudarshan, T S, “The influence of phosphorus on shrinkage porosity in cast irons”, Materials Letters. Vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 186-191. Nov. 1999
7. Carl R Loper Jr and R. Gundlach: ‘Inoculation, what is it and how does inoculation work’, International inoculation conference, Illinois, USA, 1998.
8. G. F. Ruff and J. F. Wallace: ‘Effects of solidification structure on the tensile properties of grey iron’, AFS Transactions, 1977, 85, pp. 179-202.
9. A. T. Rushworth: ‘The effect of holding time on various inoculants in flake and nodular graphite irons’, M. Sc. Thesis, Birmingham University, 1965.
10. G.L. Riviera, R.E. Boeri and J.A. Sikora, “Solidification of Gray Cast Iron”, Scripta materialia, Paper 50, pp 331-335, 2004.
8 th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
POROUS CERAMIC MATERIALS
Emilija Fidancevska Ss Cyril and Methodius University, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy
Ruger Boskovic 16, 1000 Skopje Republic of Macedonia
Keywords: porosity, biomaterials, wastes, glass, glass ceramics
ABSTRACT Creation of porous ceramic materials based on hydroxyapatite, titania and alumina for biomedical application is the first approach of this paper and on the other hand porous materials made of wastes i.e. fly ash and metallurgical slag is the other point which this paper deals with. Different methods for creation of porous structure are discussed manly using polyurethane foam, H2O2 and C-fibers as porogens. 1. INTRODUCTION Recently, there has been an increasing interest in the applications of porous ceramics for variety of applications. Porous ceramics may be classified into four basic structures: (1) tangle fibre networks, (2) closed cell structures, (3) open cell structures, and (4) membranes. The application of these ceramics is obviously determined by their unique structure [1]. Different manufacturing processes for cellular ceramics have been proposed, including replica of polyurethane foam, direct bowing of ceramic suspension, and the use of sacrificial fillers, extrusion or the bonding of fibres [2]. This method allows the direct adjustments of porous characteristics by the amount, size, shape and distribution of the pore-forming agents [1, 3]. Porous ceramics find numerous applications in various engineering fields, including filtration (molten metals, particulate from diesel exhausting gases), radiant burners, catalyst supports, biomedical devices, kiln furniture, reinforcement for metal matrix composites, bioreactors, thermal protection systems, supports for space mirrors, components in solid oxide fuel cells, lightweight sandwich structure, heat exchangers etc. [4]. The present paper deals with the creation of porous materials for biomedical applications and on the other hand the paper presents the usage of wastes (metallurgical slag, fly ash and waste glass) for creation of porous structure. A proper bone substitute besides being bioactive, it should also be able to guide bone regeneration into the defect. For this reason bone substitute materials and tissue engineering scaffolds are designed in macro porous form in order to provide a correct blood supply inside the implant as well as satisfactory bone in-growth and osteointegration [5,6,7]. On the other hand the paper presents the usages of wastes (metallurgical slag, fly ash and waste glass) for creation of porous structure. Their recycling is one of the tasks in the field of the environment protection which should be solved in near future. This industrial waste material as the main oxide constituents contains Fe203, Al203, Si02, Mg0, Na20 as well as small amounts of ecologically hazardous oxides such as Cr203, Ni0, and Mn0. By means of multi barrier system [8, 9] and the combinations of different types of industrial toxic waste and non-toxic waste (glasses), ecologically compatible products, could be developed by powder technology. Using waste glass, the sintering temperature is significantly reduced due
to the presence of liquid phase. Ecologically hazardous components are fixed at the molecular level in the silicate phase and inserted additionally in the matrix based material, which either has no toxic components or contains them in ecocompatible concentration. The obtained new glass-ceramics possess significantly lower leaching behaviour (leaching rate) and significantly higher mechanical properties. 2. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE 2.1. Materials In this investigation materials used for creation the porous structures for biomedical application were: biohydroxyapatite, titania and alumina. Commercial biohydroxyapatite powder (Merck Company, Darmstadt, Germany) with particle size 1±0.5 μm and the ratio Ca/P=1.63 was used for this investigation, and Ti02 was synthetized by hydrolysis procedure using C12H28TiO4 as precursor for titania. Transitional nano aluminium oxide powder (99.88wt.%; IBU-tech Company, Germany) was synthetized by pulse reactor technique at 8500C from aluminium tri-sec-butylat. Porous glass ceramics from wastes were created by using fly ash (thermal power plant REK Bitola, Republic of Macedonia), ferrochromium slag (Ferroalloys Work, Dugi Rat, Croatia; coded as Dalmacija) and waste glass from TV monitor using the multi barrier principle. 2.2. Methods for creation of porous structures 2.2.1 Creation of a porous structure using hydrogen peroxide H202 with concentration of 4% was used as a creator of porous structure. A slip consisted of powder, deflocculant Dolapix CE64 and H202 (10:4:3) was continuously mixed at room temperature. During the mixing a visible formation of bubbles of free oxygen was not noticed. The slip was then poured into aluminium frames. After drying at room temperature for 24h and at 105oC/6h, the porous (foam) material was sintered. Hydroxyapatite was sintered at 1200oC/1h and titania at 1300oC/ 3h . 2.2.2. Creation of a porous structure by use of C-fibre In a very dense pulp (consisted of powder, water and deflocculant Dolapix CE64), C-fibres (Toko Rayon C Ltd) with diameter of 500 μm have been embedded as bundles. After drying of the systems using the same procedure described in 2.2.1, sintering was performed within the temperature range from 20 to 1200oC with heating rate of 1oC/min and holding time at 1200oC for 2h. 2.2.3 Creation of a porous structure by use of polyurethane foam Open-celled macrostructures were fabricated by coating the skeletons of polyurethane foam with ceramic slurry followed by firing the resultant structure to pyrolyse the substrate and sinter the ceramic body. Polyurethane with density of 30 kg/m3 was used as substrate which was coated with slurry of the powder system. Dispersed, aqueous slurry was produced using Dolapix CE 64 as a deflocculant. The slurry containing 30% solid, 35% Dolapix CE 64 and the rest distilled water, coherently coats the polyurethane substrates. The foam was squeezed and dipped into the slurry, looking in that case like a sponge. During the expansion to the original shape and size, the foam was impregnated by the mentioned slurry. After drying of the system using the same procedure described in 2.2.1, the coated substrates were heated up to 1100oC in a schedule which minimized disruption during pyrolysis and allowed the ceramic body to reach full density. The heating schedule consisted of a heating rate of
0.5oC/min up to 800oC and rapid heating of 10oC/min from 800 to 1100oC, 0.5h soak time at 1100oC, and cooling in the furnace. 2.2.4. Creation of a porous structure by using industrial waste Based on the multi barrier concept [9], ferrochromium slag with granulation (-0.125 + 0.063mm) was mixed with 20wt.% TV glass, pressed at 20 MPa and sintered at 950oC/2h. Fly ash waste with 50wt.% TV glass was used as material for creating porous structure. Polyurethane foam was used as porogen (load was 0.5 g suspend./cm3) and the porous sample was sintered at 950oC/0.5h 2.3. Characterization Powder morphology and microstructure of the sintered porous samples were determined by scanning electron microscopy (Leica S 440i). Specific surface area of the powders was determined by 5-point-BET measurements (Micromeritics Gemini 2370). X-ray diffraction method (Philips PV 15-1 difractometer, operating at CuKα-radiation) was used for determination of phase composition. Cold isostatic pressing (Weber Pressen KIP 3010) was used for pressing transitional nano alumina powder. Sintering was realized in chamber furnace according to the schedule characteristic for appropriate porous material. Density of the sintered samples was determined by Archimedes method. Mechanical properties (E-modus and bending strength) were determined by three point bending tester (NETZSCH 401). 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 3.1. Hydroxyapatite porous structure The porous structure of hydroxyapatite produced by the method described in 2.2.1 is presented in Fig.1. The macrostructure was seen to be partially heterogeneous, i.e. regions of high and low densities were observed. The total porosity of this system was 68±5%. The pores are interconnected among each other and with a size of 100 to 3000μm. The microstructure of the pore wall–skeleton is shown in Fig.2. E-modulus, bending strength and compressive strength of this system were 1.6±0.4 GPa, 2±0.3 MPa and 7±2 MPa, respectively. The value of bending strength is close to that one presented in [10]. Ioku et al [11] refers to the value of compressive strength of 12.5 MPa for hydroxyapatite with porosity of 60±5%. Table I presents the values of E-modulus, bending strength and compressive strength of cortical and cancellous bone [12,13] and Fig. 3 shows the pores morphology of human cancellous bone.
Figure 1. Hydroxyapatite porous structure Figure 2. Microstructure of the densified created by H202 (4 mas.%) as porogen , skeleton (bar 1μm) sintered at 1200oC/1h (bar 1mm)
Table 1. E-modulus, bending strength and compressive strength of cortical and cancellous bone
Properties
Cortical bone Cancellous bone
E-modulus, GPa 7-25 0.05-0.5 Bending strength, MPa 50-150 / Compressive strength, MPa 130-180 2-12
Fig.3 Macrostructure of cancellous human bone (bar 1 mm) Based on the mechanical properties presented in Table I could be concluded that porous hydroxyapatite obtained by H202 as a pores creator, could be ranged between cortical and cancellous bone and potentially applied in medicine. Using procedure described in 2.2.2, the porous compacts with total porosity of 50±5% were obtained. The diameter of the pore channel was in the range 300-500 μm as shown in Fig. 4 (a and b). E-modulus, bending strength and compressive strength of this system were E=5±0.4 GPa, σ= 4±0.3 MPa and K= 11±2 MPa, respectively. a b c
Figure 4. Macrostructure of cell foam, using C-fibres Figure 5. Porous structure created as pores creator (a) axial (b) radial by polyurethane foam (bar 1mm)
Pores with dimensions in the range 200-400 μm were obtained by using the polyurethane foam, as shown in Fig.5. Total porosity of the compact was 65±4%. E-modulus, bending strength and compressive strength of this system were: E= 1.3±0.4 GPa, σ=1.6±0.3 MPa, K=5±1 MPa, respectively. Part of the porosity was open and interconnected, but the largest porosity was composed of closed pores. 3.2. Titania porous structure Titania produced by hydrolysis method has a specific surface area of 8.3 m2/g.The powder was agglomerated, the agglomerate size was in the range 0.5-2 μm and the primary particles had dimensions of 6-100 nm. Figure 6 (a) presents the porous structure of titania fabricated by applying the procedure described in 2.2.1. The integral porosity of 58±5% was obtained and the E-modulus, bending
strength and shear modulus of this system were: E=20GPa, σ=18MPa, G=17GPa, respectively. Titania porous structure was obtained by applying the procedure 2.2.2. The diameter of the pore channel was in the range of 200-400 μm as shown in Fig.6(b) and total porosity of 55±5% was obtained. E-modulus, bending strength and shear modulus of this system were: E=23GPa, σ=21MPa, G=19GPa, respectively. There was no interconnection between the formed tubular pores. Pores with dimensions in the range of 600-800 μm were obtained by using the polyurethane foam, Fig.6(c). Total porosity of the compact was 51±4%. E-modulus, bending strength and shear modulus of this system were: E= 26GPa, σ=23MPa, G=21 GPa, respectively. Part of the porosity was open and interconnected, but the largest porosity was composed of closed pores. This particular kind of pore structures with low pore interconnectivity is of relatively low interest in functional ceramics.
a b c Fig.6 . Ti02 porous structure created by usages of: a. H202 as porogen (x100), b. C-fibres as porogen ( bar 20μm) and c. polyurethane foam (bar 200 μm) 3.3. Alumina porous structure The specific surface area and tap density of the alumina powder was 111,5 m2/g and 37.55 g/dm3
, respectively. The size of the particles was 10-60 nm. XRD shows that the powder is consisted of δ, θ, γ and α phases. After cold isostatic pressing at 500 MPa and sintering in the interval RT-1500oC/30 min, density of 0.73TD was obtained. Open porosity of the compacts was 28%. The microstructure, Fig.7 is of a vermicular network [14] in which both, the pores and the pore channels are the same scale as α-Al203 grains. The elongated pores have a size of 0.5-1.0 μm. E-modulus and bending strength of this porous system were 140 GPa and 91 MPa, respectively. The presence of vermicular microstructure, geometry and interconnection of the pores as well as the bioinert properties of alumina allows whole spectrum of potential application in the functional ceramics. Using the procedure described in 2.2.2, the porous compact with total porosity of 53±5% was obtained. The diameter of the pore channel was in the range 2000-4000 μm as shown in Fig.8. Part of the porosity was open and interconnected, but the largest porosity was composed of closed pores. E-modulus, bending strength and shear modulus of this system were: E= 93±8GPa, σ=21±6MPa, G= 19±4GPa, respectively. This particular kind of pore structure with low pore interconnectivity is of low interest for medical purpose, in particular for tissue engineering scaffold applications.
Figure 7. SEM micrograph of the fractured Figure 8. Structure of alumina created by surface of α-Al203, sintered at 1500oC, H2O2 as porogen (x50) (bar 1μm)
3.4. Porous glass ceramics obtained from industrial waste Typical open pore structure created of fly ash and 50wt.% TV glass by using polyurethane foam as porogen is shown in Fig.9 [15]. Pores with dimensions in the range 600-1500 μm were obtained. The pores are interconnected. Integral porosity of the porous glass ceramics system was 74±5%. Mechanical properties of the porous system were: E-modulus 1.6±0.5 GPa and bending strength 3.4±1.1 MPa.
Figyre 9. Porous structure created Figure 10. SEM micrographe of the composite of fly ash-glass composite by using Dalmacija (-0.125+0.063mm)-20wt.% TV glass, polyurethane foam as porogen,(bar 2mm) sintered at 9500C/2h (bar 100 μm) Figure 10 illustrates porous structure of the composite consisted of 20wt.% TV glass and slag Dalmacija with granulation (-0,125+0.063mm) sintered at 9500C/2h. The porosity of the composite was 26.8±3.5%. The mechanical properties of the composite i.e. bending strength and E-modulus were σ = 35±3,5MPa and E=25.4±3,4GPa. The durability (expressed as mass lost) of the composite was determined after 24, 168 and 720h in 0,1M HCl and the values were 0.202, 0.471 and 0.662%, respectively. The fabricated porous composite was further examined for the purpose to be used as diffuser for water purification.
4. CONCLUSION - Porous hydroxyapatite fabricated by H202 as a pores creator (porosity 68±5%, E-modulus:1.6±0.4 GPa, bending strength: 2±0.3 MPa and compressive strength: 7±2 MPa) could be ranged between cortical and cancellous bone and potentially applied in medicine; - Porous alumina with vermicular microstructure (open porosity of 28%) and mechanical properties (E-modulus 140 GPa and bending strength 91 MPa) presents potential material with a whole spectrum of application in the functional ceramics. - Porous composite Dalmacija (-0.125+0.063mm)-20wt. % TV glass, sintered at 9500C/2h with porosity 26.8±3.5% and mechanical properties (σ = 35±3,5MPa and E=25.4±3,4GPa) presents potential material which can be used as diffuser for water purification.
5. REFERENCES [1]. Hirschfeld D.A., Li T.K., Liu D.M.: Processing of Porous Oxide ceramics, Key Eng. Mater., 1996, 115, 65-80 [2]. Colomo P.: Conventional and novel processing methods for cellular ceramics, Philos. Trans.R.Soc. A, 2006, 364(1838), 109-124 [3]. Liu D.M: Influence of porosity and pore size on the compressive strength of porous hydroxyapatite ceramic, 1997, 23(2), 135-139 [4]. She J.H, Ohji T.: Fabrication and characterization of highly porous mullite ceramics, Mater. Chem.Phys., 2003, 80, 610-614 [5]. Tsuruga E., Takita H., Itoh H., Wakisaka Y., Kuboki Y., Pore size of porous hydroxyapatite as the cell-substratum controls BMP-induces osteogenesis, J.Bioche, 1997, 121, 317-324 [6]. Hing K.A., Annaz B., Saeed S., Ravell P.A., Buckland T.: Microporosity enhances bioactivity of synthetic bone draft substitutes, J.Mater.Sci.:Mater.Med., 2005, 16, 467-475 [7]. Chang B.S., Lee C.K., Hong K.S., Youn H.J., Ryu H.S., Chang S.S., Park K.W.: Osteoconduction at porous hydroxyapatite with various pore configurations, Biomaterials, 2000, 21, 1291-8 [8]. Fidancevska E., Mangutova B., Milosevski D., Milosevski M., Bossert J.: Obtaining of dense and highly porous ceramic materials from metallurgical slag, Sci.Sint., 2003, 35, 85-91 [9]. Ondracek G.:Berg- und Huttenmannische Monatshefte, 1994, 139, 273 –279 [10]. Slosarczyk A., Higly porous hydroxyapatite material, Powder.Met.Int., 1989, 21(4), 24 [11]. Ioku K., Kurosawa H., Shibuya K., Yokozeki H., Hayashi T., Bioceramics,Vol7 Ed.O.H.Anderson and Yli-Urpo,Butterford-Heinemann,1994, p.97 [12]. Hench L.: Bioceramics: from concept to clinic, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1991, 74(7), 1487 [13]. Ravaglioli A., Krajewski A., Bioceramics, Chapman & Hall, London, 1996, p.44 [14]. Fidancevska E., Bossert J., Vassilev V., Adziski R., Milosevski M., Design of ceramic microstructure of nanoscaled transitional alumina, Nanostructuresd materials for advanced technological application, J.P.Reithmaier et al.(eds.), Nanostructured Materials for Advanced Technological Applications, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. 2009 [15]. Fidancevska E., Milosevski M., Technical report of INCO Copernicus project 2003
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
PREDNOST PROIZVODNJE VISOKOKVALITETNIH BAKRENACA U
TOPIONICAMA KOJE PRERAĐUJU SULFIDNE KONCENTRATE BAKRA
ADVANTAGE OF HIGH GRADE MATTE PRODUCTION IN SULFIDE
COPPER CONCENTRATES SMELTERS
Ljubiša Mišić, dipl.ing.met. Tatjana Apostolovski-Trujić, dipl.ing.met.
Saša Ivanović, dipl.ing.met. Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju
Zeleni bulevar 35, Bor, Srbija
REZIME U ovom radu dat je uporedni pregled količina energije sumpora i kiseonika za proizvodnju visoko kvalitetnih bakrenaca (65-70% bakra) iz koncentrata bakra, u zavisnosti od sastava različitih koncentrata bakra. Sumpor i kiseonik kreiraju visok potencijal za egzotermalanu toplotu tokom procesa oksidacije sa povećanjem sadržaja FeS2. Ali ovu prednost degradira povećanje količine šljake i gasa, što uključuje potrebu za dodatnom energijom i troškovima. Suprotan efekat stvaraju halkozin Cu2S ili bornit Cu5FeS4 u koncentratu. To znači da se količine produkata prerade: šljaka i otpadni gas moraju smanjiti. Manja količina produkata prerade rezultira manjim zahtevima za fosilnim gorivima i industrijskim kiseonikom. Sve prednosti / posledice upoređivane su u zavisnosti od rezultatih mineraloških sastava koncentrata iz Rusije, Latinske Amerike, Afrike i domaćih koncentrata. ABSTRACT This paper compares how energy of sulfur and oxygen requirement for production high grade matte (65-70 % Cu) from sulfide concentrates of copper vary with their composition. There are created high potential for exothermal heat during oxidation process from concentrates of increasing FeS2 content. But this benefit of energy is degraded with increasing slag and off-gas production, which involve extra treatment energy and cost. The opposite of that is more chalcocite Cu2S or bornite Cu5FeS4, in concentrates. This means that furnace products: slag and off-gas which is evolved must also decrease. As а benefit of small amounts of furnace products result in a lessened requirement for fossil fuel and industrial oxygen. All benefits/consequences result as a different mineralogical composition of Russian, Latin American, African and domestic concentrates are also compared.
8th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
REVIEW OF THERMODYNAMIC SIMULATION MODELS IN COPPER MATTE PRODUCTION -
THE IMPURITIES BEHAVIOUR ANALYSIS
Emina D. Požega, Mining and metallurgy institute
Zeleni bulevar 33, 19210 Bor J 12, 19210 Bor, Serbia
Dragana T. Živković, University in Belgrade,
Tehnical faculty in Bor, Serbia
Lidija D. Gomidželović, Mining and metallurgy institute
Zeleni bulevar 33, 19210 Bor, Serbia
Vlastimir K. Trujić, Mining and metallurgy institute
Zeleni bulevar 33, 19210 Bor, Serbia Keywords: modeling, copper metallurgy, simulation, thermodynamics, software ABSTRACT Modeling and simulation, including computer simulation/calculation software or program and mathematical representations of physics and chemistry of complex metallurgical systems, have been increasingly used to assist: process development and design, process evaluation and optimization, production scheduling and planning, process control, and business evaluation. Review of thermodynamic simulation models for copper matte production in the conventional copper smelting process were presented in this paper, with special emphasize on thermodynamic analysis of impurities behavior in copper metallurgy.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
DOBIJANJE SREBRA I BAKRA VISOKE ČISTOĆE IZ ISTROŠENE POSREBRENE BAKARNE ŽICE
REFINMENT SILVER AND CUPRUM HIGH PURITY FROM SPENT SILVER OVER CUPRUM WIRE
Silvana Dimitrijević,dipl.inž.met
Dragan Marković, dipl.inž.met.
Suzana Dragulović, dipl.inž.tehn.
Radiša Todorović dipl.inž.met
Saša Ivanović, dipl.inž.met.
Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju, Zeleni bulevar 35, Bor, Srbija
e-mail: [email protected]
Ključne reči: posrebrena bakarna žica, prerada, srebro, bakar REZIME U novije vreme povećan je interes za recikliranjem metala čime se smanjuje količina otpada kao i troškovi tretiranja otpadnih voda. Cilj ovog rada bio je da se iz istrošene posrebrene bakarne žice valorizuju srebro i bakar a da se nečistoće, kao što su olovo, kalaj, antimon, kadmijum uklone. Srebro i bakar visoke čistoće (99,99%) iz istrošene žice dobijeni su kombinacijom pirometalurških, elektrometalurških i hemijskih postupaka u laboratorijama i poluindustrijskim postrojenjima Instituta za rudarstvo i metalurgiju u Boru.
Key words: recrystalization temperature, tin and tellurium low-alloyed copper
ABSTRACT Recycling of secondary raw’materijals recently become more interesting, mainly due to reduced quantities of waste and price of waste water treatment. Aim of this work was recycling and production of copper ana silver from rub out copper wire plated with silver. Silver and copper high purity (99,99%) from rub out copper wire realized by combining pyro-metallurgy, electro-metallurgy and chemical treatment in laboratory and pilot production in Institute of Mining and Metallurgy Bor.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION AND THERMODYNAMIC PREDICTING OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA IN Ga-GeSb0.855 SYSTEM
Ana Kostov1, Dragana Živković2, Dragan Manasijević2, Duško Minić3, Živan Živković2
1 Mining and Metallurgy Institute Bor, Serbia, E-mail: [email protected] 2 University of Belgrade, Technical Faculty Bor, Serbia
3 University of Priština, Faculty of Technical Sciences Kosovska Mitrovica, Serbia
Keywords: DTA, phase diagram, Ga-Ge-Sb system ABSTRACT Experimental investigation and thermodynamic predicting of phase equilibria in Ga-GeSb0.855 system, which is of a practical importance in electric - semiconductors industry, are presented in this paper. Results of experimental investigation are done by different thermal analysis (DTA) and SEM-EDX analysis, and thermodynamic predicting is done by PANDAT thermo-chemical software. The experimental and calculated values are shown a good agreement as well as the obtained phase diagram of the investigated system.
8 th
Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION AND THERMODYNAMIC CALCULATION IN Pb-Zn-Ag SYSTEM
Dragana T. Živković1, Duško M. Minić2, Dragan M. Manasijević1, Aleksandra M. Mitovski1, Ljubiša T. Balanović1, Živan D. Živković1
1 – University of Belgrade, Technical Faculty, Bor, Serbia
2 – University of Priština, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Kosovska Mitrovica, Serbia
Keywords: extractive metallurgy of lead, desilverizing, Pb-Zn-Ag system, thermodynamics, phase equilibria ABSTRACT Ternary Pb-Zn-Ag system is typical for some physicochemical processes going on in refining phase in the extractive metallurgy of lead. Therefore, investigation of mentioned system is important from both theoretical and practical research of the phenomena occurring during the lead desilverizing process.The results of experimental investigation (DTA) and thermodynamic calculation of phase equilibria in Pb-Zn-Ag system (CALPHAD method + PANDAT software) are presented in this paper.
8 th
Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
THERMAL ANALYSIS OF THE TERNARY SYSTEM Bi-Cu-Sn
Dragan M. Manasijević1, Duško M. Minić2, Dragana T. Živković1, Nadežda M. Talijan3, Aleksandar S. Grujić3, Saša R. Marjanović1
1 – University of Belgrade, Technical Faculty, Bor, Serbia 2 – University of Priština, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Kosovska Mitrovica, Serbia
3Institute of Chemistry, Technology and Metallurgy, Belgrade, Serbia
Keywords: Lead-free solders, Bi-Cu-Sn ternary system, Thermal analysis, DTA, DSC ABSTRACT Interaction of lead-free solders with copper substrate represents an important phenomenon in the issue of reliability of solder joints and is typical for the Bi-Cu-Sn system, as one the high-temperature solder system recently suggested in literature and soldering practice. New experimental results on thermal analysis of the Bi-Cu-Sn alloys, including DTA and DSC measurements for two isopleths from bismuth corner with molar ratio of copper and tin equal to 1/3 and 1/1 and three isopleths from tin corner with molar ratio of bismuth and copper equal to 3/1, 1/1 and 1/3, are presented in this paper.
8 th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Inorganic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27.-28. April 2010
NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE CHILL WHEEL COOLING DURING
CONTINUOUS FREE JET MELT-SPINNING
Blaž Karpe, Borut Kosec, Milan Bizjak, Tomaž Kolenko University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Natural Sciences and Engineering
Ljubljana Slovenia
Keywords: rapid solidification, metallic materials, heat transfer balance, heat transfer coefficient, numerical modeling
ABSTRACT New method for determining contact resistance through variable heat transfer coefficient is introduced which takes into account physical properties of the casting material, process parameters and contact time/length between metal melt or metal ribbon and substrate and enables cooling and solidifying rate prediction before the experiment execution. The calculations show that contact resistance between metal melt and chilling wheel has a great influence on melt cooling and wheel heating rate, and must not be neglected in numerical calculations, even if its value is very low. Influence of process parameters on cooling and solidifying rate and consequently on microstructure development over ribbon thickness are outlined. It can be concluded from the results, that process parameters which determine the thickness of the melt puddle in the downstream have major influence on cooling and solidifying rate of the ribbon. Among thermal properties, the thermal diffusivity of the metallic melt, solidified ribbon and wheel material has major influence on cooling and solidifying rate of the melt and solidified ribbon respectively. In the case of continuous casting, heat balance of the wheel is calculated and influence of the chill wheel cooling mode on cooling rate of metallic ribbon is analyzed.
8 th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Inorganic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27.-28. April 2010
THE PRECIPITATION KINETICS OF RAPIDLY SOLIDIFIED Al - BASED ALLOYS
Milan Bizjak, Ladislav Kosec, Blaž Karpe
University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Natural Science and Engineering Ljubljana, Slovenia
Goran Dražič
Jožef Stefan Institute, Jamova 39 Ljubljana, Slovenia
Keywords: Rapid solidified Al alloys, Kinetics of precipitation, In-situ measurement of electrical resistivity
ABSTRACT
Aluminium alloys are widely used as an industrial material, usually for lower temperature applications. For synthesis of new aluminium alloys with good mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, combine development of powder metallurgy and rapid solidification was necessary. This article describes the synthesis and analysis of rapidly solidified Al-TM alloys produced by melt spinning method. As cast alloys were rapidly solidified in the form of thin ribbons, thicknesses between 30 and 75 microns and heat threaded at a constant heating rate in argon or vacuum atmosphere up to 600°C. Kinetics and sequence of microstructural changes during heating was analyzed by in-situ measurements of electrical resistivity. This method allows accurate detection of transformations between metastable and stable phases of rapidly solidified Al-TM alloys at a given temperature. After determining the temperature of transition points, quenched microstructures were analyzed with transmission electron microscopy. It can be concluded from the results of investigation that precipitation from supersaturated solution is the most frequent reaction in these types of alloys. Its kinetics is highly dependent upon solidification rate achieved through the cross-section of as cast ribbon, which is in direct connection with ribbon thickness.
8
th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation
„Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
MICROSTRUCTURE AND CHARACTERISATION OF RAPIDLY SOLIDIFIED Au-La RIBBONS
T. Zupančič Hartner1,2, R. Rudolf1,2, B. Kušić1, I. Anžel1
1Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maribor, Slovenia
2Zlatarna Celje d.d., Department for technological Development, Slovenia
ABSTRACT In this research influence of lanthanum as a micro-alloying element in pure gold was investigated. Rapidly solidified ribbons of Au-0.5 wt.% La have been made by melt spinning technique. On prepared samples microstructure was investigated and micro-hardness was measured. Microstructure analysis in cross-section of the melt-spun ribbons reveals three different regions from wheel to air side: fine equiaxed grains, zone with a columnar microstructure and coarse equiaxed grains. Very fine precipitates inside the grains, the eutectic micro-segregation at the grain boundaries and some other features have been observed in the metastable rapidly solidified microstructure. Non-homogeneous microstructure in cross section was accompanied with significant differences in micro-hardness values. This indicates strong influence of changeable solidification conditions during melt spinning on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Microstructure and corresponding strengthening achieved by lanthanum and by rapid solidification is discussed.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
UTICAJ SADRŽAJA δ-FERITA NA MEHANIČKA SVOJSTVA
AUSTENITNOG NEHRĐAJUĆEG ČELIKA
INFLUENCE OF DELTA FERITE ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF AUSTENITE STAINLESS STEEL
Mr.Sc. Almaida Gigović-Gekić1, Dr. Sc. Mirsada Oruč2
1.Univerzitet u Zenici, Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, 72 000 Zenica 2. Univerzitet u Zenici Metalurški institut“Kemal Kapetanović“, 72 000 Zenica
Ključne riječi: austenitni nehrđajuči čelik, delta ferit, mehanička svojstva REZIME Zahvaljujući karakterističnim svojstvima kao što su duktilnost, otpornost prema habanju, otpornost prema visoko temperaturnoj koroziji, otpornost prema puzanju i dr. austenitni nehrđajuči čelici su našli široku primjenu u industriji. U austenitnim čelicima osim osnovne austenitne mikrostrukture može bit prisutan i delta ferit. Delta ferit nastaje u toku solidifikacije i ostaje prisutan u mikrostrukturi i na sobnoj temperaturi. Prisustvo delta ferita ima negativan uticaj na svojstva, posebno deformabilnost čelika kao i na osjetljivost prema interkristalnoj koroziji. U ovom radu su predstavljeni rezultati ispitivanja mehaničkih svojstava za austenitni nehrđajući čelik u zavisnosti od sadržaja delta ferita. Key words: austenite stainless steel, delta ferrite, mechanical properties ABSTRACT Thanks to the characteristic properties such as ductility, resistance to abrasion, resistance to high temperature corrosion, resistance to creep and other properties, austenitic stainless steels have found wide application in industry. The delta ferrite can be a second phase in austenite stainless steel. The delta ferrite occurs during solidification and remains present in the microstructure at room temperature. The presence of the delta ferrite has a negative impact on properties, especially the deformability of steel as well as sensitivity to intercrystal corrosion. This paper presents the results of testing of mechanical properties for austenitic stainless steel depending on the content of delta ferrite.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
FAKTORI KOJI UTIČU NA TOPLOOTPORNOST LEGURE NA BAZI NIKLA – IN.100
FACTORS INFLUENCE ON HEAT RESISTANCE OF IN-BASED
ALLOY – IN.100
Radiša Todorović, dipl.ing.met, Dr Ana Kostov, dipl.ing.met. LjubinkaTodorović,dipl.hem.
Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju Bor 19210 Bor, Srbija, E-mail:[email protected]
Ključne reči: legura IN.100 , intermetalni talog γ’ , veličina čestica , trajna čvrstoća REZIME Granica puzanja i trajnja čvrstoća su dve najznačajnije mehaničke karakteristike toplootpornih materijala na osnovu kojih se može izvesti ocena toplootpornosti specijalnih legura koje su namenjene za rad na povišenim temperaturama pri odgovarajućim složenim opterećenjima. Navedene karakteristike su u direktnoj zavisnosti od makro i mikrostrukture, karbidne faze kao i odgovarajućih mikrokonstituenata. U radu je naveden uticaj prisustva legirajućih elemenata, uslova topljenja i livenja kao i očvršćavanja na veličinu i raspored izlučenih čestica prisutnih faza i morfologiju karbida, a što se skupa odražava na granicu puzanja i trajnu čvrstoću a time i na toplootpornost legure. ABSTRACT Creep limit and long-time strength areth two most significant mechanical propertise of high-temperature resistant materials. On the basis of these properties, one can estimate high-temperature resistance of special alloys intendend for service at elevated temperatures under the corresponding complex loads. The above mentioned properties are directly related to macro and micro structures, carbide phase, as well as to the relevant micro constituents. The paper discusses the effect of the presence of alloying elements, the conditions of melting and casting, as well of herdening on both the siye and arrangement which all together the high-temperature resistance of an alloy.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
MIKROSTRUKTURA, MEHANIČKE I ELEKTRIČNE OSOBINE
LEGURA TERNARNOG Bi-Cu-In SISTEMA
Ajka Aljilji1, Duško Minić1, Vladan Čosović2, Milan Kolarević3, Dragan Manasijević4 i Dragana Živković4
1- Univerzitet u Prištini, Fakultet tehničkih nauka, Kos. Mitrovica, Srbija
2 – Institut za Hemiju, Tehnologiju i Metalurgiju, Beograd, Srbija 3 – Univerzitet u Kragujevcu, Mašinski fakultet, Kraljevo, Srbija
4 - Univerzitet u Beogradu,Tehnički fakultet, Bor, Srbija Ključne reči: Bi-Cu-In sistem, mikrostruktura, tvrdoća, električna provodljivost REZIME Bezolovne lemne legure na bazi bakra posebno predstavljaju moguću zamenu za standardni olovno-kalajni lem. Za kompletno definisanje osobina ternarnog Cu-In-Bi sistema izvedena su ispitivanja mikrostrukture, tvrdoće po Brinelu i električne provodljivosti legura datog sistema. Ispitano je vići broj legura za tri kvazibinarna preseka, sa molarnim odnosom Bi:Cu=1, Cu:In= 1:3, Bi:In=1. Pomoću optičke mikroskopije određene su mikrostrukture legura na sobnim uslovima. Primenom CALPHAD metode izvršen je proračun izotermalnog preseka na 250C . ABSTRACT Lead free solder alloys based on copper are possible substitution for standard Pb-Sn solders. For the completed definition of the properties of ternary Cu-In-Bi system there were conducted microstructure investigations, hardness by Bruinell and electric conductivity of alloys. Numerous alloys were investigated for three quasi binary cross sections with molar ratio Bi:Cu=1, Cu:In= 1:3, Bi:In=1. By the application of optical microscopy there were defined micro structures of the alloys on ambient temperature. By application of CALPHAD method a calculation of isothermal cross section is made at 250C
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
MIKROSTRUKTURA, MEHANIČKE I ELEKTRIČNE OSOBINE LEGURA TROJNOG Cu-In-Sb SISTEMA
Duško Minić1, Ajka Aljilji1, Milan Kolarević2, Jasna Stajić-Trošić3
Dragan Manasijević4 i Dragana Živković4
1- Univerzitet u Prištini, Fakultet tehničkih nauka, Kos. Mitrovica, Srbija 2- Univerzitet u Kragujevcu, Mašinski fakultet, Kraljevo, Srbija
3- Institut za Hemiju, Tehnologiju i Metalurgiju, Beogradu, Srbija 4 – Univerzitet u Beogradu,Tehnički fakultet, Bor, Srbija
Ključne reči: Cu-In-Sb trojni sistem, mikrostruktura, tvrdoća i električna provodljivost.
REZIME Bezolovne lemne legure na bazi bakra posebno predstavljaju moguću zamenu za standardni olovno-kalajni lem. Za kompletno definisanje osobina trojnog Cu-In-Sb sistema izvedena su ispitivanja mikrostrukture, tvrdoće po Brinelu i električne provodljivosti legura datog sistema. Ispitano je vići broj legura za tri kvazibinarna preseka, sa molarnim odnosom Sb:Cu=1, Cu:In= 1, Sb:In=1. Primenom optičke mikroskopije određene su mikrostrukture legura. Primenom CALPHAD metode i softverskog paketa PANDAT 8.1. izvršen je proračun izotermalnog preseka na 250C. Eksperimentalno dobijene faze u mikrostrukturi se uklapaju sa prisutnim fazama na proračunatom preseku na 250C. ABSTRACT Lead free solder alloys based on copper are specially possible substitution for standard Pb-Sn solders. For the completed definition of the properties of ternary Cu-In-Sb system there were conducted microstructure investigations, hardness by Bruinell and electric conductivity of alloys. Numerous alloys were investigated for three quasi binary cross sections with molar ratio Sb:Cu=1, Cu:In= 1, Sb:In=1. By the application of optical microscopy there were defined micro structures of the alloys. By application of CALPHAD method and software PANDAT 8.1. a calculation of isothermal cross section is made at 250C. Experimentally obtained phases in micro structures have a good agreement with present phases in calculated section at 250C.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
UTICAJ ALUMINIJA I TITANA NA TEMPERATURU REKRISTALIZACIJE SUPERLEGURE
NIMONIC 80A
INFLUENCE OF ALUMINUM AND TITANIUM ON A TEMPERATURE OF RECRYSTALLIZATION OF SUPERALLOY
NIMONIC 80A
Mr. Omer Beganović, dipl. inž. Branka Muminović, dipl. inž.
Belma Fakić, dipl. inž. UNIVERZITET U ZENICI - Metalurški institut “Kemal Kapetanović”
Z E N I C A
Prof. dr.Faik Uzunović, dipl. inž. UNIVERZITET U ZENICI - Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale
Z E N I C A
Ključne riječi: Superlegure, mehanizmi ojačavanja, rekristalizacija REZIME Superlegura Nimonic 80A se uglavnom koristi u precipitaciono ojačanom stanju koje je rezultat izdvajanja finih čestica γ' faze Ni3(Al,Ti). Standardna termička obrada ove superlegure se sastoji od rastvarajućeg žarenja na 1080oC/8h i precipitacionog žarenja na 700oC/16h. Nakon rastvarajućeg žarenja najveći dio aluminija i titana se nalazi u presićenom čvrstom rastvoru, dok se nakon precipitacionog žarenja najveći dio aluminija i titana nalazi izdvojen u precipitatima γ' faze. Često se nakon rastvarajućeg, a prije precipitacionog žarenja, vrši hladna ili češće topla deformacija superlegure radi ujednačavanja zrna po veličini ili dodatnog ojačavanja. Budući da se nakon takve deformacije obavlja potpuna ili djelomična rekristalizacija potrebno je poznavati uticaj aluminija i titana, kada se nađu u čvrstom rastvoru, na odvijanje rekristalizacionih procesa. Key words: Superalloys, strengthening mechanisms, recrystallization SUMMARY Superalloy Nimonic 80A is generally used in precipitation strengthened condition that is result of precipitation of fine particles of γ´ phase Ni3(Al,Ti). Standard heat treatment of the superalloy consists of solution annealing at 1080oC/8h and precipitation aging at 700oC/16h. After the solution annealing most of the aluminum and titanium is in super saturated solid solution, while after the precipitation aging most of the aluminum and titanium is precipitated into particles of γ´ phase. Often after the solution annealing and before the precipitation aging, it is made cold, or more often worm deformation of the superlalloy, to harmonize the grain size or to achieve an additional strengthening. Since that after such deformation a complete or a partial recrystallization is performed, it is necessary to know the influence of aluminum and titanium, when found in solid solution, on recrystallization process.
8 th
Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „METALLIC AND NONMETALLIC MATERIALS“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
RECRYSTALLIZATION TEMPERATURE OF COLD DEFORMED Au-0,5La ALLOY
Bojana Kušić Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Smetanova 17, 2000 Maribor Slovenia
Tjaša Zupančič-Hartner
Zlatarna Celje d.d. Kersnikova 19, 3000 Celje
Slovenia
Prof. dr. Ivan Anžel Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Institute of materials technology Smetanova 17, 2000 Maribor
Slovenia Keywords: recrystallization, Au-La alloy, second phase particles ABSTRACT Recrystallization temperature of cold deformed Au-0,5La alloy has been studied. 24-carat microalloyed gold containing 0,5% of La was prepared by induction vacuum melting using high purity elements as starting materials. Such small addition of La microalloying results in the microstructure with small second phase particles at gold grain boundaries or even within the grains causing very effective dispersion strengthening. Microalloying of Au by La combined with cold deformation improves mechanical properties of the alloy and has a significant impact on the recrystallization temperature. Series of experiments have been performed by annealing at temperatures in the range from 397ºC to 773º C for 1h. Depending on measured microhardness different etchants have been used and compared. Based on experimental data a recrystallization map that gives the correlation between degree of deformation, annealing temperature and hardness has been made which can be used as a guide for the appropriate thermomechanical treatments in industrial praxis.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27, -28. april 2010.
UTJECAJ VREMENA IZOTERMALNOG POBOLJŠANJA NA MIKROSTRUKTURNE KARAKTERISTIKE UZORAKA OD
AUSTEMPEROVANOG NODULARNOG LIVA
INFLUENCE OF AUSTEMPERING TIME ON MICROSTRUCTURE OF AUSTEMPERED DUCTILE IRON
Dr. Sci. Hasan Avdusinovic
Dr. Sci. Sreto tomašević Dr. Sci. Fuad Begovac
Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Zenica
Ključne riječi: austemperovani nodularni liv, austenit, acikularni ferit. martenzit
REZIME
Austemperovani nodularni liv –ADI je materiJal koji ima znatno više vrijednosti zatezne čvrstoće od klasičnog nodularnog liva uz zadržavanje duktilnih svojstava polaznog stanja prije termičke obrade. Karakteristična ausferitna mikrostruktura, koja se sastoji od acikularnog ferita i austenita, daje ovom materijalu tako izuzetna mehanička i duktilna svojstva. Zadatak istraživanja, prezentiranog u ovom radu, je određivanje veze između mikrostrukturnih karakteristika i vremena izotermalnog poboljšanja uzoraka od austemperovanog nodularnog liva legiranog sa bakrom i niklom. Key words: austempered ductile iron, ausferrite, austenite, acicular ferrite, martensite
SUMMARY
Austempered ductile iron-ADI is a material that has significantly higher tensile strength than conventional ductile iron while retaining ductile properties of original condition (condition before heat treatment). Characteristic ausferrite microstructure, consisting of ferrite and austenite, gives these material so special mechanical and ductile properties. The task of research, presented in this paper, is correlation between the microstructure of the treated samples and time of austempering phase during heat treatment.
8 th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Inorganic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27.-28. April 2010
INDUCTIVE HEATING AND QUENCHING OF PLANETARY SHAFTS
FOR THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
Borut Kosec, Blaž Karpe, Aleš Nagode University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Natural Sciences and Engineering
Ljubljana, Slovenia
Metoda Ličen ISKRA Avtoelektrika d.d.
Šempeter, Slovenia
Gorazd Kosec, Jure Bernetič ACRONI d.o.o.
Jesenice , Slovenia
Keywords: planetary shaft, carbon steel, temperature field, inductive heating, quenching ABSTRACT Our work discusses a complex process of inductive heating and quenching of carbon steel CK 45 planetary shafts for diesel engine starters. During their exploitation planetary shafts assembled in starters are subjected to high thermal and mechanical loads. Surface temperature measurements during the inductive heating process were realized in the industrial environment. The intensity and homogeneity of temperature fields on the surface of the planetary shafts were measured by thermographic camera. On the measurements base and theoretical knowledge, a mathematical model for temperature conditions determination in the shaft during the entire process of heating and quenching was carried out. On the basis of developed mathematical model a computer program was developed, and used for analyses and induction hardening process optimization of planetary shafts.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem “METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27 - 28. april 2010.
EKSPERIMENTALNA ISPITIVANJA TVRDOĆE ZAVARENOG SPOJA ČELIKA
EXPERIMENTAL TESTING OF THE STEEL WELDED JOINT
HARDNESS
dr.sc. Fadil Islamović, docent Univerzitet u Bihaću, Tehnički fakultet
Bihać mr.sc. Fatka Kulenović, v/a
Univerzitet u Bihaću, Tehnički fakultet Bihać
dr.sc. Dženana Gačo, docent Univerzitet u Bihaću, Tehnički fakultet
Bihać Esad Bajramović, dipl.ing.maš.
Univerzitet u Bihaću, Tehnički fakultet Bihać
Ključne riječi: čelični lim, tehnologija zavarivanja, osnovni metal (OM), zona uticaja toplote (ZUT), metal zavara (MZ), tvrdoća, rezervoar, stari materijal, novi materijal, predgrijavanje. REZIME: Uticaj izabrane tehnologije zavarivanja čeličnih ploča, na mehanička i eksploatacijska svojstva, detaljno je ocjenjivan na osnovu više aspekata koja najpotpunije opisuju ponašanje osnovnog materijala, zavarenog spoja i komponenti zavarenog spoja. U ovom radu dati su rezultati mjerenja tvrdoće po presjeku (OM-ZUT-MZ-ZUT-OM) prema EN 1043. U cilju ocjene stanja starog materijala od koga su napravljeni vertikalni cilindrični rezervoari u Bihaću zapremine 5000 m3, urađena su ispitivanja i na starom materijalu. S obzirom na vrstu materijala (Č.0361), za zavarivanje ispitnih uzoraka su primjenjene četiri izabrane tehnologije zavarivanja i to: tehnologija A - REL postupak sa elektrodom EVB 50 bez predgrijavanja, tehnologija B - REL postupak sa elektrodom EVB 50 sa predgrijavanjem, tehnologija C - MAG postupak sa žicom VAC 60 bez predgrijavanja, i tehnologija D - MAG postupak sa žicom VAC 60 sa predgrijavanjem. Generalno, ova ispitivanja treba da daju odgovor na pitanje da li je moguća rekonstrukcija postojećih jednokomornih u višekomorne rezervoare, kao i projektovanje i izrada potpuno novih višekomornih rezervoara. ABSTRACT: The influence of the steel plate selected welding technology on the mechanical and exploitation characteristics was evaluated in detail, based on several aspects that most completely describe the behavior of the base material, welded joint, and welded joint components. The paper gives an overview of the cross-section hardness measurement (BM-HAZ-WM-HAZ-BM) according to the EN 1043. In order to evaluate the condition of the old material, that 5000 m3 volume vertical cylindrical tanks in Bihać were made of, testing on the old material was conducted as well. Considering the type of the material (S.0361), four selected welding technologies were applied for the welding of the test samples: technology A - REL procedure with electrode EVB 50 without pre-heating, technology B - REL procedure with electrode EVB 50 with pre-heating, technology C - MAG procedure with wire VAC 60 without pre-heating, and technology D - MAG procedure with wire VAC 60 with pre-heating. In general, these testing should give an answer to question whether the reconstruction of the existing single-chamber to multiple-chamber tank is possible, as well as the design and construction of the complete new multi-chamber tanks.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27. -28. april 2010
PROCENA PREOSTALOG VEKA TRAJANJA MATERIJALA BUBNJA
KOTLA SA ASPEKTA MIKROSTRUKTURE
ASSESSMENT OF RESIDUAL LIFE MATERIAL BOILER DRUMS IN VIEW OF MICROSTRUCTURE
Z. Karastojkovića, R. Popovića, Z. Kovačevićb, Z. Janjuševićc a - High Technical College, Blvd. Dr Z. Djindjića 152a,11070 Novi Beograd, Serbia
b - Institute for Testing of Materials, Blvd. vojvode Mišića 43, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia e-mail: [email protected]
c - Institute for Nuclear and Other Mineral Raw Materials, Franchet d′Eparais 86, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia
Mr Zoran Karastojković, viši predavač
High Technical College Novi Beograd, Serbia
Dr Radivoj Popović, profesor High Technical College Novi Beograd, Serbia
Ključne reči: mikrostrukturne promene, oštećenja, mikroskopija, metoda replike REZIME U radu je prikazana korelacija između preostalog veka života i mikrostrukturnog stanja materijala, uključujući i merenje tvrdoće, na primeru bubnja kotla iz termoelektrane instalisane snage 210 MW. Nakon 20 i više godina rada, pod uticajem temperature i naprezanja, u površinskom sloju materiala bubnja kotla došlo je do mikrostrukturnih promena uzrokovanih nastajanjem mikropora, mikrošuplina, zatim mikroprslina kao i makroprslina, u uslovima puzanja. Procena mikrostrukture i nastalih oštećenja izvršena je prema preporukama Evropske komisije - Residual Life Assessment and Microstructure, korišćenjem svetlosne mikroskopije. Rad uključuje i opis primenjene tehnike za mikrostrukturna ispitivanja komponenti nedestruktivnom metodom - metodu replika. Keywords: microstructural changes, damage, microscopy, replica method ABSTRACT The paper describes the correlation between the residual life and microstructural state of material, including hardness measurements, at the drum boiler material from power plant 210 MW of installed power. After more than 20 years in service, under the influence of temperature and strain, in the surface layer of drum boiler material have occurred microstructural changes caused by formation micropores, microcavities, then microcracks and macrocrack, in creeping conditions. Assessment of microstructures and caused damage is done according to the recommendations of the ECCC Management Committee - Residual Life Assessment and Microstructure, using light microscopy. This paper includes a description of techniques for microstructural examination of components of non-destructive method - known as replica method.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem “ METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI “ Zenica, BiH, 27 – 28. april 2010
KONTROLA ATMOSFERE U PEĆIMA ZA TERMIČKU OBRADU
ATMOSPHERE CONTROL IN FURNACES FOR THERMAL TREATMENT
Dr. Jusuf Duraković
Dr. Diana Ćubela Mr. Almaida Gigović-Gekić
Univerzitet u Zenici Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale
Ključne riječi: termička obrada, zaštitna atmosfera, kontrola ABSTRAKT U zavisnosti od vrste čelika i postavljenih zahtjeva za kvalitet gotovog proizvoda često je neophodno koristiti zaštitnu atmosferu u peći. Odgovarajućom zaštitnom atmosferom materijal se štiti od dodatnog naugljeničavanja ili razugljeničavanja, oksidacije i sl. Za kvalitetan proizvod neophodna je stabilnost zaštitne atmosfere tj. kontrola njenog sastava. Ovaj rad tretira problem kontrole atmosfere u protočnoj peći, čija je uloga bila da zaštiti proizvod kako od naugljeničenja tako i razugljeničenja površine. Endogas se proizvodi u endogeneratoru. U peći se termički tretiraju vijci koji se putem trake transportuju kroz protočnu peć. Key words: heat treatment, protecting atmosphere, control RESUME Depending on the type of steel and set requirements for the quality of the finished product is often necessary to use a protective atmosphere in the furnace. Appropriate protective atmosphere protect a material from further carbonization or decarbonization, oxidation, etc. Stability of the protective atmosphere, ie. control of its composition, is necessary for the product quality. This paper treats the problem of controlling the atmosphere in the continous furnace, whose role was to protect the product that from carbonization and from decarbonization of the surface. Endogas is produces in the endogenerator. Screws are thermal treated in the flow furnace.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
MODIFIKOVANI BAKAR: EKOLOŠKA ALTERNATIVA ZA Cu-Cd LEGURU
MODIFIED COPPER: ECOLOGICAL ALTERNATIVE TO Cu-Cd ALLOY
Aleksandra Ivanović, dipl.inž.met. Silvana Dimitrijević, dipl.inž.met. Vesna Marjanović, dipl.inž.rud.
Vesna Cvetković-Stamenković, inž.met.
Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju, Zeleni bulevar 35, Bor, Srbija
e-mail: [email protected]
Ključne reči: temperatura rekristalizacije, niskolegirani bakar sa kalajem i telurom REZIME Ovaj rad obuhvata istraživanje mogućnosti zamene legura Cu-Cd legurama bakra sa netoksičnim legirnim elementima koji uspešno mogu da zamene Cd u legurama bakra, čineći ih ekološki prihvatljivim. Dodavanje malih količina kalaja, telura ili oba elementa ima uticaja na pojedine mehaničke osobine, elektroprovodljivost kao i na temperaturu rekristalizacije. Poznavanje ovih zavisnosti omogućava proizvođaču da odabere optimalni sadržaj Sn i Te u bakru kako bi se dobili električni provodnici relativno velike zatezne čvrstoće a znatno povišene temperature omekšavanja hladno deformisanog metala (trolna žica ). Key words: recrystalization temperature, tin and tellurium low-alloyed copper ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to investigate ability of substitute Cu-Cd alloys with similar alloys without toxic element Cd. On the basic of knowledge on the effect of these allying elements on properties opened the possibility for substitution of Cu-Cd alloys, used for trolleywire, with low alloyed copper with different combination of tin and tellurium.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI” Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
UTICAJ INDIJUMA NA OSOBINE NEKIH BEZOLOVNIH LEMNIH LEGURA
THE INFLUENCE OF INDIUM ON SOME
LEADFREE SOLDER ALLOYS CHARACTERISTICS
Aleksandra Milosavljević* Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju
Zeleni bulevar 35, 19210 Bor *[email protected]
Dragana Živković
Univerzitet u Beogradu, Tehnički fakultet u Boru VJ 12, 19210 Bor
Nadežda Talijan, Aleksandar Grujić
Institut za hemiju, tehnologiju i metalurgiju Njegoševa 12, 11000 Beograd
Ključne reči: indijum, bezolovne lemne legure REZIME U radu je analiziran uticaj indijuma na karakteristike nekih bezolovnih lemnih legura na bazi kalaja, a sa dodatkom srebra i/ili bakra. Iz širokog spektra bezolovnih lemova, legure koje se u svetu najviše koriste su SAC legure (Sn-Ag-Cu), koje međutim imaju ograničenu primenu, pre svega sa aspekta temperature topljenja koja je još uvek visoka u odnosu na standardni olovno-kalajni lem. Iz tih razloga kao jedno od mogućih rešenja jeste dodatak indijuma, prevashodno u smislu sniženja tačke topljenja legure. Pored toga, sadržaj indijuma u leguri mora biti ograničen zbog uticaja na mikrostrukturu samog lema, tj. negativnih uticaja na primenu u praksi. Key words: indium, leadfree solder alloys ABSTRACT The influence of indium on some leadfree solder alloys characteristics based on tin, with silver and copper is presented in this paper. In the world, SAC alloys (Sn-Ag-Cu), are the most commercial leadfree solders although they still have high melting temperature with respect to standard lead-tin solder. Considering these facts, one of possible solutions is addition of indium for melting temperature decreasement. Beside that, the indium content in alloy must be limited because of negative influence on practical usage.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
KOROZIJA HIRURŠKIH INSTRUMENATA U DEZINFEKCIONIM SREDSTVIMA
CORROSION OF SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS IN ANTISEPTIC FUNDS
M. Cacan, S. Islamović, S. Gojak, S. Gutić Univerzitet u Sarajevu, Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Zmaja od Bosne 33-35, Sarajevo Ključne riječi: korozija, hirurški instrumenti, dezinfekciona sredstva REZIME Nehrđajući čelici spadaju u najotpornije materijale na koroziju, zbog čega imaju raznovrsnu primjenu. Neke od tih primjena su u farmaceutskoj, prehrambenoj industriji kao i u medicini gdje se koriste za izradu hirurških instrumenata i ostalog pribora za tu namjenu. Međutim, ipak može doći do pojave korozije i to najčešće u jakim korozionim sredinama kao što su dezinfekciona sredstva. Promjene na hirurškim instrumentima koje mogu izazvati dezinfekciona sredstva se mogu pratiti voltametrijskim metodama kao što su linearna i ciklična voltametrija. U ovom radu korištena je voltametrija sa linearnom promjenom korozionih potencijala. Rezultati koji su dobiveni pokazuju da se brzina korozije hirurških instrumenata mijenja u zavisnosti od prirode, sastava i koncentracije dezinfekcionog sredstva. Key words: corrosion, surgical instruments, antepsitic funds ABSTRACT Stainless steels are the materials most resistant to corrosion, which have varied uses. Some of these applications in the pharmaceutical, food industry and in medicine which is used for making surgical instruments and other equipment for that purpose. However, though there may be effects of corrosion, mostly in strong corrosion areas such as antiseptic agents. Changes in surgical instruments that can cause antiseptic funds can be traced voltammetry methods such as linear and cyclic voltammetry. This work was used with linear voltammetry change corrosion potential. The results obtained show that the rate of corrosion of surgical instruments, changes depending on the nature, composition and concentration antepsitic funds.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
UTICAJ POLIANILINSKE PREVLAKE NA KOROZIONE KARAKTERISTIKE VISOKOLEGIRANOG NEHRĐAJUĆEG ČELIKA
THE EFFECT OF POLYANILINE COATING ON CORROSION
CHARACTERISTICS OF STEEL WITH HIGH CHROMIUM CONTENTS
Merzuk Cacan Fatima Lutvić Sanjin Gutić Safija Islamović Sabina Gojak
Prirodno-matematički fakultet, Sarajevo, Zmaja od Bosne 33-35
Ključne riječi: vodljivi polimeri, polianilin, korozija. REZIME Polianilin (PANI) je tipični predstavnik posebne vrste materijala koji se nazivaju vodljivi polimeri. Ispitivanje ovih materijala u svrhu zaštite metala od korozije zadnjih godina postaje sve intenzivnije jer oni, za razliku od klasičnih organskih prevlaka, pokazuju redoks aktivnost i električnu provodljivost. U ovom radu je ispitivana mogućnost elektrohemijske sinteze PANI na visokolegiranom čeliku i njegov uticaj na korozione karakteristike čelika u rastvorima Cl- jona. Dobiveni rezultati indiciraju da polianilinska prevlaka, osim mehaničke zaštite, pruža i određeni stepen anodne zaštite čelika. ABSTRACT Polyaniline (PANI) is typical representative of special kind of materials known as conducting polymers. Their redox activity and electrical conductivity are main reasons for growing research interest in potential applications for corrosion protection. Focus of this paper is on electrochemical synthesis of PANI on stainless steel substrates and its influence on corrosion behavior in chloride-containing solutions. Presented results indicate that polyaniline coating, in addition to mechanical protection, also provides some degree of anodic protection of steel.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
UTICAJ KONCENTRACIJE 1-FENIL 5-MERKAPTO TETRAZOLA NA ELEKTROHEMIJSKO PONAŠANJE
MESINGA U RASTVORU BORAKSA
INFLUENCE OF CONCENTRACION OF 1-PHENIL-5-MERCAPTO TETRAZOLE ON ELECTROCHEMICAL
BEHAVIOR OF BRASS IN BORAX SOLUTION
Zorica Ljubomirović, dipl.inž. tehn Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju, Bor
Prof. Dr. Milan Antonijević, dipl.inž.tehn.
Marija Petrović, dipl.inž.tehn. Milan Radovanović dipl.inž.tehn
Tehnički fakultet, Bor Ključne reči: mesing, 1-fenil-5-merkapto tetrazol,boraks REZIME Korozija bakra i njegovih legura je jedan veoma rasprostranjen problem sa kojim se industrija danas susreće. U ovom radu ispitivan je uticaj koncentracije inhibitora 1-fenil-5-merkapto tetrazola (PMT) na elektrohemijsko ponašanje mesinga u rastvoru boraksa. Metode koje su korišćene u toku rada su: merenje potencijala otvorenog kola i linearna voltmetrija Polarizaciona merenja su vršena u rastvoru boraksa koji je sadržao različite koncentracije inhibitora (1,7·10-6 – 8,5·10-3mol dm-3)PMT. Stepen pokrivenosti elektrode inhibitorom raste sa porastom koncentracije inhibitora PMT. Postignute visoke vrednosti stepena pokrivenosti ukazuju na to da je PMT dobar inhibitor mesinga u alkalnoj sredini. Adsorpcija inhibitora na površini mesinga odvija se prema Lengmirovoj adsorpcionoj izotermi. Key words: brass, 1-phenil-5-mercapto tetrazole, borax. ABSTRACT Nowadays, corrosion of copper and its alloys is a widespread problem in the industry. The effect off concentracion of 1-phenil-5-mercapto tetrazole (PMT) on electrochemical behavior of brass in borax solution was investigated and results were presented in this work. Used methods was: open circuit potential measurements and linear voltammetry. The polarization measurements were conducted in 0,1M borax solution containing various concentrations of PMT(1,7·10-6 - 8,5·10-3mol dm-3) of PMT. The electrode surface coverage degree increases with inhibitor concentration. The recorded high values of surface degree indicated that PMT is good brass corrosion inhibitor in alkaline media. The adsorption of PMT on the brass surface obeyed the Langmuir’s adsorption isotherm.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
PLEMENITI METALI KAO MATERIJALI ZA ELEKTRIČNE KONTAKTE
PRECIOS METALS AS MATERIALS FOR ELECTRICAL CONTACTS
Marjanović Vesna, Cvetković-Stamenković Vesna, Ivanović Aleksandra
Institut za rudarstvo i metalurgiju, Zeleni bulevar 35, Bor, Srbija
e-mail: [email protected]
Ključne reči: plemeniti metali, Au, Ag, Pl, Pd, električni kontakti REZIME Najznačajnija i najraznovrsnija oblast primene plemenitih metala je oblast električnih kontakta. Oko 15% celokupne proizvodnje srebra u svetu prerađuje se u materijale potrebne za izradu električnih kontakta. Upotreba srebra i legura srebra je najpovoljnija u pogledu cene, međutim, nisu apsolutno otporni kontaktni materijali. Tehnički značaj kao kontaktni materijal ima i čitav niz legura zlata. Platina i paladijum spadaju u apsolutno otporne kontaktne materijale, ali je njihova primena ograničena iz ekonomskih razloga. Keywords: precious metals, Au, Ag, Pl, Pd, electrical contacts ABSTRACT Diverse and the most important area of usage the precious metals is the area of electrical contacts. About 15% of total production of silver in the world belong into is processed the most in the materials needed for making the electrical contacts. The use of silver and silver alloys is advantageous in terms of price, however, the contact materials were not absolutely resistant. A range of gold alloys has a tehnical importance as the contact material. Platinum and palladium is absolutely resistant contact materials, but their usage is limited due to the economic reasons.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem "METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI", Zenica, BiH 27-28. april 2010.
ČELICI ZA POBOLJŠAVANJE PREMA EUROPSKIM STANDARDIMA
STEELS FOR QUENCHING AND TEMPERING ON EUROPEAN
STANDARDS
Ivan Vitez, redoviti profesor u trajnom zvanju Vlatko Marušić, redoviti profesor
Dragomir Krumes, redoviti profesor u trajnom zvanju Andrijana Milinović, dipl.ing. strojarstva
Strojarski fakultet, Trg Ivane Brlić-Mažuranić 2, 35000 Slavonski Brod, Hrvatska
Ključne riječi: čelici za poboljšavanje, europski standardi, kemijski sastav, mehanička
svojstva, oznake čelika REZIME Čelici za poboljšavanje su velika i važna grupa konstrukcijskih nelegiranih posebnih i legiranih posebnih čelika koji su zbog kemijskog sastava podesni za očvrsnuće i koji u kaljenom i popuštenom stanju imaju dobru žilavost uz danu vlačnu čvrstoću. Garantirana svojstva čelika za poboljšavanje ranije su bila utvrđena u EN 83-70, te u HRN C.B9.021 i DIN 17200, a sada su propisana u temeljnom standardu pr EN 10083:2005, te u standardu pr EN 10277:2005. U radu je dan usporedni pregled oznaka čelika za poboljšavanje prema EN, HRN i DIN s komentarom, te pregled kemijskog sastava i svojstava čelika za poboljšavanje prema novom standardu pr EN 10277:2005-Dio 5. Key words: steels for quenching and tempering, european standards, chemical composition,
mechanical properties, steel designations ABSTRACT Steels for quenching and tempering are big and important group of structural unalloyed especial and alloyed especial steels which because of their chemical compositions are suitable for hardening and in the quenched and tempered conditions have good toughness at a given tensile strength. Prescribed properties of steels for quenching and tempering was earlier given on EN 83-70, then on HRN C.B9.021 and DIN 17200, and now are prescribed in basic standard pr EN 10083:2005, and on pr EN 10277:2005. This work gives a comparison of designations steels for quenching and tempering on EN, HRN and DIN standards with comments and a survey of chemical composition and properties steels for quenching and tempering on new standard pr EN 10277:2005-Part 5.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem “METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27.-28.april 2010.
SAVREMENI TRENDOVI U PROIZVODNJI NEHRĐAJUĆIH ČELIKA
STAINLESS STEELS, MODERN PRODUCTION TRENDS
Šaban Žuna, dipl. ing.
ArcelorMittal Zenica
Ključne riječi: nehrđajući čelik, krom, pasivizacija, dupleks, precipitacija, senzitivizacija, sekundarna metalurgija, vakumski postupci, troskina faza.
REZIME Nakon što su (prije otprilike 50 godina) prihvaćene standardne marke nehrđajućih čelika, napori su usmjereni ka iznalaženju jeftinijih postupaka masovne proizvodnje, što je zavisilo od razvoja sekundarne metalurgije. Posljednja unapređenja su omogućila ekonomičnije uklanjanje ugljika iz čelika, posebno razvoj AOD i VOD postupka koji omogućavaju sniženje sadržaja ugljika na manje od 0,003%. Uz tako nizak sadržaj ugljika, nehrđajući čelici su otporni na senzitivizaciju, a problemi se javljaju tek nakon dužeg držanja na kritičnoj temperaturi. Posljednje tri dekade su karakteristične po uvođenju „supertrenda“ tj. nehrđajućih čelika dodatno obogaćenim kromom, niklom i drugim legirajućim elementima radi postizanja otpornosti koroziji u agresivnim sredinama ili na povišenim temperaturama. Nehrđajući čelici predstavljaju još uvijek veoma interesantan materijal za koji se može očekivati porast potražnje u budućnosti i dobar primjer za metalurgiju „po mjeri“. Key words: stainless steel, chromium, pasivisation, duplex, precipitation, sensitization, secondary metallurgy, vacuum technologies, slag phase
ABSTRACT As these standard grades became accepted (about 50 yearg ago), the emphasis changed to finding cheaper mass-production methods, depending on development of secundary metallurgy. Recent developments have enabled more economical removal of carbon from the steel, primarily through the development of the argon oxygen decarburisation (AOD) and the vacuum oxygen decarburisation (VOD) processes. Both of these production methods make carbon levels below 0.03 % possible. At these low carbon levels, the steels are generally considered to be resistant to sensitisation, with problems only occurring after prolonged holding times in the critical temperature range. The last three decades have seen the introduction of the "supertrend" i.e. stainless steels, enriched with chromium, nickel and other alloying elements to obtain corrosion resistance in very corrrosive envronment or high temperatures. Stainless steel, a good examples for „tailor“ metallurgy, is still a very interesting material that can be expected to find increasing use in the future.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem ''METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI'' Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
PRILOG STARATEGIJI RAZVOJA NOVIH METALNIH MATERIJALA U BiH
CONTRIBUTION TO STRATEGIC DEVELOPMENT OF NEW
METALLIC MATERIALS IN B&H
Prof.dr. Mirsada Oruč, dipl.inž. Mr. Milenko Rimac, dipl.inž.
UNIVERZITET U ZENICI – Metalurški Institut ''Kemal Kapetanović'' ZENICA
Mr. Nafija Šehić – Mušić
PRIVREDNA / GOSPODARSKA KOMORA F BiH Ključne riječi: Strategija, metalni materijali, nove tehnologije, istraživanje, razvoj. REZIME Tehnički napredak i industrijski razvoj mogući su samo ako za to postoje adekvatni materijali. Razvoj i primjena novih materijala i tehnologija, danas spada u glavne pokretačke discipline nauke i tehnike. Primjena novih materijala podstiće razvoj konstrukcionih proizvoda sa poboljšanim eksploatacionim osobinama, koji bi se mogli razvijati i primjeniti u BiH. Zato je sasvim jasno zašto se zadnjih dvadeset godina razvoj materijala odvija po novom obrazcu – materijal kao vrijednost, a ne po klasičnom – materijal kao resurs. U radu je dat kratki osvrt na mogućnosti definisanja strategije razvoja novih materijala i tehnologija u naučno-istraživačkim institucijama u FBiH i BiH. Korištena su iskustva industrijski razvijenih zemalja, zemalja iz okruženja te vlastita saznanja. Dat je pregled novih materijala i tehnologija, kao i mogućnosti njihove primjene, u lancu od fundamentalnog do razvojnog istraživanja i primjene. U radu se predlažu i neke konkretne aktivnosti koje bi mogle da dovedu do efikasnije implementacije istraživanja i razvoja. Key words: Strategy, metal materials, new technologies, research, development. SUMMARY Technical progress and industrial development are possible only if there are adequate materials. Today development and application of new materials and technologies are among the main driving disciplines of science and technology. Application of new materials encourages the development of products with improved structural characteristics of exploitation, which could be developed and applied in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Therefore, it is completely clear why development of materials in the last twenty years is carried out in a new way - material as a value, and not in a classic way - material as a resource. This paper gives a brief overview of the possibility of defining development strategy of new materials and technologies in scientific research institutions in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. We used the experience of industrialized countries, countries from the region, and our own findings. An overview of new materials and technologies, as well as their applicability in the chain from fundamental research to the development and application is given. The paper suggests some concrete activities that could lead to more effective implementation of research and development results.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „ METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
ULOGA KARAKTERISTIKA STIJENSKIH MATERIJALA U METODOLOŠKIM TOKOVIMA IZBORA DROBILICA I MLINOVA
THE ROLE OF CHARACTERISTICS OF ROCK MATERIALS IN METHODOLOGY FLOWS REGARDING BREAKERS AND MILLS
CHOICE
dr. sc. Ifet Šišić docent Biotehnički fakultet u Bihaću
dr. sc. Nedžad Alić docent
Rudarsko-geološko-građevinski fakultet u Tuzli Ključne riječi: stijenski materijal, karakteristike, izbor mašina. REZIME Metodološko rješenje izbora mašina za usitnjavanje treba dati odgovore i logične tokove mnogim prerađivačima mineralnih sirovina, kako da na sistemetizovan način dođu do odluke o izboru, zasnovane na optimalnim rješenjima, vrijednostima i veličinama koje karakterišu proces usitnjavanja. Poznavanjem činjenica da se tehničko-tehnološki faktori proizvodnog procesa ispoljavaju kroz karakteristike stijenskih materijala, stadijalnost i tokove postupaka usitnjavanja (shema) i kvalitet usitnjenih proizvoda, odgovornost izbora procesnih mašina i uređaja zauzima visoko mjesto u investicijama prerade stijenskih materijala. Čvrsti stijenski materijal se usitnjava, počev od veličine komada, max1500 [mm], pa do stotih dijelova milimetra, a na koloidnim mlinovima još i više. Na osnovu usvojenog modela usitnjavanja, baziranog na međusobno ovisnoj relaciji: ulazna sirovina ↔ procesne mašine i uređaji ↔ tehnika izvođenja procesa ↔ izlazni proizvod, ipak najveću „nepoznanicu“ čini mineralna sirovina, tj. stijenski materijal. Keywords: rock material, characteristics, the choice of machines. ABSTRACT Methodological solution of choice for cutting machines should provide answers and logical flows for many manufacturers of mineral resources about how to reach decisions in a systematic way based on optimal solutions, values and sizes that characterize the process of fragmentation. Knowing the fact that technical and technological factors of the production process are manifested through characteristics of rosk materials, grading and fragmentation process flows (Scheme) and fragmented product quality, the responsibility of the election process machinery and equipment occupies a high position in the investment processing of rock materials. Rock solid material was divided beginning by the size of pieces, max1500 [mm] to the hundreth of a milimeter, and the colloidal mills fragmenedt it even finer. Based on the adopted model of fragmentation, based on the mutually dependent correlation: the entry of raw materials ↔ processing machines and devices ↔ process performance technology ↔ output product, yet an „unknown quantity“ are mineral raw materials, namely rock materials.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
ISPITIVANJE I KARAKTERIZACIJA GLINA SREDNJE BOSNE
ESTIMATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF MIDDLE BOSNIA
CLAYS
Marina JOVANOVIĆ1, Jelica ZELIĆ2
1Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Zenica, FBiH 2Kemijsko-tehnološki fakultet, Split, RH
Ključne riječi: glina, kemijska analiza, rendgenska difrakcijska analiza, toplinska analiza, infracrvena spektroskopija REZIME Primjenom različitih tehnika kemijske i fizikalne analize (kemijska, rendgenska difrakcijska i termička analiza, infracrvena spektroskopija) izvšeno je ispitivanje i karakterizacija pet različitih uzoraka gline s užeg područja srednje Bosne. Na osnovi mineraloških, kemijskih i fizikalnih osobina, sve gline su kaolinitno-ilitne gline. Uz kaolinit i ilit (tj. hidratizirani muskovit) „sive“ gline sadrže i klorit, a „obojene“ hematit i getit. Sve gline sadrže i značajne količine slobodnog kvarca i pokazuju različitu plastičnost. Iako su „sive“ gline s lokaliteta Klokoti i Bilalovac nekad korištene za vatrostalne smjese, a ostale gline kao opekarske sirovine, razina ispitanosti ovih glina je jako niska. Istraživanja prikazana u ovom radu ukazuju na mogućnost šire uporabe ovih glina. Key words: clay, chemical analysis, XRD, TG/DTA, IR spectroscopy ABSTRACT An examination and characterization of five different clays from middle Bosnia area was done using different techniques of chemical and physical analyzes (the chemical analyze, the X-ray diffraction, the thermal analyzes, the IR spectroscopy). Based on mineralogical, chemical and physical properties these clays are kaolinitic-illitic clays. The “gray clays” contain chlorite among kaolinite and illite (e.g. hydrous muscovite) while the “colored clays” contain hematite and goethite. All clays contain also a significant amount of free quartz and they display different plasticity. Despite the fact that the “gray clays” from deposits Klokoti and Bilalovac have been used as raw materials for refractory mixtures and other clays were used as brick raw materials, the level of examinations of these clays is very low. Current research is emphasizing on capability of wider applications of these clays.
VII Nučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem
„METALNI I NEMETALNI ANORGANSKI MATERIJALI“ Zenica 27-28.april.2010
ISPITIVANJE KVALITETA GLINE I MOGUĆNOSTI NJENE EKSPLOATACIJE SA LOKALITETA „ULICE“
INVESTIGATION OF CLAY QUALITY AND THE POSSIBILITY OF
ITS EXPLOITATION ON THE LOCALITY „ULICE“
D.Lazić1, J.Penavin-Škundrić2, S.Sladojević2, Lj.Vasiljević1, R. Smiljanić3, D.Kešelj1, D. Smiljanić3
1.Tehnološki fakultet Zvornik 2.Tehnološki fakultet Banja Luka 3. Fabrika glinice“Birač“Zvornik
Ključne riječi: kvalitet gline, glineni minerali, mineraloški sastav, plastičnost REZIME Gline su osnovne plastične sirovine za proizvodnju keramičkih proizvoda. To su fino disperzni sistemi, različite raspodjele veličine zrna, sa znatnim učešćem koloidne frakcije. Kvalitet gline, pored količine i vrste glinenih minerala, u velikoj mjeri određen količinom i vrstom prisutnih primjesa u njoj. Predmet ovog rada je ispitivanje kvaliteta gline hemijski i mineraloški. U radu je određivan hemijski sastav uzoraka gline sa lokaliteta „Ulice“ na sledeće komponente: SiO2, Al2O3, TiO2, Fe2O3, P2O5, Cr2O3,V2O5, MgO, CaO, Na2O, K2O, MnO, ZnO i gubitak žarenjem(gž). Korištene eksperimentalne metode su: gravimetrija, spektrofotometrija., volumetrija, atomsko-apsorpciona spektrofotometrija, termička analiza i X-ray difrakciona analiza. Dobijeni rezultati govore da najveći sadržaj glinenih minerala ima uzorak 6, a najmanji uzorak 1. Uzorak 6 ima najveći sadržaj MgO, što ukazuje na prisustvo ilita. Svi uzorci imaju povećan sadržaj SiO2. Prema mineraloškoj analizi u uzorcima je prisutan: ilit, kaolinit, smektit-montmorilonit, kvarc, muskovit, klinohlor, a prisustvo karbonata i minerala gvožđa nije značajno identifikovano. ABSTRACT Clays are basic plastic raw materials for production of ceramic products. These are fine dispersion systems with different grain size distribution, with a significant part of colloidal fractions. Apart from the quantity and type of clay minerals, the quality of clay is also largely affected by the quantity and type of impurity present in it. The subject of this paper is chemical and mineralogical examination of the clay quality. The paper determined the chemical composition of clay samples from the locality “Ulice” concerning the following components: SiO2, Al2O3, TiO2, Fe2O3, P2O5, Cr2O3, V2O5, MgO, CaO, Na2O, K2O, MnO, ZnO and loss on ignition (LOI). Experimental methods used are: gravimetry, spectrophotometry, volumetric method, atomic-absorption spectrophotometry, thermal analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis. The obtained results show that the highest content of clay minerals is found in sample 6, and the smallest one in sample 1. Sample 6 has the highest content of MgO, which indicates the presence of illite. All samples have a higher content of SiO2. According to mineralogical analysis the samples contain: illite, kaolinite, smektit-montmorillonite, quartz, muscovite, klinochlor, where as the presence of carbonate and iron minerals was not significantly identified.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
POTENCIJALNOST LEŽIŠTA DOLOMITA „TUNEL“ KOD KONJICA I MOGUĆNOSTI NJIHOVE PRIMJENE
POTENTIALITION OF DOLOMITE DEPOSIT „TUNEL“ NEAR
KONJIC AND POSSIBILITES OF USAGE
Mevlida OPERTA1, Nijaz ŠKRIPIĆ 2 & Senaid SALIHOVIĆ3 1 Prirodno-matematički fakultet u Sarajevu, Zmaja od Bosne 33-35.
2 Institut za geologiju, Građevinski fakultet u Sarajevu. 3 Rudarsko-geološko-građevinski fakultet u Tuzli, Univerzitetska br. 2.
[email protected], [email protected] Ključne riječi: dolomit, rezerve, ispitivanja, primjena, građevinska industrija. REZIME Ležište dolomita “Tunel”se nalazi sa lijeve strane rijeke Neretve, uz put Konjic-Spiljani u ataru sela Polje Bijela. Osnovni litološki član ležišta je bankoviti dolomit trijaske starosti. Pri istraživanju ležišta u periodu 2001-2002. godine utvrđene su rezerve dolomita i izvedena ispitivanja kako sa aspekta hemijskih i mineraloško-petrografskih karakteristika, tako i fizičko-mehaničkih osobina dolomita. Na osnovu svih izvedenih ispitivanja dolomita utvrđen je spektar njihove primjene u građevinskoj industriji. Key words: dolomite, reserves, investigations, usage, building industry. ABSTRACT dolomite deposit „Tunel“ is situated on the left side of river Neretva, along the road Konjic-Spiljani nearby to village Polja Bijela. The basic lithological element is triassic age dolomite stratified in thick beds. On the basis of field investigation from 2001-2002, dolomite reserves were verificate. During this period, chemical, mineralogic-petrographic characteristics as well as physical and mechanical properties of dolomite were determined. On the basis of these results, spectrum of dolomite usage in building industry was determined.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
KERAMIČKO-TEHNOLOŠKE OSOBINE OPEKARSKE GLINE
„ČAVKA“
A. Šeper, A. Kobilica, M. Jovanović
Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Zenica, FBiH
Ključne riječi: opekarska glina, keramičko-tehnološke osobine gline REZIME Opekarske gline spadaju u grupu glina nižeg kvaliteta. Njihov minerloški sastav je kompleksan jer pored osnovnih minerala gline sadrže i mineralne primjese. Da bi se koristile kao opekarske sirovine gline moraju da zadovolje određene keramičko-tehnološke uslove. U ovom radu je ispitivan kompozit s ležišta „Čavka“ kod Busovače. U okviru ispitivanja određena je vlažnost, stadnardna konzistencija, plastičnost, gustoća i ponašanje gline pri sušenju i pečenju. Rezultati ispitivanja su pokazali da se radi o kvalitetnoj opekarskoj sirovini visoke plastičnosti. Na osnovu rezultata ispitivanja pločica pečenih na temperaturama 860, 960 i 1060°C može se zaključiti da glina sa ovog lokaliteta ima zadovoljavajuće osobine upijanja vode, brzine upijanje vode, prividne poroznosti i skupljanja za proizvodnju opeka. Key words: brick caly, ceramic-technological properties of clay ABSTRACT Brick clays belong to low grade clays. Mineralogical composition of these clays is complex because they consist of different clay minerals and various impurity minerals. The clays must accomplish certain ceramic-technological requirements to be used as brick raw materials. In this paper we analyzed composite from the deposit “Čavka” near Busovača. In this investigation we determined humidity, normal consistency, plasticity, density values as well as drying and firing behavior. The results of the analyses approve that this clay is a quality brick raw material of high plasticity. On the base of investigation of the referent tiles fired at 860, 960 and 1060°C it could be concluded that clay from this deposit has satisfactory properties for brick manufacturing: water absorbtion, water absorbtion rate, apparent porosity and shrinkage.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
MINERALOŠKO-PETROGRAFSKA I TEHNOLOŠKA SVOJSTVA GLINE LEŽIŠTA „GOLO BRDO“ KOD VISOKOG
MINERALOGICAL-PETROGRAPHIC AND TECHNOLOGICAL
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLAY DEPOSIT „GOLO BRDO“ NEAR VISOKO
Dr. Amra Hamzabegović,dipl.ing.geol.
Zemaljski muzej BiH Sarajevo
Prof.dr. Milan Stević, redovni profesor Rudarsko-geološko-građevinski fakultet
Tuzla Dževad Alijagić, dipl.ing.geol.
IGM doo Visoko Visoko
Ključne riječi: ležište, glina, minerali ABSTRAKT U radu su dati rezultati ispitivanja mineraloško –petrografskih i tehnoloških karakteristika gline sa ležišta „Golo Brdo“ kod Visokog. Mineraloško-petrografski sastav je određen primjenom: hemijske analize, diferencijalno termičke analize (DTA), X-ray difrakcije i elektronskim mikroskopom. Rezultati dobijeni ispitivanjem tehnoloških karakteristika pokazuju razlike svojstava uzoraka uslovljene uglavnom velikom razlikom u raspodjeli veličine čestica. Rezultati su pokazali da se radi o glini visokog kvaliteta koja je pogodna osim za proizvodnju cigle i za proizvodnju crijepa. ABSTRACT The results of mineralogical-petrografic and tehnological characteristics of clay deposit „Golo Brdo“ near Visoko are described in the paper. Mineralogical-petrographic ingredients are defined by using chemical analysis, methods of thermic analysis (DTA), X-ray diffraction and electron microscope. The results obtained during investigation of technological characteristics showed the difference of features by great differences in grain size distribution. The results have shown that the tested clay is of a high quality, suitable for production bricks and tiles.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem “METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI” Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
GEOLOŠKA GRAĐA, POTENCIJALNOST I KVALITATIVNE ODLIKE
GLINA LEŽIŠTA “KEČKOVAC” PO BUŠOTINI B-9
GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURE, POTENTIALITY AND QUALITATIVE FEATURES CLAY RESERVOIR "KEČKOVAC" BY WELL B-9
Amir Baraković, vanr. prof.,
Rudarsko-geološko-građevinski fakultet Univerziteta u Tuzli Petar C. Katanić,dipl.ing.geologije,“Sočkovac”a.d. Sočkovac
Damir Baraković, mr.sc.dipl.ing.geologije, Gračanica REZIME Cilj rada je definisanje geološke građe, litološkog sastava, morfostrukturnih odnosa, potencijalnosati i kvalitativnih parametara glina i pijeska u ležištu «Kečkovac», na osnovu najnovijih istraživanja i ispitivanja reprezentativnih uzoraka jezgra istražne bušotine B-9, a u svrhu utvrđivanja novih saznaja o geološkim, strukturno-tektonskim odnosima, kvalitativnim odlikama i potencijalnosti keramičkih polimineralnih glina i kvarcnog pijeska u ležištu.
Rezultati ispitivanja su determinisali produktivnu seriju polimineralnih keramičkih glina i kvarcnog pijeska u ležištu koje predstavlja kompleksan morfoskulpturni oblik bez izražene postrudne tektonike, sa znatnom potencijalnošću i definisanim kvalitetom.
Ovim se došlo do novih saznanja o geološkoj građi, genezi i kvalitativnim odlikama ležišta glina, upotpunjen katastar prirodnih resursa Bosne i Hercegovine i mogućnost njihove valorizacije. Ključne riječi: keramička polimineralna glina, geološka građa, kvarcni pijesak, kvalitet,
potencijalnost ABSTRACT
The aim of paper is defining the geological structure, composition litology morfostructure relations potentiality and qualitative parameters of clay and sand in the reservoir "Kečkovac," based on the latest research and testing of representative samples of the core investigative wells B-9, in order to determine more about the new geological, structural -tectonic relations, qualitative characteristics and potentiality of ceramic polimineralnih clay and quartz sand in the reservoir. Test results are determine productive series polimineral ceramic clay and quartz sand in the reservoir, which is a complex morfoskulptur form without the expressed postrudne tectonics, with significant potentiality and defined quality. This has been a new knowledge about the geological structure, genesis and qualitative characteristics of clay deposits, complete cadastre of natural resources of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the possibility of their evaluation Keywords: ceramic semi-mineral clay, polimineralna ceramic clay, geological materials,
quartz sand, quality, potentiality
VIII Naučno / stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem “METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI” Zenica, BiH, 27-28.april 2010
ACTIVATED SINTERING OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE FROM SEAWATER WITH TiO2 ADDITION
AKTIVIRANO SINTERIRANJE MAGNEZIJEVA OKSIDA IZ
MORSKE VODE UZ DODATAK TiO2 Vanja Martinac, Prof. Ph. D, Tomislav Maleš, Bachelor of Chem. Eng., Miroslav Labor,
Assist. Prof. Ph. D Faculty of Chemistry and Technology, Teslina 10/V, 21000 Split, Croatia
REZIME Cilj ovog rada bio je ispitati utjecaj dodatka TiO2 u količini od 1 mas. % magnezijevom oksidu dobivenom iz morske vode 80 %-tnim načinom taloženja dolomitnim vapnom, na sadržaj borovog (III) oksida u sinteriranom magnezijevu oksidu. Kod pripreme uzorka primijenjen je kombinirani način ispiranja taloga magnezijeva hidroksida (3+2), tj. ispiranje dekantacijom vršeno je tri puta zaluženom destiliranom vodom pH vrijednosti 12.50 i dva puta destiliranom vodom pH vrijednosti 5.56. Ispiranje na filtar papiru vršeno je također kombiniranim načinom (2+3), tj. nakon što je uzorak ispran dva puta zaluženom destiliranom vodom slijedi višekratno (tri puta) ispiranje svježom destiliranom vodom. Zatim je izvršeno aktivirano sinteriranje uzoraka MgO (80 %-tno taloženje) iz morske vode, pri temperaturi 1700 ºC uz vrijeme izotermnog zagrijavanja jedan sat, sa svrhom da se utvrde svojstva sinteriranih uzoraka (gustoća, poroznost i sadržaj B2O3) u ovisnosti o načinu ispiranja taloga magnezijeva hidroksida i utjecaju dodanog TiO2.. Key words: substoichiometric precipitation, magnesium oxide, activated sintering ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of the TiO2 addition in the amount of 1 mass % to magnesium oxide obtained from seawater by 80 % precipitation with dolomite lime, on the content of boron (III) oxide in sintered magnesium oxide. The combined method of rinsing of the magnesium hydroxide precipitate was used in sample preparation (3+2), i.e. rinsing by decanting was done three times by alkalised distilled water with pH of 12.50 and twice by distilled water with pH of 5.56. Rinsing on filter paper was also done using the combined method (2+3), i.e. after the sample had been rinsed twice with alkalised distilled water, it was rinsed with fresh distilled water three times. Then activated sintering of seawater-derived MgO (80 % precipitation) samples took place at 1700 oC and 1h of soaking at the maximum temperature, with the aim of determining the properties of sintered samples (density, porosity and B2O3 content) relative to the method of rinsing the magnesium hydroxide precipitate and the effect of the TiO2 added.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJAL Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
PROMJENA ENERGETSKIH KARAKTERISTIKA AKTIVNE MASE OLOVNIH BATERIJA DODATKOM H3PO4 U ELEKTROLIT
CHANGE OF THE ENERGY CHARACTERISTICS IN AN ACTIVE MASS OF THE LEAD BATTERIES BY ADDING H3PO4 IN THE
ELECTROLYTE
Dr.sc. Nurudin Avdić ECEA d.o.o Sarajevo
Sarajevo Ključne riječi: energetske karakteristike, sekundarni izvor struje, fosforna kiselina, stacionarne olovne baterije, životni vijek.
REZIME Vječita borba za maksimalno iskorištenje energije sekundearnih izvora struje, kao i njihovo brzo i maksimalno obnavljanje uz minimalan utrošak energije i vremena, nagnalo je istraživače da dodavanjem raznih komponenti kako u tehnološkom procesu proizvodnje tako i u gotov proizvod pokušaju poboljšati njihove karakteristike. Poboljšanje energetskih karakteristika stacionarnih namaznih olovnih baterija pogotovo je važno nakon učestalih i dugotrajnih pražnjenja izazvanih prekidima ili havarijom sistema za napajanje Druga važna karakteristika životni vijek, veoma skupih olovnih baterija niti u kom slučaju nije smjela biti umanjena u korist povećanja kapaciteta. Jedna od komponenti koja se dodavala u elektrolit gotovih akumulatora u cilju poboljšanja njegovih karakteristika jeste i rastvor fosfornrne kiseline, čime se bavi i ovaj rad. Key words: energy characteristic, secondary power sources, phosphoric acid, stacionari led-acid batteries, expire date. ABSTRACT Permanently struggle for the maximum utilization of energy secondary sources of electricity, as well as, their speed and maximum recovery with minimal power consumption and time, prompted the researchers to adding various components to the technological production process and in an attempt to improve the final product characteristics. Improving the energy characteristics stationary lead-acid batteries is important, especially after frequent and long interruptions caused by the discharge or average system power. Another important characteristic of life, very expensive lead-acid batteries, or in any case should not be diminished in favor of increasing capacity. One of the components that are added to the final battery electrolyte in order to improve its characteristics and is fosfornrne-acid solution. This paper deals with described problems.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
KEMIJSKA REAKTIVNOST I VEZIVANJE HIDRAULIČNOG VAPNA
PRAĆENI PROCESIMA NJEGOVE HIDRATACIJE
CHEMICAL REACTIVITY AND BINDING OF HYDRAULIC LIME ATTENDED WITH PROCESSES OF HIS HYDRATION
dr. sc. Petar Krolo, red. prof., Tihomir Kosor, sveučilišni prvostupnik inženjer kemijskog inženjerstva,
dr. sc. Pero Dabić, izv. prof., Kemijsko-tehnološki fakultet u Splitu, Teslina 10 / V, 21000 Split, Hrvatska
Ključne riječi: hidraulično vapno, reaktivnost,hidratacija REZIME Predmet ovog rada je određivanje i praćenje kemijske reaktivnosti preko procesa hidratacije dva različito pripremljena hidraulična vapna istog indeksa cementacije. Mjerenja su provedena sukladno standardima: HRN EN 459-2 te HRN EN 196-3. Dobiveni rezultati pokazuju da kemijska reaktivnost ovisi i o načinu pripreme i mogućim visokotemperaturnim procesima stvaranja hidraulične komponente u takvom produktu. Veću kemijsku reaktivnost pokazuju hidraulična vapna s većim udjelom nevezanog CaO i njihovo vrijeme vezivanja je produljeno, dok hidraulična vapna kod kojih je dio vapna već reagirao s hidraulitičnom komponentom iz letećeg pepela pokazuju nižu kemijsku reaktivnost i kraće vrijeme vezivanja. Key words: hydraulic lime, reactivity, hydration ABSTRACT The subject of this paper is to determine and monitor the chemical reactivity through the hydration process of two prepared different hydraulic lime with same cementation index. Measurements were carried out in accordance with the standards: HRN EN 459-2 and HRN EN 196-3. The results show that the chemical reactivity depends on the preparation manner and possible high temperature process of creating hydraulic components in this product. Higher chemical reactivity indicates hydraulic lime with a larger share of the unbound CaO and their bonding time was prolonged, while the hydraulic lime which is part of the lime has reacted with hidraulic component of fly ash showed lower chemical reactivity and shorter bonding time.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
OPTIMIZACIJA KLASIRANJA DEKOMPOZIRANE SUSPENZIJE ALUMINATNOG RASTVORA
OPTIMIZATION OF SEPARATION DECOMPOSED SUSPENSION
SODIUM ALUMINATE SOLUTION
Radenko Smiljanić, magistar tehničkih nauka Fabrika glinice “Birač“ AD
Zvornik, RS, BiH
Dragica Lazić, Živan Živković Tehnološki fakultet Zvornik, RS, BiH
Dragana Smiljanić
Fabrika glinice “Birač“ AD Zvornik, RS, BiH
Ključne riječi: aluminijum-hidroksid, koncetracija, čvrsta faza, dekompozirana suspenzija, hidroseparator REZIME Nakon razlaganja aluminatnih rastvora, u procesu dobivanja glinice Bajerovim postupkom, slijedi faza klasiranje dekompozirane suspenzije. Tada se javlja problem učinka hidroseparatora, prvenstveno zbog njegove dimenzionalne nepromjenljivosti. Kako se mijenja granulometrijski sastav dekompozirane suspenzije i koncetracija čvrste faze u tečnoj, tako se javljaju i oscilacije u kvalitetu klasiranja na hidroseparatorima. U ovom radu su ispitani pojedinačni uticaji ovih parametara, a zatim njihov zajednički uticaj na stepen klasiranja u proizvodnim uslovima. Nakon njihovog definisanja dato je tehničko-tehnološko rješenje pomoću koga se stepen klasiranja dekompozirane suspenzije može držati pod kontrolom. Key words: aluminum hydroxide, concentration, solid phase, decomposed suspension, hydro-separator ABSTRACT Separation stage of decomposed suspension in Bayer process for producing alumina comes after decomposition sodium aluminate solution. Then there is a problem in hydro-separator performance primarily because of its dimensional stability. With the change of granulometric composition of decomposed suspension and concentration of solid phase in liquid occur oscillations in the quality of separation in hydro-separator. In this paper the individual influences of these parameters were investigated, and then their joint influence on the degree of separation in the production conditions. After defining these parameters, given the technical - technological solution through which the degree of separation in decomposed suspension can be kept under control.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
ISPITIVANJE ADSORPCIONIH MOGUĆNOSTI CaFeO3
PEROVSKITA
EXAMINATION OF ADSORPTION POTENTIALS OF CaFeO3 PEROVSKITE
Slavica Sladojević , Jelena Penavin-Škundrić b , Dragica Lazić , a c
Branko Škundrić , Darko Bodroža , Saša Zeljković d a b
a Tehnološki fakultet, Banjaluka, Univerzitet u Banjaluci, Bosna i Hercegovina
b Prirodno matematički fakultet, Banjaluka, Univerzitet u Banjaluci, Bosna i Hercegovina c Tehnološki fakultet, Zvornik, Univerzitet u Istočnom Sarajevu,Bosna i Hercegovina
d Akademija nauka i umjetnosti Republike Srpske, ANURS, Bosna i Hercegovina Ključne riječi: perovskit, adsorpcija, propionska kiselina, maslačna kiselina, amonijak REZIME U radu je ispitivana mogućnost upotrebe novih nanomaterijala tipa perovskita kao adsorbensa različitih (kiselinsko-baznih) polutanata iz vodene sredine, jer je njihova proizvodnja ekonomski i ekološki opravdana i bazirana na domaćim resursima. Ispitivanje adsorpcionog kapaciteta CaFeO3 perovskita vršeno je praćenjem adsorpcije organskih kiselina – propionske i maslačne i amonijaka u simuliranoj otpadnoj vodi u temperaturnom intervalu od 283 K do 303 K. Količina adsorbovanog amonijaka i organskih kiselina određena je klasičnim analitičkim metodama. Rezultati su pokazali da je adsorpcioni kapacitet CaFeO3 perovskita najveći kada je adsorbat propionska kiselina, neznatno manji kada je adsorbat maslačna kiselina i najmanji kada je amonijak. Key words: perovskite, adsorption, propionic acid, butyric acid, ammonia ABSTRACT The study examined the possibility of usage of new nanomaterials of perovskite type as adsorbents of different (acid-base) pollutants from the water environment, since their production is economically and ecologically justified and based on domestic resources. The examination of adsorption capacity of CaFeO3 perovskite was conducted by observing adsorption of organic acids – propionic and byturic ones and ammonia in a simulated waste water in the temperature interval from 283 K to 303 K. The quantity of adsorbed ammonia and organic acids was detemined by the classical analytic methods. The results showed that the adsorption capacity of CaFeO3 perovskite is biggest when propionic acid is adsorbate, slightly less when adsorbate is butyric acid and least when it is ammonia.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
UTICAJ POVRŠINSKI AKTIVNE MATERIJE – PAM NA ADSORPCIONE OSOBINE MORDENITA
INFLUENCE OF SURFACE ACTIVE MATTER – SAM ON
ADSORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF MORDENITE
Zora Levi 1 , Darko Bodroža 1 , Slavica Sladojević 1 , Dragica Lazić , 2
Jelena Penavin-Škundrić , Pero Dugić 3 3
1 Tehnološki fakultet, Banjaluka, Univerzitet u Banjaluci, Bosna i Hercegovina 2 Tehnološki fakultet, Zvornik, Univerzitet u Istočnom Sarajevu, Bosna i Hercegovina
3 Prirodno matematički fakultet, Banjaluka, Univerzitet u Banjaluci, Bosna i Hercegovina Ključne riječi: surfaktant, mordenit, adsorpcija, acetatna kiselina, laurinska kiselina, amonijak REZIME Ova studija je pokušaj da se sintetski zeolit mordenit modifikuje sa površinski aktivnom supstancom (PAM). Zeolit je korišten kao matriks u koji su uvođeni organski molekuli, kako bi se prilagodili za adsorpciju organskih supstanci. Cilj je bio da se površina zeolita iz primarno hidrofilne prevede u hidrofobnu, što omogućava jaku interakciju sa organskim isparenjima i organskim komponentama rastvorenim u vodi. Adsorpcija je ispitana sa organskim kiselinama (acetatnom i laurinskom) i amonijakom na PAM – modifikovanim i nemodifikovanim uzorcima mordenita. Mordenit je modifikovan anjonskim surfaktantom (Genapol), koji je po sastavu natrijeva so-alkildiglikol-etersulfat. Rezultati adsorpcije amonijaka i organskih kiselina iz vodenog i alkoholnog rastvora, obrađeni preko Freundlichove adsorpcione izoterme, na temperaturama 20, 25 i 30 0C dokazuju da modifikacijom mordenita surfaktantom dolazi do promjene tipa adsorpcije iz fizičke adsorpcije u hemisorpciju, zavisno da li je u pitanju organska kiselina ili vodeni rastvor amonijaka. Key words: surfactant, mordenite, adsorption, acetic acid, lauric acid, ammonia. ABSTRACT This study is an attempt to modify synthetic zeolite mordenite with the surface active substance (SAM). The zeolite was used as a matrix in which organic molecules were introduced in order to be adjusted to adsorption of organic substances. The objective was to transfer the zeolite surface from primarily hydrophilic to hydrophobic one, which enables a strong interaction with organic vapors and organic components dissolved in water. Adsorption was examined with organic acids (acetic and lauric acid) and ammonia on SAM – modified and unmodified samples of mordenite. Mordenite was modified with the anionic surfactant (Genapol), which is a sodium salt -alkyldiglycol-ethersulfate by its composition. The results of adsorption of ammonia and organic acids from the water and alcohol solution, processed through Freundlich adsorption isotherm, at the temperatures of 20, 25 and 30 0C, prove that modification of mordenite by a surfactant results in the change of the type of adsorption from physical adsorption to chemisorption, depending on whether organic acid or water solution of ammonia is in question.
8 th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
THE EFFECT OF MgO ADDITION ON THE SYNTHESIS OF MULLITE FROM RICE HUSK ASH AND TECHNICAL ALUMINA
Ranko Adziski, Emilija Fidancevska Ss Cyril and Methodius University, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy
Rudjer Boskovic 16, Skopje Republic of Macedonia
Dragan Milovski
BOMEX-Refractory Pehcevo
Republic of Macedonia Keywords: rice husk ash, reaction sintering, mullite ABSTRACT Rice husk ash, precursor of silica, and technical alumina were used as raw materials for synthesis of mullite by activated reaction sintering. High-energy ball milling was applied to the mixtures for mullite synthesis, resulting in refined powders with particles size less than 100 nm after 3 h milling. Consolidation was realized by cold isostatic pressing (P=500 MPa), and sintering (1200–1500 0C). Phase-pure mullite was obtained after sintering at temperature of 1500 0C/2h. The synthesized mullite possessed 93% TD, and the mechanical properties, such as E-modulus and bending strength, were 109±5 GPa and 154±2 MPa, respectively. By adding MgO to the initial mixture, the temperature/time needed to obtain phase-pure mullite was decreased to 1400 0C/1h. At the same time, the mechanical properties were increased. The synthesized mullite samples possessed 97% TD, and E-modulus and bending strength were 120±3 GPa and 200±4 MPa, respectively. Further, the addition of MgO influenced on the microstructure of the sintered mullite samples. By increasing the temperature/time of sintering to 1500 0C/2h, a homogenous microstructure with anisotropic mullite grain growth was obtained. This might be useful in the fabrication of reinforced ceramics based on mullite and other materials.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
FABRICATION OF MAGNEZITE-CHROMITE REFRACTORY USING DIFFERENT BINDERS
Dragan Milovski1, Vojo Jovanov2, Ranko Adziski2, Emilija Fidancevska2
1BOMEX REFRACTORY, Industriska 6, Pehcevo, Republic of Macedonia
2University Ss. Cyril and Methodius, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, Ruger Boskovic 16, 1000 Skopje, Republic of Macedonia
Keywords: Magnesite-chromite refractory, binder, pressing, sintering ABSTRACT Magnesite-chromite refractory presents one of the products fabricated in “BOMEX REFRACTORY”, Pehcevo, Republic of Macedonia. Chrome ore, iron concentrate and sinter magnesite were used as raw materials for fabrication of magnesite-chromite refractory (BOMAG-VPH quality). The raw materials were characterized from chemical, physical and structural aspects and particular granulometry was used for this purpose. The final products were formed by pressing and sintering. In the present investigation, comparison was made between two types of binders (magnesium sulphate and sodium polyphosphate) used in the process of consolidation (pressing) and their influence on the technological parameters and properties of the final products were followed. Magnesite-chromite refractory fabricated by using magnesium sulphate as a binder was consolidated at P = 150 MPa and T = 16800C/8h. The sintered samples exhibited the following characteristics: bulk density– 3.10g/cm3, apparent porosity – 13.92%, compressive strength – 61.41 N/mm2, reversible linear expansion at 17000C – 1.60% and thermal shock resistance – 14 cycles. Compared to the magnesite–chromite refractory fabricated in the presence of magnesium sulphate as a binder, the refractory fabricated in the presence of sodium polyphosphate as a binder was consolidated at lower pressure (140 MPa) and temperature (16000C/8h). The bulk density and apparent porosity of the refractory were 3.12g/cm3 and 12.14%, respectively, while the mechanical and thermal properties were improved: compressive strength – 96.95 N/mm2, reversible linear expansion at 17000C – 1.62% and thermal shock resistance – 18 cycles. The microstructure of the fabricated magnesite chromite refractory was followed by SEM. Fabricated magnesite-chromite refractory (BOMAG-VPH quality), finds the application in metallurgy for building containers, convectors, etc.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“, Zenica, BiH, 27 – 28. april, 2010.
PRIMJENA EKSPANDIRANOG POLISTIRENA ZA PROIZVODNJU IZOLACIONIH I AMBALAŽNIH MATERIJALA I UPRAVLJANJE
NASTALIM OTPADOM APPLICATION OF EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE FOR PRODUCTION
OF INSULATING MATERIAL AND PACKING MATERIAL AND MANAGEMENT WITH PRODUCED WASTE
Pero Dugić, generalni direktor
Rafinerija ulja Modriča
Zoran Petrović, Vojislav Aleksić, Vladan Mićić, Mitar Perušić Tehnološki fakultet Univerziteta u Istočnom Sarajevu, Karakaj bb, Zvornik
Ključne riječi: ekspandirani polistiren, termoizolacioni materijali, ambalaža, upravljanje, otpadom, reciklaža REZIME Izuzetno dobre termoizolacione karakteristike ekspandiranog polistirena, kao i potreba za štednjom energije dovela je do sve veće njegove primjene u građevinarstvu, kao i izradi ambalaže za različite proizvode. Ekspandirani polistiren ima prednost u odnosu na većinu ostalih termoizolacionih materijala, a primjenom istog ostvaruju se ne samo ekološki već i ekonomski efekti. U proizvodnji građevinskog stiropora i ambalaže, kao i pri njihovoj primjeni dolazi do stvaranja određene količine otpada, a upravljanje istim nije adekvatno riješeno. Cilj ovog rada je bio se analiziraju ekološki i ekonomski efekti nastali primjenom stiropora, kao i da se predloži način efikasnog upravljanja otpadom, kao i neki postupci reciklaže pogodni za male preduzetnike i škole. Key words: expanded polystyrene, thermoisolation material, packing material, waste management, recycling ABSTRACT Very good thermoisolation properties of expanded polystyrene as well as save energy requirement was brought about expansion of expanded polystyrene application in building and also in making packaging for many products. Expanded polystyrene has priority in regard to most of other thermoisolation materials, and with application these ecological and economical effects are achieved. In production of building polystyrene and package, as well as at theirs application some waste are generation and management with herewith did not adequate solve. The purpose of this paper has been to analyse ecological and economical effects arisen with polystyrene application, as well as to suggest method for management waste, as some methods of recycling suitable for small enterpreneurs and schools.
8 th
Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
INTERNAL STRESSES IN POLYMERIC MATERIALS
BASED ON AMINOPLAST UNUTRAŠNJA NAPREZANJA KOD POLIMERNIH MATERIJALA NA
BAZI AMINOPLASTA
Nikola Vukas, Izet Horman Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Sarajevo
Vilsonovo šetalište 9, 71000 Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina Ključne riječi: unutrašnja naprezanja, aminoplasti, konzolna metoda. REZIME U radu su prezentirani rezultati istraživanja unutrašnjih naprezanja kod filmova polimernih materijala na bazi aminoplasta formiranih na čvrstoj podlozi. Unutrašnja naprezanja se javljaju kao posljedica promjene volumena u periodu otvrdnjavanja i adhezije filma i podloge. Kontrolisana su zaostala unutrašnja naprezanja u otvrdnutom filmu. Za određivanje unutrašnjih naprezanja korištena je konzolna metoda. Istraživanja su provedena sa tri transparentna materijala. Kao podloga za istraživanje korištene su tanke čelične trake. Intenzitet zaostalih unutrašnjih naprezanja iztraživanih materijala iznosi od 2,64 do 8,88 MPa. Kod materijala iste hemijske osnove značajan uticaj na intenzitet unutrašnjih naprezanja ima struktura materijala, odnosno sadržaj isparljivih komponenti, tako da materijali sa manjim sadržajem isparljivih komponenti imaju manja zaostala unjutrašnja naprezanja. Key words: internal stresses, aminoplast, cantilever method. ABSTRACT This study presents the results of investigation of internal stresses by films of aminoplast-based polymer materials formed on solid ground. The internal stresses occur as result of volume changes during hardening and adhesion of the film and substrate. Controlled the residual internal stresses to harden the film. Internal stresses was determined by use of the cantilever method. The investigations were carried out with three transparent materials. Thin steel strips was used as the basis for investigated. The intensity of residual internal stresses the investigated materials is from 2,64 to 8,88 MPa. Materials of the same chemical base, a significant impact on the intensity of internal stresses has the structure of materials, so that materials with a lower content of volatile components have lower residual internal stresses.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH 27-28. april 2010.
ISPITIVANJE UTICAJA KONCENTRACIJE SiO2 I TEMPERATURE PRECIPITACIJE NA DEAGLOMERABILNOST PRECIPITIRANOG
SiO2 METODOM RASPRŠAVANJA LASERSKE SVJETLOSTI
INVESTIGATION THE EFFECT OF THE SiO2 CONCENTRATION AND PRECIPITATION TEMPERATURE ON SILICA DISPERSION BY
LIGHT SCATTERING METHOD
Adnan Mujkanović1, Petar Petrovski1, Ljubica Vasiljević2 , Gordana Ostojić2 1 - Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Univerzitet u Zenici
2 - Tvornica glinice „Birač“ Zvornik Ključne riječi: precipitirani SiO2, deaglomerabilnost, metoda rasijavanja laserske svjetlosti REZIME Precipitirani SiO2 spada u skupinu najviše korištenih aktivnih punila za ojačanje gume. U radu je ispitana mogućnost korištenja metode rasijavanja laserske svjetlosti za ocjenu deaglomerabilnosti precipitiranog SiO2. Sintetizirani su uzorci amorfnog SiO2 dvostepenom precipitacijom iz rastvora Na-metasilikata pri različitim temperaturama i koncentracijama SiO2. Stepen disperzije punila u matriksu predstavlja jedan od glavnih faktora koji utiče na efekat ojačanja gume. Stepen disperzije punila je u direktnoj zavisnosti od čvrstoće aglomerata. Deaglomerabilnost precipitiranog SiO2 je ocijenjena praćenjem promjene raspodjele veličine čestica prilikom tretiranja uzoraka poljem ultrazvuka visokog intenziteta. Key words: precipitated silica, dispersion, light scattering method ABSTRACT Precipitated silica is widely used a filler material in rubber to increase its mechanical properties. The paper presents the possibility of using light scattering method for evaluating silica dispersion in rubber. The samples of precipitated silica were synthesized from sodium silicate solutions at various temperatures and SiO2 concentration. A degree of filler dispersion is one of the main factors which influences on the effect of rubber reinforcement. Light scattering technique has been used to study the breakup of agglomerates in silica. The breakup of agglomerates is helpful in the dispersion of silica in a rubber matrix without actually formulating rubber.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
ISPITIVANJE UTICAJA DODATKA ELEKTROFILTERSKOG PEPELA NA PROCES HIDRATACIJE MJERENJEM SPECIFIČNE
ELEKTRIČNE PROVODNOSTI CEMENTNIH PASTI
TESTING THE INFLUENCE OF THE ADDITION OF FLY ASH AT THE PROCESS OF CEMENT HYDRATION BY MEASURING THE
SPECIFIC ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF CEMENT PASTE
I. Bušatlić 1 , P. Dabić 2, M. Rizvanović1, N. Bušatlić 3 1 Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Univerzitet u Zenici
2 Kemijsko-tehnološki fakultet, Split 3 Srednja tehnička škola Bugojno
Ključne riječi: cement, elktrofilterski pepeo, hidratacija, specifična električna provodnost REZIME U radu je ispitivan uticaj dodatka elektrofilterskog pepela TE Kakanj na proces hidratacije cementa. Ispitivanje je izvršeno na uzorcima cementa koji su sadržali od 0 do 50 % elektrofilterskog pepela. Prvo je urađena fizikalno-kemijska karakterizacija elktrofilterskog pepela, kao i pripremljenih uzoraka cementa. Ispitivanje ranog procesa hidratacije uzoraka cementa je vršeno mjerenjem specifične električne provodnosti cementnih pasti. Rezultati su pokazali da se reaktivnost cementa, odnosno brzina hidratacije cementa u prvim satima hidratacije (do 6 sati hidratacije) smanjuje sa povećanjem sadržaja pepela u cementu. Key words: cement, fly ash, hydration, the specific electrical conductivity. ABSTRACT In this work was tested the influence of the fly ash on the process of hydration of cement in the power plant Kakanj. Testing was conducted on the samples of cement which contained from 0 to 50 % fly ash. At first physico – chemical characterization of fly ash is made and prepared samples of cement, too. The testing of the early hydration process of cement samples was done by measuring the specific electrical conductivity of cement paste. The results showed that the reactivity of cement, or speed hydration at the first hours of cement hydration (up to 6 hours of hydration) decreases with increasing ash content in cement.
8th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation "Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials" Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
GEOPOLIMERNA VEZIVA PRIPRAVLJENA S LETEĆIM PEPELOM IZ HRVATSKE TERMOELEKTRANE
GEOPOLYMERIC BINDERS PREPARED BY USING THE CROATIAN
COAL-FLY ASH
Jelica ZELIĆ, Full Prof. PhD, Dražan JOZIĆ, Assist. Prof. PhD, Mario Nikola MUŽEK, PhD. student, Draga KRPAN-LISICA, Senior Lecturer MSc. Faculty of Chemistry and Technology, Teslina 10/V, 21000 Split, Croatia
e-mail: [email protected] (J. Zelić). Ključne riječi: geopolimeri, leteći pepeo klase F, alkalijska aktivacija
REZIME U radu je istraživan utjecaj različitih uvjeta priprave na razvoj čvrstoća i nastalih faza u geopolimernim vezivima, tj. u alkalijski aktiviranim alumosilikatnim materijalima, pripravljenim primjenom letećeg pepela (klase F) iz hrvatske termoelektrane ložene na ugljen i vodenog stakla kao aktivatora. FTIR, XRD i SEM/EDS korišteni su za identifikaciju nastalih faza i za praćenje napredovanja reakcije. Također je raspravljen razvoj mehaničkih čvrstoća pripravljenih geopolimernih mortova u odnosu na nastale produkte reakcije. Keywords: geopolymers, class F fly ash, alkaline activations ABSTRACT The reported research examined the effect of different curing conditions on the strength development and phases formed in geopolymeric binders, i.e. the alkali activated aluminosilicate materials, prepared by using the Croatian coal-fly ash (ASTM Class F) and water-glass as alkali activator. FTIR, XRD and SEM/EDS have been used to identify the new phases and to follow the progress of their formation. In addition, the evolution of mechanical properties of prepared geopolymers has also been discussed in terms of products formed at different times of reaction.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem «METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI» Zenica, BiH, 27-28.april 2010.
KINETIKA HIDRATACIJE PC I SVOJSTVA NASTALOG
CEMENTNOG KOMPOZITA UZ DODATAK ZEOLITNOG OTPADA KOJI SADRŽI Zn2+- IONE
PORTLAND CEMENT HYDRATION KYNETICS AND PROPERTIES
OF THE INCURRED CEMENT COMPOSITE IN ADDITION OF WASTE ZEOLITE CONTAINING Zn2+-IONS
dr. sc. Petar Krolo, red. prof.,
Robert Bulat, dipl. ing. kemijske tehnologije., dr. sc. Pero Dabić, izv. prof.,
Kemijsko-tehnološki fakultet u Splitu, Teslina 10 / V, 21000 Split, Hrvatska
Ključne riječi: hidratacija cementa, cementni kompozit, štetni otpad REZIME Ispitivan je utjecaj prirodnog zeolitnog tufa koji je zasićen Zn2+- ionima na hidrataciju te fizikalno mehanička i reološka svojstva nastalih cementnih kompozita. Kao uzorci korištene su mješavine od 50 mas. % industrijskog cementa i 50 mas.% zeolitnog tufa zasićenog Zn2+ ionima uz voda-kruto omjer V/K = 0.5 te dodatak 0,3 mas.% aditiva plastifikatora otopljenog u vodi za hidrataciju. Kinetika hidratacije praćena je diferencijalnom mikrokalorimetrijom, dok su fizikalno-mehaničke i reološke karakteristike praćene prema važećim Standardima za cementne kompozite. Dobiveni rezultati pokazuju kako zeolitni dodatak utječe na kinetiku hidratacije cementnih kompozita te kakva svojstva pokazuju solidifikacijom realizirani cementni kompoziti.
Key words: cement hydration, cement composite, harmful waste ABSTRACT It was examined the effect of the natural zeolite tuff saturating Zn2+ - ions on hydration and physical and mechanical and rheological properties of the resulting cementitious composites. As the samples were used a mixture of 50 wt. % industrial portland cement and 50 wt. % zeolite tuff saturated with Zn2+ ions with water-solid ratio of V/K = 0.5 and the addition of 0.3 wt.% additives plasticizers dissolved in water for hydration. Hydration kinetics is attended by differential microcalorimetry, while the physical and mechanical and rheological characteristics attended by the applicable standards for cement composites. The results show that the addition of zeolite affects the hydration kinetics of cementitious composites and show what are properties of solidification realized cement composites.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem “ METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI “ Zenica, BiH, 27 – 28. april 2010
CRVENI MULJ KAO BAZA ZA SINTEZU ŽELJEZOVITIH CEMENATA
RED MUD AS BASE FOR FERROUS CEMENT SYNTHESIS
Janko Mikić 1, Miro Sudar 2 1 Fabrika glinice “ Birač “ Zvornik, BiH
2 Univerzitet u Istočnom Sarajevu, Tehnološki fakultet Zvornik, BiH
Ključne riječi : crveni mulj, glina, krečnjak, željezoviti cementi REZIME Korišćenje crvenog mulja, otpadnog produkta i balasta u proizvodnji glinice, dugogodišnja mora naučnih radnika iz oblasti industrijske metalurgije, jednog će dana svakako postati stvarnost. Tome će, između ostalog, pomoći i ekspanzija cementne industrije, po pitanju asortimana proizvoda i raznolikosti sirovinske osnove. U ovom radu su date teoretske postavke takvog pokušaja, kao i računski pokazatelji pripreme šarže i dobijanja klinkera, koji bi posjedovao dosta cijenjenih i kvalitetnih osobina za specijalnu upotrebu. Određene poteškoće, zbog povećanog sadržaja alkalija i otežanog sinterovanja ovakve sirovinske smjese , nisu nepremostive. Key words : red mud, clay, limestone, iron cements. ABSTRACT Consumption of red mul, of huge ballast in alumina production is nightmare for scienists who are working in the area of industrial metallurgi, one dey will become reality. Among other things of cement industry is going to help regrading assortment of products and diversity of raw material base. In this document, theoretical bases of the mentioned attempt are presented, as well as calculated indicators of charge preparation and obtaining klinker which would has and lot of good quality characters for special use. Certain difficulties, due increased content of alkali and harder sintering of this material mixture, are not insuperable.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
UTICAJ SILICIJSKE PRAŠINE NA OSOBINE CEMENTA TIPA CEM II/B – W 42,5N U TVORNICI CEMENTA KAKANJ
EFFECT OF SILICA FUME ON THE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CEMENT TYPE CEM II/B – W 42,5N IN CEMENT PLANT KAKANJ
Msc Nevzet Merdic dipl.ing Msc. Nedzad Haračić, dipl. ing
Kakanj cement plan Selima ef. Merdanovica 146,
BiH, 72240 Kakanj
Dr.sc. Zijad Pašić Doc. dr.sc Ilhan Bušatlić
Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale Travnička cesta 1, BiH, 72000 Zenica
Ključne riječi: silicijska prašina, cement, pritisna čvrstoća REZIME U ovom radu je analiziran uticaj dodatka silicijske prašine na osobine cementa CEM II/B – W 42,5N. Silicijska prašina visoke pucolanske aktivnosti se smatra kao dobar dodatak letećem pepelu. Povoljno djelovanje dodatka silicijske prašine na čvrstoću portland cementa sa dodatkom pepela se pripisuje njegovoj veoma velikoj pucolanskoj aktivnosti i finoći dajući pri tome efekt filera – male čestice silicijske prašine popunjavaju prostor između cementnih zrna. Višak C-S-H koji je proizveden u pucolanskoj reakciji može prema tome popuniti pore u otvrdnutoj pasti i naknadno smanjiti ukupnu poroznost. Isto tako se smanjuje i srednja veličina pora. Prema BAS EN 197-1, sadržaj silicijske prašine (SF) može ići do 10%. Keywords: Silica fume, cement, compressive strength ABSTRACT Influence of the silica fume addition to CEM II/B – W 42,5N was studied in this paper. Silica fume of high pozzolanic activity was considered as a good addition to fly ash. The beneficial influence of silica fume addition on the strength of fly ash cement is attributed to its very high pozzolanic activity and fineness, giving a filler effect – small silica fume particles enter the space between cement grains. The excess of C-S-H gel produced in the pozzolanic reaction can thus still fill pores in hardened paste and consequently the total porosity decrases. The mean pore diameter is also reduced. The proportion of silica fume is limited to 10% according BAS EN 197-1
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
KORIŠTENJE PEĆNE PRAŠINE ZA PROIZVODNJU CEMENTA U TVORNICI CEMENTA KAKANJ
USAGE OF CEMENT KILN DUST FOR CEMENT MANUFACTURING
IN CEMENT PLANT KAKANJ
Msc Nevzet Merdic dipl.ing Msc. Nedzad Haračić, dipl. ing
Kakanj cement plan Selima ef. Merdanovica 146,
BiH, 72240 Kakanj
Dr.sc. Zijad Pašić Doc. dr.sc Ilhan Bušatlić
Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale Travnička cesta 1, BiH, 72000 Zenica
Ključne riječi: cement, pećna prašina, čvrstoća REZIME Cement kiln dust (CKD) ili pećna prašina je fino zrnati, čvrsti materijal koji nastaje nakon dekarbonizacije u rotaconoj peći. CKD se nosi toplim gasovima kroz rotacionu peć i skuplja se u vrećasti filter. Veći dio CKD predstavlja neizreagovani materijal koji obuhvata sirovinsko brašno pri različitim uslovima pečenja i čestice klinkera. Sastav CKD varira kod cementara što zavisi od komponenata koje se koriste za proizvodnju sirovinskog brašna. U ovom radu se ispituju hemijske i fizičko-mehaničke osobine cementa koji sadrži CKD u količini od 3 %, 4 % i 5 %.. Keywords: cement, cement kiln dust, strength ABSTRACT Cement kiln dust is a fine grained, solid material which is produced in the rotary kiln after decarbonization. Cement kiln dust is carried by hot gasses in a cement kiln and collected by a baghouses filter. Much of the material comprising CKD is incompletely reacted raw material, including a raw mix at various stages of burning, and particles of clinker.The composition of CKD varies among plants and it depends of constituents for kiln feed production. The chemical and physical-mechanical properties of the cement which contains 3%, 4% and 5% CKD were made in this study.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. April 2010.
KARAKTERIZACIJA ELEKTROFILTERSKOG PEPELA IZ TE GACKO I MOGUĆNOSTI NJEGOVE PRIMJENE
CHARACTERIZATION OF FLY ASH FROM TPP GACKO AND
POSSIBILITIES OF ITS USAGE
P. Petrovski 1, I. Bušatlić 1, S. Govedarica 2, D. Miloševic 2, N. Bušatlić 3 1. Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Univerzitet u Zenici
2. Rudnik i termoelektrana Gacko 3. Srednja tehnička škola Bugojno
Ključne riječi: pucolanski dodaci cementu, karakterizacija elektro-filterskog pepela, građevinski materijali. REZIME Elektrofilterski pepeo je otpadni materijal koji se dobije spaljivanjem sprašenog uglja u termoelektranama. Poznato je da se ovaj odpadni materijal može koristiti kao sekundarna sirovina u industiji građevinskih materijala, prvenstveno u industriji cementa i betona. U ovom radu je izvršena kompleksna karakterizacija (određene su hemijske, mineralne i fizičke karakteristike) elektrofilterskog pepela TE Gacko koji pripada klasi (C), kao i ispitivanje mogućnosti njegove upotrebe prije svega u građevinarstvu. Key words: cement additives, characterisation of fly ash, building materials. ABSTRACT The fly ash is a waste material obtained by burning coal in the thermal power plants. It is known that this waste material can be used as secondaty raw material in industry of building materials, primarily in the cement and concrete productions. In this paper complex valuation (chemical, physical and structural characteristics) of fly ash from thermal power plant Gacko which belongs to class C according to ASTM standard, was performed as well as an investigation about its usage in building materials production.
VIII Naučno/ stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28.april 2010
UTICAJ AGREGATA ZA PROIZVODNJU ASFALTA I HRAPAVOST
KOLOVOZNIH KONSTRUKCIJA
THE IMPACT OF AGGREGATES PRODUCTION IN THE ROUGHNESS OF THE ASPHALT ROAD CONSTRUCTION
Mr.sc. Edis Softić, dipl.ing.građ., Tehnički Fakultet Bihać Dr.sc. Nedžad Alić, dipl.ing.rud, Dr. sc Admir Softić, dipl. ing. rud., RGGF Tuzla
Ključne riječi: hrapavost, kolovozne konstrukcije, sigurnost. REZIME Cilj rada je upoznavanje zakonitosti pojedinih i zbirnih uticaja karakterističnih sastava asfaltnih mješavina izloženih saobraćaju, a koji izravno utiču na sigurnost u drumskom saobraćaju. Vršena su ispitivanja na pet vrsta asfaltnih mješavina prema njenom mineraloško-petrografskom sastavu. Rezultati ispitivanja mogu sa primjenjivati na taj način da se postigne zadovoljavajuća hrapavost završnog sloja kolovozne konstrukcije koja bi imala izravan uticaj na sigurnost na drumskom saobraćaju. Dobivenim zakonitostima se ustanovilo da je prednost asfalt betona izrađenog od magmatskih stijena u odnosu na asfalte proizvedene od stijena krečnjačkog porijekla izražena u velikoj mjeri. Key words: roughnes, roadway construction, certainty. ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is cognition legality of individual and collective influence of the characteristic composition of asphalt mixture exposed to traffic and that directly affect the safety of road traffic. Tests were performed on five types of asphalt mixture to its mineralogical-petrographic composition. Test results can be applied with this method to achieve satisfactory roughness roadway construction final layer structure which would have a direct impact on safety in road traffic. Obtained laws to determine the benefits asphalt concrete made of igneous rocks in relation to the asphalt produced from the limestone rocks of origin are expressed in largely.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
PRIMJENA DPV I DPASV METODA KOD ODREĐIVANJA CINKA
THE APPLICATION OF DPV AND DPASV METHODS IN DETERMINING OF ZINC
Farzet Bikić, docent, Mirsada Rizvanović, redovni profesor
Univerzitet u Zenici, Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale u Zenici Ključne riječi: DPV, DPASV, voltametrija, polarografija, kapajuća živina elektroda, polutalasni potencijal, jačina struje. REZIME U ovom radu su prikazani rezultati određivanja donjeg koncentracionog limita diferencijalne pulsne voltametrije (DPV) i diferencijalne pulsne anodne striping voltametrije (DPASV) na primjeru određivanja cinka. Ispitivanja su sprovedena na uređaju potenciostat/galvanostat 263A-2, koristeći softverski paket PowerPULSE. Rezultati pokazuju da je najniža koncentracija cinka koja se može određivati DPV metodom cca 1 mg/l, dok se primjenom DPASV metode cink može određivati u koncentracijama nižim od 30 μg/l. To znači da se DPASV metodom može određivati cink u vodama I klase u kojima je dozvoljena koncentracija cinka 50-80 μg/l. Kao radna elektroda u eksperimentu je primijenjena kapajuća živina elektroda, način rada HMDE. Key words: DPV, DPASV, voltammetry, polarography, mercury drop electrode, half-wave potential, current. ABSTRACT This paper presents the results of determining the lower concentration limit of Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) and Differential Pulse Anodic Striping Voltammetry (DPASV) in the case of determination of zinc. Tests were conducted on the device potentiostat/galvanostat 263A-2, using the software package PowerPULSE. The results show that the lowest concentration of zinc that can be determined with DPV method is about 1 mg/l, while using DPASV method of zinc can be determined at concentrations lower than 30 μg/l. This means that the DPASV method can determine zinc in the water class I in which the permitted concentration of zinc 50-80 μg/l. As a working electrode in the experiment is applied Mercury Drop Electrode, HMDE mode.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
KVALITATIVNA ANALIZA MOTORNOG ULJA FT-IR SPEKTROFOTOMETRIJOM
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ENGINE OIL WITH FT-IR
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
Farzet Bikić, docent, Univerzitet u Zenici, Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale u Zenici
Ključne riječi: FT-IR spektrofotometrija, ulje, kontaminacija, degradacija REZIME U radu su prikazani i diskutovani rezultati kvalitativne FT-IR analize motornog ulja HD-SAE 30. Ispitivana je degradacija ulja kao posljedica kontaminacije antifrizom. Kontaminacija je simulirana dodatkom antifriza u novo ulje. Pripremljena su četiri uzorka, miješanjem novog ulja i korištenog antifriza u različitim volumnim odnosima. Ispitivanje je provedeno na uređaju FT-IR spektrofotometar, Spektrum 100, PerkinElmer. Key words: FT-IR spectrophotometry, spectrometer, oil, contamination, degradation ABSTRACT The paper presents the results and discussed of qualitative FT-IR analysis of engine oil HD SAE-30. Investigated is degradation of oil as a result of contamination with antifreeze. Contamination was simulated by adding antifreeze to the new oil. Prepared are four samples, mixing the oil and used antifreeze in various volume relations. Testing was conducted on the device Spectrum 100 FT-IR spectrophotometer, PerkinElmer.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
KONDUKTOMETRIJSKA METODA ODREĐIVANJA
PRIHVATLJIVOG DODATKA OTPADNOG MULJA I ZASIĆENOG ZEOLITA IZ POGONA POCINČAVANJA U CEMENTU
CONDUCTOMETRICAL METHOD OF DETERMINATION OF
ACCEPTABLE WASTE MUD AND SATURATED ZEOLITE ADDITION FROM A ZINC PLATING PLANT IN CEMENT
Pero Dabić, izv. prof., Petar Krolo, red. prof.,
Damir Barbir, dipl. inž., Marica Maretić, student Kemijsko-tehnološki fakultet, Teslina 10/V, 21000 Split, Hrvatska
Ključne riječi: portland cement, otpadni zeolit, solidifikacija REZIME Istraživan je utjecaj dodataka mulja iz pogona pocinčavanja i cinkom zasićenog zeolita na specifičnu provodnost cementne paste CEM I pri 20 °C i uz vodo-cementni omjer, V/C = 0.4. Dobivene krivulje specifične provodnosti imaju tipičan oblik s naglašenim pikom maksimalne provodnosti, ali se on pojavljuje u kasnijim vremenima što je veći udjel dodataka. Matematičkom obradom podataka određeno je koliki je udjel smjese mulja i zasićenog zeolita prihvatljiv u sustavu cement-voda-dodatci s ciljem njegove uspješne solidifikacije i stabilizacije. ABSTRACT It was invesigated the influence of mud additives from a zinc plating plant and zeolite saturated with zinc on the specific conductivity of cement paste CEM I at 20 ° C and the water-cement ratio, W / C = 0.4. Specific conductivity curves have a typical shape with pronounced maximum of conductivity, but it appears in later times with larger share of addition.With mathematical treatment of data is determined a mixture share of mud and saturated zeolite acceptable in cement-water-additives system with the aim of his successful solidification and stabilization.
VIII Naučni/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28.april 2010
PRIMJENA KALIBRACIONIH ETALONA U XRF (X-RAY FLUORESCENCE) SPEKTROMETRIJSKOJ ANALIZI
APPLICATION OF CALIBRATION STANDARDS IN XRF (X-RAY
FLUORESCENCE) SPECTROMETRIC ANALYSIS
Msc Nevzet Merdic dipl.ing Msc. Nedzad Haračić, dipl. ing
Kakanj cement plan Selima ef. Merdanovica 146,
BiH, 72240 Kakanj
Prof. dr Petar Petrovski, Prof. dr Mirsada Rizvanović
Doc. dr.sc Ilhan Bušatlić Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale
Travnička cesta 1, BiH, 72000 Zenica
Ključne riječi: Kalibracioni etaloni, tačnost XRF analize, referentni materijal, certificirani referentni materijali, standardni referentni materijali, kontrolni etaloni
REZIME Cilj ovoga rada jeste da se u kratkim crtama prikaže koliki je zaista značaj korištenja odgovarajućih kalibracionih etalona za tačnost XRF analize. S tim u vezi u ovom radu data su objašnjenja nekih od najvažnijih pojmova kada su u pitanju XRF standardi ili etaloni. Naime, da bi se uradila kvalitetna XRF spektrometrijska analiza odnosno da bi se dobili analitički rezultati zadovoljavajuće tačnosti neophodna je primjena odgovarajućih kalibracionih etalona. Ovi etaloni uključuju rude, metale i legure, stijene, minerale, otpadne produkte, kao i mnoge druge metalne i nemetalne materijale. Okolinski problemi, tj. problemi zaštite životne sredine također su doprinijeli razvoju etalona za ovu oblast, pa su se iz tog razloga razvili kalibracioni etaloni za različite industrijske otpade, izotopične materijale i sl. Svaka analitička laboratorija u cilju dobivanja što kvalitetnijih odnosno tačnijih rezultata trebala bi da koristi certificirane kalibracione etalone pri izvođenju odgovarajućih kalibracija. Key words: Calibration standards, accuracy of XRF analysis, reference material, certified reference materials, standard reference materials, monitor standards ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to shortly present how much is really importance of using suitable calibration standards for XRF analysis accuracy. Because of this, explanation some of the most important notion when we are talking about XRF standards was given in this paper. Namely, to make high quality XRF spectrometric analysis or to get satisfy accuracy of analitical results it is necessary to apply corresponding calibration standards. These standards include ores, metals and alloys, rocks, minerals, waste products as many other metallic and nonmetallic materials. Environmental problems are also contributed developing of standards for this field and because of this reason calibration standards for different industrial wastes, isotopic materials etc was developed. In order to get accurate results each analytical laboratory should use certified calibration standards during performing corresponding calibrations.
VIII Naučni/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28.april 2010
ON-LINE KONTROLA KVALITETA POMOĆU PGNAA ANALIZATORA I XRF SPEKTROMETRA
ON-LINE QUALITY CONTROL WITH PGNAA ANALYZER AND
XRF SPECTROMETER
Msc Nevzet Merdic dipl.ing Msc. Nedzad Haračić, dipl. ing
Kakanj cement plan Selima ef. Merdanovica 146,
BiH, 72240 Kakanj
Prof. dr Petar Petrovski, Prof. dr Mirsada Rizvanović
Doc. dr.sc Ilhan Bušatlić Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale
Travnička cesta 1, BiH, 72000 Zenica
Ključne riječi: PGNAA analizator, XRF spektrometar, neutronski izvor, hemijska analiza
REZIME PGNAA (Prompt Gamma Neutron Activation Analysis) analizator je mjerni sistem namijenjen za kontinuirano praćenje hemijskog sastava materijala koji se nalazi na pokretnoj transportnoj traci. Analiziranje se vrši na način da se svake minute na displeju dobiju informacije o hemijskom sastavu analiziranog materijala. Kao neutronski izvor koristi se Kalifornijum Cf-252 sa vremenom poluraspada od 2,646 godina. PGNAA analizator je baziran na analizi i obradi emitiranih gama zraka koji dolaze od atoma koji se aktiviraju za vrijeme „bombardovanja“ analiziranog materijala. Tako dobiveni signal se dalje procesuira preko detektora, da bi se na kraju taj signal izrazio u težinskim procentima. Ukoliko se ovaj mjerni sistem koristi u kombinaciji sa XRF (X-ray fluorescence) spektrometrom moguće je dobiti izuzetno tačne rezultate hemijskih analiza različitih vrsta materijala, te na taj način pojednostaviti proizvodni proces. Key words: PGNAA analyzer, XRF spectrometer, neutron source, chemical analysis ABSTRACT PGNAA (Prompt Gamma Neutron Activation Analysis) analyzer is measuring system with purpose to continuously follow the chemical composition of material on the mobile conveyor belt. Analyzing is performing on way that every minute is on the disply information about chemical composition of analysed materijal. As neutron source we use Californium Cf-252 with a half-life of 2,646 years. PGNAA analyzer is based on analysis and interpretation of emitted gamma rays which comes from atoms activated during the „bombarding“ of analysed material. Such obtained signal is processing across detector and the signal has been expressed in weight percent at the end. If this measuring system we use in combination with XRF (X-ray fluorescence) spectrometer then is possible to get very accurate chemical analysis results of different kind materials and on that way simplify production process.
8 th
Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27-28. April 2010
IMPLEMENTATION OF IMAGE ANALYSIS ON THERMAL SHOCK AND CAVITATION RESISTANCE TESTING OF LOW CEMENT HIGH
ALUMINA CASTABLE
S. Martinovic, Institute for Technology of Nuclear and other Raw Mineral Materials,
Franchet d’Esperey 76, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia M. Dojcinovic ,
University of Belgrade, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, Karnegijeva 4, POB 3503, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia
J. Majstorovic, University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mining and Geology, Djusina 4, Belgrade, Serbia
T. Volkov-Husovic
University of Belgrade, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, Karnegijeva 4, POB 3503, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia
Keywords: Low cement castable, sintering temperature, ultrasonic measurements, cavitation resistance
ABSTRACT In the recent decades, the use of unshaped monolithic refractories has been increasing greatly because of their significant advantages over other shaped refractory bricks of the same class. Low cement high alumina castable was synthetised and sintered at 1600 °C in order to monitore surface changes during thermal shock and cavitation testing. Water quench test was applied as experimenthal method for thermal stability testing. Image analysis of the surface of the samples showed some level before water quench test, at the surface, and inside the sample. During testing, level of destruction of the surface was increasing. Damage of the surface and inside the sample during water quench test is correlated to the number of quench experiment with excellent coefficient of correlation (R2=0,922). Cavitation damage is often tested for the metallic materials. As many composites and ceramic materials are expected to replace some of the metallic components, the goal of this investigation was to apply cavitation testing on the ceramic sample. Cavitation damage of alumina based refractory specimen was performed using the modified vibratory cavitation set up. Erosion rates were chosen as for the metallic samples. Mass loss during experiment showed the excellent correlation with the time. Image Pro Plus Program was applied for surface analysis during testing. Obtained results showed that surface erosion is in strong correlation with time, and erosion of the sample surface was below 25 % of the surface area before testing. Results presented in this paper showed that investigated material exhibited excellent mechanical properties, very good thermal shock behaviour and very good cavitation erosion. New future application of this material could be expected in conditions where cavitation resistance is needed.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem ,,METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI'' Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
STANJA ELEMENTARNIH POBUĐENJA U SUPERREŠETKAMA KRISTALNIH ORGANSKIH MATERIJALA
ELEMETARY STATES OF EXCITATION IN CRYSTALLINE
ORGANIC SUPERLATTICES MATERIALS
Siniša M. Vučenović, viši asistent Medicinski fakultet Banja Luka,
Banja Luka, Republika Srpska, BiH
Svetlana Pelemiš, viši asistent Tehnološki fakultet Zvornik,
Zvornik, Republika Srpska, BiH Blanka Škipina, viši asistent
Tehnološki fakultet Banja Luka, Banja Luka, Republika Srpska, BiH
Jovan P. Šetrajčić, redovni profesor Departman za fiziku PMF Novi Sad,
Novi Sad, Vojvodina, Srbija Ključne riječi – superrešetke, eksitoni, zakon disperzije, Grinove funkcije
REZIME Superrešetke su takva klasa modela strukture materijala gdje su međusobno spojeni tanki filmovi sa određenim pravilnim i periodičnim rasporedom. U ovom radu su teorijski određeni spektri energija koje eksitonske kvazičestice mogu imati u ovim strukturama. Broj slojeva filma koji čine osnovne periodično ponavljajuće motive unutar superrešetke, kao i odnos eksitonskog transfera energije unutar svakog motiva (filma) i eksitonskog transfera energije između susjednih motiva pokazali su se kao bitni parametri koji utiču na ponašanje izračunatih veličina u spoljašnjem elektromagnetnom polju. Key word: superlattice, excition, law of dispersion ABSTRACT The superlattices are such structured class of the materials where ultra thin films are mutually interconnected with regular and periodical pattern. In this research we have theoretically calculated the energy spectra which these quasi-particles could have in these structures. The number of the film layers (which makes base of the periodically repeating motive inside superlattice) and the ratio between exciton energy transfer inside each motive (film) and exciton energy transfer between neighbor motives seems to be significant parameters which have influence on the calculated values behavior in external electromagnetic field.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
UTICAJ MEHANIČKIH KARAKTERISTIKA MATERIJALA NA
STABILNOST I SIGURNOST KONSTRUKCIJE ZIDANIH SAKRALNIH TORNJEVA
INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS ON THE STABILITY AND SAFETY OF MASONRY SACRAL TOWERS
STRUCTURES
dr.sci. AMIR ČAUŠEVIĆ, dipl.ing.građ. Arhitektonski Fakultet Patriotske lige 30, Sarajevo, Bosna i Hercegovina
Ključne riječi: ziđe, mehaničke osobine materijala, toranj, minaret, stabilnost REZIME Arhitektonska vertikala nije isključivo asocijacija na religiju.Toranj je termin koji najpribližnije definiše arhitektonsku vertikalu i njenu materijalizaciju. A. J. Butler and H. Thiersch vide porijeklo tornjeva u uzorima antičkih svetionika . Kod sakralnih objekata prisutan je kontinuitet graditeljske misli – arhitektura religijskih objekata i arhitektura tornjeva uz njih. Toranj je forma koja je karakteristična za sakralne objekte i specifikum arhitektonske izražajnosti istih. Potreba je da se ukaže na propuste i prednosti ostvarenih realizacija i predlože novi pristupi projektovanja ovog tipa konstrukcije, sve sa namjerom da se formulišu naučno utemeljene tehnički prihvatljive preporuke za njihovo projektovanje i građenje . U radu su prezentirani rezultati za ukupno 10 minareta i crkvenih tornjeva, historijskog i kulturnog naslijeđa, koji su kroz svoju historiju bili ugroženi sa konstruktivnog aspekta, ili su doživjeli kolaps. Modeli su urađeni upotrebom programa SAP2000 V12 uvažavajući poznate karakteristike ugrađenog materijala i poznate dimenzije elemenata, sa ciljem određivanja stabilnosti i sigurnosti konstrukcije. Provedene su analize sa promijenjenim mehaničkim karakteristikama materijala od kojih je toranj izgrađen i to: modul elastičnosti, Poasonov koeficijent i zapreminska težina materijala za slučajeve boljih i lošijih karakteristika materijala u odnosu na stvarno stanje. Key words: masonry, mechanical properties of materials, tower, minaret, stability ABSTRACT High vertical form in architecture demonstrates tendency towards something higher or divine, something beyond the ordinary life, more than something earthly, as if it is leading us, or helping us to hear voice and sound, or perhaps to see more clearly. High vertical form in architecture is not exclusively associated with religion. It is by all means a power, and demonstration of power. In the case of construction intervention at such objects, two problems immediately emerge: the first concerns usual and expected approach, in most number of cases, to keep the role and geometry of constructive, now damaged elements. This situation can be additionally complicated by request, or better to say need, which is very often present, to strengthen those elements with respect to its original state. Other, perhaps even bigger problem, concerns the possibility of embedding.In this article 10 minarets and church towers are presented, carefully chosen as a representative from threatened cultural heritage towers. The computer program SAP 2000 was used to analyze the towers with shell elements. Analysis have been conducted with altered mechanical properties of materials towers are built as follows: modulus of elasticity, Poison’s coefficient Poison’s and specific weight of the material for the cases of better material characteristics and bad characteristics of the material in relation to the actual situation.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
VAKUMIRANA OSTAKLJENJA
VACUUM INSULATION GLASS
mr Salihbegović Amira, dipl.ing.arh. Arhitektonski fakultet
Sarajevo
Ključne riječi: reduciranje toplinskih gubitaka, smanjenje emisije CO 2 kroz nove tehnologije proizvoda, vakumirana ostakljenja, visoke termalne i akustične performanse, primjena u građevinarstvu REZIME Primjenom novih tehnologija i znastveno-istraživačkih dostignuća u oblasti građevinarstva nastoje se ostvariti povoljniji uvjeti za ostvarivanje strategije održive gradnje. Danas, istraživanjima na polju vakum i nanoznanosti, razvijene su tehnike za novu generaciju proizvoda u građevinarstvu, sa veoma visokim termoizolacionim, akustičnim i drugim karakeristikama. Pored vakumiranih panela, realizovana su i vakumirana ostakljenja, transparentne strukture omotača objekta, kao energetski najučinkovitija ostakljenja, čijom upotrebom bi se smanjile emisije štetnih plinova. Key words: reduction of heat losses, reduction of CO2 emission by new product technologies, vacuum insulation glas, high acoustic and thermal performances, aplication in construction industry ABSTRACT Application of new technologies and scientific research achievements in construction are trying to achieve better conditions for the realization of the strategy of sustainable construction. Today, research in the field of vacuum and nanoscience, have developed techniques for next generation products in the construction industry, with very high thermo-insulation, acoustic and other characteristics. Beside vacuum-panel, vacuum glasses are realized, transparent layer structure of the building, as the most efficient energy glass, whose use would reduce emissions (of harmful gases).
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
ENERGETSKA UČINKOVITOST U ZGRADARSTVU
UZ PRIMJENU DOMAĆIH MATERIJALA
ACHIEVING BUILDING ENERGY EFFICIENCY BY USING LOCAL MATERIALS
Nerman Rustempašić, mr.sci. dipl.ing. arhitekture Univerzitet u Sarajevu, Arhitektonski fakultet Sarajevo
Ključne riječi: energetska učinkovitost, zakonska regulativa, utopljavnje zgrada,
REZIME Obnova većine stambenih objekata devastiranih u cjelini ili djelimično, obavljena je na način da su vanjski zidani zidovi od opečnih (ili još gore betonskih) elemenata, omalterisani samo iznutra, a izvana je ostala gola opeka. Situacija je dodatno pogoršana obnovom samo dijela stambenog objekta, najčešće prizemlja, a na katu nije čak postavljena ni stolarija sa ostakljenjem. Bosna i Hercegovina, da bi pristupila Evropskoj uniji, moraće usvojiti sve evropske norme, a momentalno je najaktuelnija štednja energije. Po novoj EnEV propisano je da zid od opeke mora zadovoljiti koeficijent toplotne provodljivosti od 0,24 W/m2K, a obnovljeni objekti ne mogu udovoljiti ni trideset procenata traženih vrijednosti. Obzirom na činjenicu da su većinu obnova objekata finansirale i nadzirale/bez poštivanja domaće zakonske regulative/ zemlje EU, Bosna i Hercegovina će sigurno imati pristup sredstvima iz predpristupnih europskih fondova, pa je neophodno naći put da se objekti ne samo "utople" nego da se smanji emisija štetnih gasova u atmosferu. Ovo je prilika da mi sa domaćim građevinskim materijalima (otpaci drveta, cement, gips i dr.) proizvedemo ploče koje će vlasnici obnovljenih objekata moći sami ugraditi uz minimalna ulaganja. Rezultat bi bio da se pokrene građevinska proizvodnja, a ušteda energije bi bila nemjerljiva. U radu će biti prezentovani prijedlozi građevinskih elemenata na bazi raspoloživih domaćih materijala, kao i upotreba recikliranih nus proizvoda koji danas predstavljaju ekološki balast, a koji će riješiti uštedu energije u zgradarstvu i smanjiti emisiju štetnih gasova u atmosferu.
Key words: energy efficiency, legislative, warming the building
ABSTRACT The most common way to restore housing units devastated during the war, has been done by using the masonry to create outer walls (or worse- concrete walls), coated only from the inside. Situation is getting worse by restoring the building only partially, in most cases the ground floor, without having the carpentry on upper floors. In order to enter European Union Bosnia and Herzegovina must adopt European Norms, and the most common related topic today is energy efficiency. According to the new EnEV masonry wall must have U= 0, 24 W/m2K. Restored buildings cannot achieve the thirty percent of this value. Due to the fact that most of these buildings have been financed and monitored by European countries (without taking regard on the local legislative), Bosnia and Herzegovina should have an access in the European funds, which is important fact if we want to reduce environmentally harmful gasses emission. This is a chance to give a chance to the local building materials (such as wood, plaster, cement, etc.), by producing the elements which could be built in, without large expenses. The final result would be enhancement of the local production and the energy savings would be recognizable. This paper work aims to present suggestions of the building materials based on the available resources, as well to present models of usage, concerning recycled materials which represent ecological ballast in their unprocessed form. This kind of an approach might contribute to energy saving, and might reduce the environmentally harmful gasses emission.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
TEHNOLOGIJA PRERADE ČELIČANSKE TROSKE U
ARCELORMITTAL ZENICA
PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY OF STEEL SLAG IN ARCELORMITTAL ZENICA
Prof. dr Sulejman Muhamedagić, dipl.inž. metalurgije
Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale Univerzitet Zenica, Zenica
mr. Ćazim Talam, dipl. inž. tehnologije
Ashun d.o.o. Ilijaš Ključne riječi: čeličanska troska, reciklaža, prerada, građevinski materijal REZIME U procesu proizvodnje gvožđa i čelika nastaje nus-proizvod troska. Troska ima različite hemijske i mineraloške osobine u zavisnosti od procesa proizvodnje i njene prerade, što utiče i na područje njene primjene. U ovim procesima nastaju slijedeće troske: visokopećna (VP), konvertorska (BOF), elektropećna (EAF) i troska iz procesa sekundarne metalurgije (LF). U ovom radu je predstavljen budući postupak reciklaže, tehnologija prerade čeličanske troske i proizvodnja građevinskih materijala u ArcelorMittal Zenica. Key words: steel slag, recycling, processing, building/constructing materials. ABSTRACT During iron and still processing an additional product occurs and that is slag/cinder. Slag/cinder have different chemical and mineralogy characteristics depending on manufacturing and processing of slag, what can affect at area of its application. In those processes the following types of slag obtain: blast furnace slag (BF), convector (BOF), electro furnace (EAF) and slag that came out of process of secondary metallurgy (LF). In this paper the future recycling process, processing technology of steel-mill slag and production of building/constructing materials within the plant “ArcelorMittal” Zenica are presented.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
MENADŽMENT RECIKLIRANJA U PROCESU PROIZVODNJE GVOŽĐA I ČELIKA
RECYCLING MANAGEMENT IN IRON AND STEEL PRODUCTION
Aida Mahmutović, doc. dr. , Lejla Torlaković, Sedin Vilić, Fahir Vardo, Admir Jusufović, Eldin Merdić, Saudin Omić
Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale / Univerzitet Zenica Ključne riječi: „Zero-Waste“ - proizvodnja, metalurgija, recikliranje, ekologija. REZIME Čelik je i dalje vodeći materijal u svijetu. Industrija gvožđa i čelika bazira svoju proizvodnju na principima tzv. „Zero-Waste“ – proizvodnje. Danas se u procesima proizvodnje i prerade gvožđa i čelika ne ulažu samo napori u optimizaciju tehnologije, nego se intenzivno i kontinuirano radi i na poboljšanju svojstava čeličnih proizvoda s aspekta „uštede energije i materijala“. U ovom radu je napravljen osvrt na ova svojstva koje su u žiži interesovanja u savremenim zemljama, kao i na njihove pozitivne efekte posebno sa ekološkog aspekta koji je važan segment u domenu održivog razvoja jednog modernog društva. Key words: „Zero-Waste“- production, metallurgy, recycling, ecology. ABSTRACT Steel is still the leading material in the world. Iron and steel industry bases its production on the principles of the so-called „Zero-Waste“ - production. Today, efforts are invested not only in processes of iron and steel production and processing in order to optimize technology, but there are intense and continual works to improve the properties of steel products from the point of „saving energy and materials“. This paper makes reference to these qualities, which are in the focus of modern countries, as well as their positive effects, especially given that environmental aspect is an important element in the domain of sustainable development of a modern society.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
JAPANSKI MODEL ODRŽIVOG RAZVOJA
JAPANESE MODEL OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Doc. dr Diana Ćubela Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Univerziteta u Zenici
[email protected] Ključne riječi: čista proizvodnja, recikliranje, održivi razvoj, 3R politika, zero emisija
REZIME Nakon II svjetskog rata Japan je doživio intenzivan industrijski razvoj koji je uzeo svoj danak u izuzetnom visokom stepenu zagađenja zraka, vode i tla, što je za posljedicu imalo i veliki broj bolesti ljudi, životinja i biljaka čije su pojave dokazano uzrokovale visoke emisije štetnih materija u okoliš. Građanski pokreti krajem 50-tih godina prošlog vijeka su bili pokretačka snaga za promjenu odnosa japanskog društva prema industrijskom razvoju i njegovim štetnim posljedicama. Slijedećih dvadeset godina Japan se ubrzano industrijski razvija i istovremeno razvija i donosi zakonske akte o zaštiti okoliša. U 80-tim doživljava intenzivan industrijski razvoj nakon kojeg slijedi recesija i u tih slijedećih dvadeset godina Japan mijenja svoju politiku prema zaštiti okoliša postavljaući sebi za cilj da Japansko društvo od društva masovne proizvodnje, masovne potrošnje i masovnog odlaganja otpada pretvori u društvo okrenuto recikliranju tj. održivom razvoju. Kroz dva industrijska primjera recikliranja otpada industrije čelika će se predstaviti ideja vodilja Japanskog modela održivog razvoja. Keywords: clean production, recycling, sustainable development, 3R policies, zero emissions ABSTRACT After World War II, Japan has experienced intensive industrial development that has taken its toll in a very high level of pollution of air, water and soil, which is to result in a large number of diseases of humans, animals and plants which are proven to have caused the appearance of high emission of harmful substances in the environment. Citizens' movements in 50ths end of the last century were the driving power to change the relationship of Japanese society towards industrial development and its harmful consequences. The next twenty years Japan is rapidly evolving industry and also develops and delivers legal documents on environmental protection. The eighties experienced intensive industrial development, followed by a long recession. During this period Japan changes its policy towards environmental protection itself aims to Japanese society from the society of mass production, mass consumption and mass disposal of waste into recycling –oriented society that is facing sustainable development. Through two examples of industrial waste recycling steel industry will be present idea of Japanese models of sustainable development.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
KORIŠĆENJE SIROVOG DRVNOG OTPADA KAO GORIVA U TEHNOLOŠKE SVRHE
CRUDE WOODEN WASTE AS A TECHNOLOGICAL FUEL
Prof.dr.Veljko Đukić,dipl.inž. Panevropski Univerzitet APEIRON, Fakultet zdravstvenih nauka
Banja Luka Ključne riječi: sirovo drvo, drveni otpad, sagorijevanje REZIME Proizvodnja kvalitetne parene građe povezana je sa tehnološkim uslovima da se trupac mora odmah poslije sječe u šumi rezati na gateru, krajčiti i odložiti u parionik. Poslije parenja slijedi odležavanje, sortiranje i peletiranje. U takvim uslovima se u tehnološkom procesu javlja kao nusprodukt sirovi okorak, komadno drvo i sirova piljevina. Postavlja se pitanje šta sa njima ? U ovom radu je dat primjer jednog tehničko-tehnološko-ekološkog rješenja problema. Key words: crude wood, wooden waste, combustion ABSTRACT Production of quality steam treated wooden material requires that log must be machined immediately upon cutting in the woods, and put into steam chamber. Steam treatment follows sorting and stocking. Technological procedure provides wooden waste of different kind. What could be done with it? This paper describes one technical, technological and ecological solution.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem ”METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI”, Zenica, BiH, 27-28.april 2010
THE GAP ANALYSIS OF THE WOOD PROCESSING SECTOR IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
Ismar Alagić Ph.D., Assistant Professor
Municipality of Tešanj/University of Zenica, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering in Zenica,
Tešanj/Zenica, Bosnia and Herzegovina,
E-mail: [email protected] ; [email protected]; [email protected]
Key words: Gap analysis, wood processing sector, B&H. ABSTRACT This article is the overview of GAP Analysis of the sectors of wood processing and forestry in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The author conducted a special survey of wood processing and forestry sectors in BiH. This article outlines results of evaluation of Wood processing and forestry sectors in Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH), carried out between October 2008 and January 2009. The survey was commissioned by and for use of the Swiss Import Promotion Programme (SIPPO) which is financed by the State Secretariat of Economic Affairs (SECO) and is being carried out by OSEC for the period 2009-2011. This article provided a summary of the key factors related to the competitiveness of the wood processing sector in BiH for SIPPO programme as identification of gap analysis for that sector. The article is intended to provide a detailed model of production and export chains in BiH wood products industry. Gap analysis was conducted in order to determine points at which one or more interventions could help to significantly improve the competitiveness of the sector's small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The Gap analysis of the potential high impact proposal for points of interventions that have been identified to gain a more in-depth understanding of the market opportunities for an SIPPO programme that would offer these high impact services as core offerings. This article contained four sections:
a) A detailed model of production & export value chains in both sectors (forestry and wood processing)
b) Analysis the interaction options provided on the market by different stakeholders and organizations
c) A detailed information on the typical business services required by the producers and exporters within the value chain and
d) Proposal for Point of Interventions (POI) within pilot project. This GAP Analysis assesses the status of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SME) in BiH wood processing sector, within the model of production and export value chains in forestry and wood processing sectors. The focus of this report also highlights the proposal for Point of Interventions (POI) within the pilot project.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010.
RJEŠAVANJE OKOLINSKIH PROBLEMA U EKSPLOATACIJI I PRIPREMI STIJENSKIH MASA DIJABAZA NA POVRŠINSKIM
KOPOVIMA
POSSIBILITY CONSIDER ENVIROMENT PROBLEMS IN EXPLOATATION AND PREPARATION ROCK MASS OF DIABAZ ON
SURFACE EXPLOATATION
DENIS VEJZOVIĆ1, student NIHAD VEJZOVIĆ2, dipl.ing., student PDS-a
AIDA MAHMUTOVIĆ1, docent
1Univerzitet u Zenici, Fakultet za metalurgiju i materijale, Odsjek za nemetalne materijale 2Univerzitet u Zenici, Mašinski fakultet, Odsjek za inženjersku ekologiju
Ključne riječi: nemetalne mineralne sirovine, dijabaz, okolinski problemi, površinski kopovi. REZIME U radu je obrađena eksploatacija i prerada bazično-magmatske stijene dijabaza na površinskim kopovima Zeničko-dobojskog kantona. U procesu pripreme stijenske mase dijabaza, posebna pažnja se posvećuje kvalitetu prema definisanim standardima kao i mjerama zaštite ljudi i okoliša. Predstavljeni su štetni uticaji pri površinskoj eksploataciji i preradi stijenske mase dijabaza kao i mjere za spriječavanje i ublažavanje štetnog uticaja na ljude, mehanizaciju i okoliš. Key words: nonmetal mineral raws dust, diabaz, enviroment problems, surface exploatation. ABSTRACT In this paper exploatation and rafining basicmagmatic rock of diabaz on surface Zenica-doboj canton. In this proces of preparation rock mass of diabaz special atencion to quality of define standards like measuress of protection peoples health and enviroment are devoted. In this paper bad influence under surface exploatation and processing of rock mass of diabaz, like measures of protection and minimalising bad influence on peoples heath, enviroment and mechanisation are presented.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
UPRAVLJANJE GRAĐEVINSKIM OTPADOM U SKLADU SA EU STANDARDIMA
MANAGING THE BUILDING WASTE
ACCORDING TO EU STANDARDS
Nerman Rustempašić, mr.sci. dipl.ing. arhitekture Univerzitet u Sarajevu, Arhitektonski fakultet Sarajevo
Ključne riječi: građevinski otpad, zakonska regulativa, direktive, recikiranje, REZIME Bosna i Hercegovina je društvo u tranziciji i kao potencijalni kandidat za prijem u Europsku uniju, što podrazumjeva preuzimanje, usklađivanje i harmonizaciju sa evropskim normama i standardima iz svih oblasti pa tako i građevinarstva, kao velike i značajne grane privrede. Zadnju deceniju je u BiH veliki broj objekta rekonstruiran ili srušen da bi se na istoj lokaciji izgradili novi objekti što ima za posljedicu nastajanje velikih količina građevinskog otpada. Zbog neuređenosti zakonske regulative iz ove oblasti najveći dio građevinskog otpada završava na komunalnim deponijama ili divljim deponijama građevniskog otpada što negativno utičena okoliš i ekološki devastira širu lokaciju na kojoj se otpad odlaže. To naročito važi ako građevinski opad sadrži opasne materije poput ostataka azbestnih proizvoda, što zahtijeva posebno postupanje i odlaganje takve vrste otpada. U BiH je recikliranje građevinskog otpada neznatno dok u pojedinim europskim zemljama reciklira više od 80% građevnog otpada od rušenja objekata čime se smanjuje potreba za novom eksploatacijom sirovina iz prirode za proizvodnju građevinskih materijala i ujedno se smanjuje količina otpada koji inače često završava na divljim deponijima. U radu će se prikazati način pravilnog upravljanja građevinskim otpadom koji se primjenjuje u Evropskoj uniji kao i mogućnosti primjene kod nas harmonizacijom zakonske regulative. Key words: Buildings waste, law regulation, directives, recycling, ABSTRACT Bosnia and Herzegovina is a country going through the transition process, and as a potential EU candidate it must do a lot in order to harmonize, adjust and adopt European norms and standards. During the last decade a large number of buildings in B&H were reconstructed or destroyed in order to change function or to allow new building rise. The consequence was a large amount of building waste. In the lack of precise laws, great number of unplanned, wild landfills started to emerge as a consequence. The environmental impact is enormous, especially if the waste consists of hazardous matter, such as asbestos, which implies careful handling. B&H¸ does not recycle this kind of material almost at all, in contrary to the practice of some developed countries which recycle more than 80% of their building waste. This attitude might reduce countries material resource exploitation and might reduce the building waste. This work will try to present possibilities of waste management according to EU standards, and the possibility of the law harmonization.
8 th Scientific/Research Symposium with International Participation „Metallic and Nonmetallic Inorganic Materials“ Zenica, B&H, 27.-28. April 2010
ENVIRONMENTAL LABELING OF PRODUCTS WITH ECO-LABELS TYPE I
Igor Budak, Janko Hodolič University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Technical Sciences
Novi Sad Serbia
Borut Kosec, Mirko Soković
University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Natural Sciences and Engineering Ljubljana Slovenia
Šefket Goletić
University of Zenica, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Zenica
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Keywords: Environmental labelling, Eco label, Type I, ISO 14024 ABSTRACT Environmental labelling is the issue in the current global framework for more than 20 years. Today environmental (eco) labelling represents one of the most important tools for environmental protection improvement. In this work, an attempt has been made to give review of national and regional environmental labelling programs, as well as the role of the world’s associations in the development of the eco-labelling. Our study basis on the fundamental principles of the standard ISO 14024: 2003, with representation of actual situation in this area.
VIII Naučno/stručni simpozij sa međunarodnim učešćem „METALNI I NEMETALNI MATERIJALI“ Zenica, BiH, 27-28. april 2010
ŠTETNI EFEKTI SAOBRAĆAJA NA ŽIVOTNU SREDINU
HARMFUL EFFECTS OF THE TRAFFIC ON THE ENVIRONMENT
Prof.dr.Veljko Đukić,dipl.inž.
Panevropski Univerzitet APEIRON, Fakultet zdravstvenih nauka Banja Luka
Ključne riječi: saobraćaj, životna sredina, održivi razvoj. REZIME Najveće ugrožavanje životne sredine od sredstava kopnenog saobraćaja izraženo je kroz zagađenje vazduha, stvaranje buke i zauzimanje zemljišta i vazdušnog prostora. Neusklađenost krupnih tehnoloških promjena, koje su unapredile uslove života velikog dijela čovječanstva, sa društvenim razvojem ozbiljno je narušila životnu sredinu, pri čemu je znatan udio i naglog razvoja saobraćaja.Negativni uticaji koje prouzrokuje saobraćaj okarakterisani su kao negativni eksterni efekti.Buka se može definisati kao neželjeni ili neprijatan zvuk koji neumjereno uznemirava naše svakodnevne aktivnosti.Izvori buke su raznovrsni (saobraćaj, loše urbano zoniranje, akcidenti, domaća buka, lokalna industrija, gradilišta, muzika..), a mnogi od njih su u vezi sa urbanim razvojem. Međunarodnim dokumentima o zaštiti vazduha od klimatskih promjena predviđa se smanjenje fosilnih u korist alternativnih goriva-biogoriva, prirodnog plina i vodonika već do 2020.godine.Upotrebom alternativnih goriva smanjila bi se količina CO2, glavnog stakleničkog plina koji utiče na klimatske promjene, i dovela je na neškodljivu humanu mjeru. Key words: traffic, human environment, sustainable development. ABSTRACT Means of transport create ecological problems in the different way and amounts, the consequences being larger or smaller. Negative influence that traffic causes has been characterized as negative external effects. There are number of accidents that included dangerous chemical substances during the transport. There's given classification of external effects in traffic in this paper, and suggestions of measure for decreasing of influences of these effects on environment. Noise pollution can be defined as unwanted or unpleasant sound that unreasonable intrudes into our daily activities. There is many sources of noise (traffic, irregular urbanization, accidents, domestic noise, local industry, building states, music..), the most of them are associated with urban development. The international documents of air protection from the climate changes predict decrease of fossil and increase of the alternative fuels, such as: biofuels, natural gas and hydrogen, yet to 2020. year.Using the alternative fuels will reduce the CO2 emision, the main gas who influences on climate change, and bring it to safe human measurement.
















































































































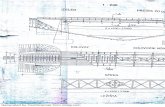







![Abstracts - COnnecting REpositoriesAgazzi, Evandro. The Conceptual Meaning of Boolean Logic [in Italian], in Evandro Agazzi and Nikla Vassallo, eds., George Boole: Philosophy, Logic,](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5eb819edb6be3717751b8cca/abstracts-connecting-repositories-agazzi-evandro-the-conceptual-meaning-of-boolean.jpg)









