Measles
-
Upload
tumalapalli-venkateswara-rao -
Category
Education
-
view
1.665 -
download
1
Transcript of Measles
Early History of MeaslesEarly History of Measles Reports of measles go back to at least Reports of measles go back to at least
700, however, the first scientific 700, however, the first scientific description of the disease and its description of the disease and its distinction from smallpox attributed to the distinction from smallpox attributed to the Muslim physician Ibn Razi(Rhazes) 860-Muslim physician Ibn Razi(Rhazes) 860-932 who published a book entitled 932 who published a book entitled "Smallpox and Measles" (in Arabic: "Smallpox and Measles" (in Arabic: Kitab fi Kitab fi al-jadari wa-al-hasbahal-jadari wa-al-hasbah). ).
Serious disease as PerSerious disease as Per WHO.WHO. It remains a leading It remains a leading
cause of death among cause of death among young children globally, young children globally, despite the availability despite the availability of a safe and effective of a safe and effective vaccine. An estimated vaccine. An estimated 197 000 people died 197 000 people died from measles in 2007, from measles in 2007, mostly children under mostly children under the age of five the age of five
Measles - ParmyxoviridaeMeasles - Parmyxoviridae MeaslesMeasles is an infection is an infection
of the respiratory system of the respiratory system caused by a virus, caused by a virus, specifically a specifically a Paramyxoviruses of the Paramyxoviruses of the genus genus MorbillivirusMorbillivirus Morbilliviruses, like other Morbilliviruses, like other paramyxoviruses, are paramyxoviruses, are enveloped, single-enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses. RNA viruses.
Measles VirusMeasles Virus The measles virus is The measles virus is
a spherical, a spherical, nonsegmented, nonsegmented, single-stranded RNA single-stranded RNA virus in the virus in the Morbil l ivirusMorbil l ivirus family, family, closely related to the closely related to the rinderpest and canine rinderpest and canine distemper viruses. It distemper viruses. It contains six contains six structural proteins, structural proteins, three that are three that are complexed to the complexed to the RNA and three that RNA and three that are associated with are associated with the viral membrane the viral membrane envelope.envelope.
Fusion ProteinFusion Protein The F (fusion) protein is The F (fusion) protein is
responsible for fusion of virus responsible for fusion of virus and host cell membranes, and host cell membranes, viral penetration and viral penetration and hemolysis. The H hemolysis. The H (hemagglutinin) protein is (hemagglutinin) protein is responsible for adsorption of responsible for adsorption of the virus to cells. the virus to cells.
There is only one serotype of There is only one serotype of Measles virus and no Measles virus and no subtypes have yet been subtypes have yet been recognizedrecognized
MeaslesMeasles More than 20 million people More than 20 million people
worldwide are affected by worldwide are affected by measles each year. Measles measles each year. Measles outbreaks are common in outbreaks are common in many areas, including many areas, including Europe. For many U.S. Europe. For many U.S. travellers and expatriates, travellers and expatriates, the risk for exposure to the risk for exposure to measles can be high, but the measles can be high, but the illness can be prevented by illness can be prevented by a measles-containing a measles-containing vaccine vaccine
Measles spread by Measles spread by RespiratoryRespiratory RouteRoute
Measles is spread through respiration (contact Measles is spread through respiration (contact with fluids from an infected person's nose and with fluids from an infected person's nose and mouth, either directly or through aerosol mouth, either directly or through aerosol transmission), and is highly contagious—90% of transmission), and is highly contagious—90% of people without immunity sharing a house with an people without immunity sharing a house with an infected person will catch it. The infection has an infected person will catch it. The infection has an average incubation period of 14 days (range 6-average incubation period of 14 days (range 6-19 days) and infectivity lasts from 2-4 days prior 19 days) and infectivity lasts from 2-4 days prior to 2-5 days following the onset of the rash. to 2-5 days following the onset of the rash.
Measles threat to Devloping Measles threat to Devloping WorldWorld
In developing In developing countries, measles countries, measles affects 30 million affects 30 million children a year and children a year and causes 1 million causes 1 million deaths. Measles deaths. Measles causes 15,000-causes 15,000-60,000 cases of 60,000 cases of blindness per year. blindness per year.
Global EpidemiologyGlobal Epidemiology Approximately 30 million measles cases are Approximately 30 million measles cases are
reported annually. Most reported cases are from reported annually. Most reported cases are from Africa. In 1998, the cases of measles per Africa. In 1998, the cases of measles per 100,000 total population reported to the World 100,000 total population reported to the World Health Organization was 1.6 in the Americas, Health Organization was 1.6 in the Americas, 8.2 in Europe, 11.1 in the Eastern Mediterranean 8.2 in Europe, 11.1 in the Eastern Mediterranean region, 4.2 in South East Asia, 5.0 in the region, 4.2 in South East Asia, 5.0 in the Western Pacific region, and 61.7 in Africa. Only Western Pacific region, and 61.7 in Africa. Only 187 confirmed cases were reported in the 187 confirmed cases were reported in the Western Hemisphere (mainly in Venezuela, Western Hemisphere (mainly in Venezuela, Mexico, and the United States) Mexico, and the United States)
Measles a Childhood InfectionMeasles a Childhood Infection
Age-specific attack Age-specific attack rates may be highest rates may be highest in susceptible infants in susceptible infants younger than 12 younger than 12 months, school-aged months, school-aged children, or young children, or young adults, depending on adults, depending on local immunization local immunization practices and practices and incidence of the incidence of the disease. disease.
Patients on Physical Patients on Physical examinationexamination
Patients tend to appear moderately ill and Patients tend to appear moderately ill and uncomfortable because of their viral prodromal uncomfortable because of their viral prodromal symptoms.symptoms.
The Koplik spots are 1-2 mm, blue-gray macules The Koplik spots are 1-2 mm, blue-gray macules on an eythematous base.on an eythematous base.
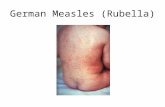
The measles rash is a Maculopapular The measles rash is a Maculopapular eythematous rash that involves the palms and eythematous rash that involves the palms and soles.soles.
Lesion density is greatest above the shoulders, Lesion density is greatest above the shoulders, where macular lesions may coalesce where macular lesions may coalesce
A rash is leading A rash is leading manifestationsmanifestations
Typically begins at the hairline Typically begins at the hairline and spreads caudally over the and spreads caudally over the next 3 days as the prodromal next 3 days as the prodromal symptoms resolve.symptoms resolve.
The rash lasts 4-6 days and The rash lasts 4-6 days and then fades from the head then fades from the head downward.downward.
Desquamation may be present Desquamation may be present but is generally not severe.but is generally not severe.
Complete recovery from the Complete recovery from the illness generally occurs within illness generally occurs within 7-10 days from the onset of 7-10 days from the onset of the rash the rash
Risk factors for infectionRisk factors for infection Children with Children with
immunodeficiency due to HIV immunodeficiency due to HIV or acquired immunodeficiency or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), leukemia, syndrome (AIDS), leukemia, alkylating agents, or alkylating agents, or corticosteroid therapy, corticosteroid therapy, regardless of immunization regardless of immunization statusstatus
Travel to areas where measles Travel to areas where measles is endemic or contact with is endemic or contact with travellers to endemic areastravellers to endemic areas
Infants who lose passive Infants who lose passive antibody prior to the age of antibody prior to the age of routine immunization routine immunization
Spread of VirusSpread of Virus The highly contagious The highly contagious
virus is spread by virus is spread by coughing and coughing and sneezing, close sneezing, close personal contact or personal contact or direct contact with direct contact with infected nasal or infected nasal or throat secretion throat secretion
Early Symptoms in Early Symptoms in MeaslesMeasles
The incubation period from exposure to The incubation period from exposure to onset of symptoms ranges from 8-12 onset of symptoms ranges from 8-12 days. The prodromal phase is marked by days. The prodromal phase is marked by malaise, fever, anorexia, malaise, fever, anorexia, and and conjunctivit is, cough, and conjunctivit is, cough, and coryzacoryza (the "3 Cs"). The entire course of (the "3 Cs"). The entire course of uncomplicated measles, from late uncomplicated measles, from late prodrome to resolution of fever and rash, prodrome to resolution of fever and rash, is 7-10 days. Cough may be the final is 7-10 days. Cough may be the final symptom to appear symptom to appear
Beginning of I l lness in Beginning of I l lness in MeaslesMeasles
Approximately 10 days after the initial exposure Approximately 10 days after the initial exposure to the virus, the classic viral prodrome occurs.to the virus, the classic viral prodrome occurs.
FeverFever Non-productive coughNon-productive cough CoryzaCoryza ConjunctivitisConjunctivitis Additional prodromal symptoms may include Additional prodromal symptoms may include
malaise, myalgias, photophobia, and periorbital malaise, myalgias, photophobia, and periorbital oedema.oedema.
Koplik Spots leading clue to Koplik Spots leading clue to MeaslesMeasles
With in 2-3 days, With in 2-3 days, the pathognomonic the pathognomonic Koplik spots Koplik spots typically arise on typically arise on the buccal, the buccal, gingival, and labial gingival, and labial mucosa mucosa
Risk factors for severe Risk factors for severe measlesmeasles
MalnutritionMalnutrition Underlying Underlying
immunodeficiencyimmunodeficiency PregnancyPregnancy Vitamin A deficiencyVitamin A deficiency
Mortali ty Rate in MeaslesMortali ty Rate in Measles The mortality rate associated The mortality rate associated
with uncomplicated measles with uncomplicated measles in immunocompetent, well in immunocompetent, well nourished children is low but nourished children is low but raises rapidly with raises rapidly with malnourishment malnourishment (marked in African children ), (marked in African children ), in immunocompromised, and in immunocompromised, and to lesser extent with age.to lesser extent with age.
Measles is highly Measles is highly contagiouscontagiousDiseaseDisease
Patients are contagious Patients are contagious from 1-2 days before from 1-2 days before onset of onset of symptoms. Healthy childrsymptoms. Healthy children are also contagious en are also contagious during the period from 3-5 during the period from 3-5 days before the days before the appearance of the rash to appearance of the rash to 4 days after the onset of 4 days after the onset of rash. On the other hand, rash. On the other hand, immunocompromised immunocompromised individuals can be individuals can be contagious during the contagious during the duration of the illness. duration of the illness.
Modified MeaslesModified Measles Modified measles occurs in children who have Modified measles occurs in children who have
received serum immunoglobulin after their received serum immunoglobulin after their exposure to measles. The measles symptom exposure to measles. The measles symptom complex may still occur, but the incubation complex may still occur, but the incubation period is as long as 21 days, with the same period is as long as 21 days, with the same symptoms as measles but milder. symptoms as measles but milder.
Atypical MeaslesAtypical Measles When they are exposed to the measles virus, a mild or When they are exposed to the measles virus, a mild or
nonexistent prodrome of fever, headache, abdominal nonexistent prodrome of fever, headache, abdominal pain, and myalgias precedes a rash that begins on the pain, and myalgias precedes a rash that begins on the hands and feet and spreads centrally.hands and feet and spreads centrally.
The rash is most prominent in the body creases and may The rash is most prominent in the body creases and may be macular, hemorrhagic vesicles, petechial, or urticarial.be macular, hemorrhagic vesicles, petechial, or urticarial.
Complications may include pneumonia, pleural effusion, Complications may include pneumonia, pleural effusion, hilar lymphadenopathy, Hepatosplenomegaly, hilar lymphadenopathy, Hepatosplenomegaly, hyperesthesia, or paresthesia.hyperesthesia, or paresthesia.
Atypical measles occurs in individuals who were Atypical measles occurs in individuals who were previously immunized with the ki l led measles previously immunized with the ki l led measles vaccine between 1963 and 1967 and who have vaccine between 1963 and 1967 and who have incomplete immunityincomplete immunity . .
Subacute sclerosing Subacute sclerosing panencephalit ispanencephalit is
SSPESSPE SSPESSPE is a neurodegenerative disease is a neurodegenerative disease
caused by persistent infection of the brain caused by persistent infection of the brain by an altered form of the measles virus. by an altered form of the measles virus. Neither the biology underlying the viral Neither the biology underlying the viral persistence nor the triggering mechanism persistence nor the triggering mechanism for viral reactivation is well understood. In for viral reactivation is well understood. In most cases, infected children remain most cases, infected children remain symptom-free for 6-15 years after acute symptom-free for 6-15 years after acute measles infection[ measles infection[
Subacute sclerosing Subacute sclerosing panencephalit ispanencephalit is
Subacute sclerosing panencephalit isSubacute sclerosing panencephalit is ((SSPESSPE) is a rare chronic, progressive ) is a rare chronic, progressive encephalitis that affects primarily children and encephalitis that affects primarily children and young adults, caused by a persistent infection of young adults, caused by a persistent infection of immune resistant measles virus (which can be a immune resistant measles virus (which can be a result of a mutation of the virus itself). 1 in result of a mutation of the virus itself). 1 in 100,000 people infected with measles develop 100,000 people infected with measles develop SSPE. SSPE is 'incurable' but the condition can SSPE. SSPE is 'incurable' but the condition can be managed by medication if treatment is started be managed by medication if treatment is started at an early stage. at an early stage.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Clinical Presentation of SSPEClinical Presentation of SSPE
Characterized by a history of primary Characterized by a history of primary measles infection usually before the age measles infection usually before the age of 2 years, followed by several of 2 years, followed by several asymptomatic years (6–15 on average), asymptomatic years (6–15 on average), and then gradual, progressive psycho and then gradual, progressive psycho neurological deterioration, consisting of neurological deterioration, consisting of personality change, seizures, myoclonus, personality change, seizures, myoclonus, ataxia, photosensitivity, ocular ataxia, photosensitivity, ocular abnormalities, spasticity, and coma. abnormalities, spasticity, and coma.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
The Progress of SSPEThe Progress of SSPE The initial symptoms of SSPE usually involve The initial symptoms of SSPE usually involve
regressive changes in intellect and personality. regressive changes in intellect and personality. Within several months, the psychological Within several months, the psychological symptoms are compounded by neurological symptoms are compounded by neurological ones, most often consisting of myoclonic jerks. A ones, most often consisting of myoclonic jerks. A relentless mental and motor deterioration then relentless mental and motor deterioration then ensues, culminating in extreme neurologic ensues, culminating in extreme neurologic dysfunction and death within several years of the dysfunction and death within several years of the onset of symptoms. Our patient's clinical course onset of symptoms. Our patient's clinical course reflected this typical natural history. reflected this typical natural history.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Diagnosis of MeaslesDiagnosis of Measles Most cases of Most cases of
Measles are Measles are diagnosed clinically, diagnosed clinically, usually in patient’s usually in patient’s home or in General home or in General practice practice
Direct Virological Direct Virological confirmation is difficult confirmation is difficult in most of the in most of the Devloping countreisDevloping countreis
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Diagnosis by MicroscopyDiagnosis by Microscopy Production of multinucleate Production of multinucleate
giant cells with inclusion giant cells with inclusion bodies is path gnomonic for bodies is path gnomonic for measles. During the measles. During the prodromal phase, such prodromal phase, such cells are detectable in the cells are detectable in the NPS (nasopharyngeal NPS (nasopharyngeal secretions). This is more secretions). This is more rapid and practical than rapid and practical than virus isolation virus isolation
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Diagnosis with Diagnosis with ImmunofluorescenceImmunofluorescence
Direct and indirect Direct and indirect immunofluorescence have immunofluorescence have been used extensively to been used extensively to demonstrate MV antigens in demonstrate MV antigens in cells from NPS specimens. cells from NPS specimens. This technique can also be This technique can also be applied to the urine as such applied to the urine as such cells may be present in the cells may be present in the urine 2 to 5 days after the urine 2 to 5 days after the appearance of the rash appearance of the rash
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Diagnosis by Viral IsolationDiagnosis by Viral Isolation Measles virus can be Measles virus can be
isolated form a variety of isolated form a variety of sources, e.g. throat or sources, e.g. throat or conjunctival washings, conjunctival washings, sputum, urinary sediment sputum, urinary sediment cells and lymphocytes. cells and lymphocytes. Primary human kidney Primary human kidney (HEK) cells are the best, (HEK) cells are the best, although primary monkey although primary monkey kidney can be used as kidney can be used as well. Continuous cell l ines well. Continuous cell l ines such as Vero cells can such as Vero cells can also be used although also be used although they are not as eff icient they are not as eff icient as primary cell l ines as primary cell l ines
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Diagnosis byDiagnosis by SerologySerology Diagnosis of measles Diagnosis of measles
infection can be made if the infection can be made if the antibody titres rise by 4 fold antibody titres rise by 4 fold between the acute and the between the acute and the convalescent phase or if convalescent phase or if measles-specific IgM is measles-specific IgM is found. The methods that found. The methods that can be used include HAI, can be used include HAI, CF, neutralization and CF, neutralization and ELISA tests. ELISA tests.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Diagnosis of SSPEDiagnosis of SSPE The presence of measles The presence of measles
specific antibodies in the specific antibodies in the CSF is the most reliable CSF is the most reliable means of laboratory means of laboratory diagnosis of SSPE. diagnosis of SSPE. Demonstration of MV-Demonstration of MV-specific antibodies in the specific antibodies in the CSF may be sufficient CSF may be sufficient with, if necessary, with, if necessary, demonstration of MV-demonstration of MV-specific restricted specific restricted heterogeneity by heterogeneity by isoelectric focusing isoelectric focusing
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Other Diseases associated Other Diseases associated with Measleswith Measles
The virus has been The virus has been l iked with Mult iple l iked with Mult iple sclerosis, Paget’s sclerosis, Paget’s disease of bone and disease of bone and Crohn’s diseaseCrohn’s disease
In all the cases tubular In all the cases tubular structures resembling measles structures resembling measles nucelocapsids have been nucelocapsids have been seen by thin section electron seen by thin section electron microscopy and microscopy and immunofluorescence methods immunofluorescence methods are used for demonostration of are used for demonostration of Measles antigens in Biopsy Measles antigens in Biopsy material.material.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Epidemiological TrendsEpidemiological Trends Measles epidemics Measles epidemics
occur every 2 year in occur every 2 year in developed countreis developed countreis in the absence of in the absence of widespread use of widespread use of vaccinevaccine
Poverty and Poverty and overcrowding overcrowding increases epidemics increases epidemics
Tropics and MeaslesTropics and Measles In tropical areas In tropical areas
particular in Africa particular in Africa children under 1 year children under 1 year of age suffer more of age suffer more attacks, and mortality attacks, and mortality rate increasesrate increases
Malnutrition is a major Malnutrition is a major contributing factor.contributing factor.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
TreatmentTreatment Severe complications from measles can be Severe complications from measles can be
avoided though supportive care that ensures avoided though supportive care that ensures good nutrition, adequate fluid intake and good nutrition, adequate fluid intake and treatment of dehydration with WHO-treatment of dehydration with WHO-recommended oral rehydration solution (to recommended oral rehydration solution (to replace fluids and other essential elements lost replace fluids and other essential elements lost from diarrhoea or vomiting). Antibiotics should from diarrhoea or vomiting). Antibiotics should be prescribed to treat eye and ear infections, be prescribed to treat eye and ear infections, and pneumonia. and pneumonia.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Treatment options in Treatment options in Developing CountreisDeveloping Countreis
All children in developing All children in developing countries diagnosed with countries diagnosed with measles should receive measles should receive two doses of vitamin A two doses of vitamin A supplements, given 24 supplements, given 24 hours apart. This can hours apart. This can help prevent eye damage help prevent eye damage and blindness. and blindness. Vitamin AVitamin A supplements have been supplements have been shown to reduce the shown to reduce the number of deaths from number of deaths from measles bymeasles by 50%.50%.
VACCINATIONVACCINATION The Vaccines are The Vaccines are
Live attenuated Live attenuated containing containing Edmonston B or Edmonston B or Schwartz strains Schwartz strains which will give which will give seroconversion seroconversion rate of 90%.rate of 90%.
The immunity The immunity produce may be life produce may be life long.long.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Measles Vaccine is cheap Measles Vaccine is cheap and Effectiveand Effective
The measles vaccine The measles vaccine (in use for 40 years) (in use for 40 years) is safe, effective and is safe, effective and inexpensive. It costs inexpensive. It costs less than one US less than one US dollar to immunize a dollar to immunize a child against measles.child against measles.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Measles vaccine is givenMeasles vaccine is given asas MMRMMR VaccineVaccine
The measles vaccine is The measles vaccine is often incorporated with often incorporated with rubella and/or mumps rubella and/or mumps vaccines in countries vaccines in countries where these illnesses are where these illnesses are problems. It is equally problems. It is equally effective in the single or effective in the single or combined form combined form
The combination The combination proved to be effective proved to be effective and safeand safe
Two doses of Measles Two doses of Measles VaccineVaccine
Continued progress Continued progress depends on ensuring depends on ensuring that all children that all children receive two doses of receive two doses of measles vaccine measles vaccine including one dose by including one dose by their first birthday, their first birthday, strengthening disease strengthening disease surveillance systems, surveillance systems, and providing and providing effective treatment for effective treatment for measles. measles.
Changing trends for a Changing trends for a Booster DoseBooster Dose
In 2007, about 82% of the In 2007, about 82% of the world's chi ldren received world's chi ldren received one dose of measles one dose of measles vaccine by their f irst vaccine by their f irst birthday through routine birthday through routine health services, up from health services, up from 72% in 2000. (Two doses 72% in 2000. (Two doses of the vaccine are of the vaccine are recommended to ensure recommended to ensure immunity, immunity, as about as about 15% of vaccinated 15% of vaccinated children fail to children fail to develop immunity develop immunity from the f irst dose.) from the f irst dose.)
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
AutismAutism andand VaccinationVaccination In UK vaccine uptake In UK vaccine uptake
has fallen recently has fallen recently due to fear over its due to fear over its safety, particularly as safety, particularly as cause of Autism.cause of Autism.
These fears These fears have now been have now been confirmed as confirmed as UnsubstantiatedUnsubstantiated..
CDC disproves Autism TheoryCDC disproves Autism Theory The official perspective of The official perspective of
the CDC is that there is the CDC is that there is no proven connection no proven connection between live-virus between live-virus vaccines and autism.vaccines and autism.
Neither the CDC nor Neither the CDC nor proponents of the vaccine proponents of the vaccine theories think that parents theories think that parents should avoid vaccines. should avoid vaccines. Clearly, vaccines have Clearly, vaccines have saved untold lives, and saved untold lives, and will continue to do so. will continue to do so.
WHOWHO andand UNICEFUNICEF are are collaboratingcollaborating
Strong routine immunization:Strong routine immunization: for children by their for children by their first birthday. first birthday.
A 'second opportunity' for measles A 'second opportunity' for measles immunizationimmunization through mass vaccination campaigns, to through mass vaccination campaigns, to ensure that all children receive at least one dose. ensure that all children receive at least one dose.
Effective surveil lanceEffective surveil lance in all countries to quickly in all countries to quickly recognize and respond to measles outbreaks. recognize and respond to measles outbreaks.
Better treatment of measlesBetter treatment of measles cases, to include cases, to include vitamin A supplements, antibiotics if needed, and vitamin A supplements, antibiotics if needed, and supportive care that prevents complications. supportive care that prevents complications.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Global Init iativesGlobal Init iatives The Measles Initiative - a collaborative The Measles Initiative - a collaborative
effort of effort of WHO, UNICEFWHO, UNICEF , the American , the American Red CrossRed Cross , the United States , the United States Centres Centres for Disease Control and Prevention,for Disease Control and Prevention, and the United Nations Foundation - and and the United Nations Foundation - and other public and private partners play key other public and private partners play key roles in advancing the global measles roles in advancing the global measles strategy strategy
Measles mortali ty reduction: a Measles mortali ty reduction: a successful init iat ivesuccessful init iat ive
Measles deaths worldwide fell by 74% between Measles deaths worldwide fell by 74% between 2000 and 2007, from an estimated 750 000 to 2000 and 2007, from an estimated 750 000 to 197 000. In addition, the Eastern Mediterranean 197 000. In addition, the Eastern Mediterranean region has cut measles deaths by a remarkable region has cut measles deaths by a remarkable 90% — from an estimated 96 000 to 10 000 — 90% — from an estimated 96 000 to 10 000 — during the same period, thus achieving the during the same period, thus achieving the United Nations goal to reduce measles deaths United Nations goal to reduce measles deaths by 90% by 2010, three years early. by 90% by 2010, three years early.
Doctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning seriesDoctortvrao’s ‘e’ learning series
Vaccination for Measles Vaccination for Measles continues to be a Top Prioritycontinues to be a Top Priority
Created for Medical Created for Medical and Paramedical and Paramedical
Students in Developing Students in Developing worldworld
Dr.T.V.Rao MDDr.T.V.Rao MDEmailEmail
[email protected]@gmail.com