Math 2 - Regular Segment 2
-
Upload
acuomo-yokel1 -
Category
Documents
-
view
74 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Math 2 - Regular Segment 2

Math 2 - AdvancedSegment 2
Mrs. Cuomo-YokelMath 2 Instructor
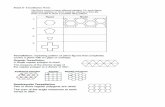
Below is the pace chart for Segment 1 success. Each week's assignments are due by Friday at 11:59pm.If all assignments are not turned in by the Sunday after the due date, you will be considered behind pace.
Activation Date of August 19, 2014
DUE DATE WEEK8/22/14 1
05.01 Scale Drawings
8/29/14 05.02 Angles and Triangles 2
05.03 Mid-Module Check
9/5/14 05.04 Circles 3
05.05 3-D Figures and Cross SectionsEnd Grace Period
9/12/14 05.10 Module Five Practice Test 405.11 Discussion-Based Assessment
9/19/14 05.12 Module Five Test 5
06.00 Module Six Checklist and Pretest
9/26/14 06.01 Understanding Probability 6
06.02 Approximating Probability
10/3/14 06.03 Mid-Module Check 7
06.04 Probability Models
10/10/14 06.05 Data Observation 8
06.10 Module Six Practice Test
10/17/14 06.11 Discussion-Based Assessment 9
06.12 Module Six Test
10/24/14 07.00 Module Seven Checklist and Pretest 10
ASSIGNMENTS (print out and cross off assignments as you complete them)
05.00 Module Five Checklist and Pretest

07.01 Representing Sample Spaces10/31/14 07.02 Understanding Compound Events 11
07.03 Probability Simulations
11/7/14 07.08 Module Seven Practice Test 1207.09 Discussion-Based Assessment07.10 Module Seven Test
11/14/14 08.00 Module Eight Checklist and Pretest 1308.01 Samples and Inferences
11/21/14 08.02 Statistical Variability and Comparing Populations 1408.03 Applications of Statistics
11/28/14 08.08 Module Eight Practice Test 1508.09 Discussion-Based Assessment08.10 Module Eight Test
12/5/14 08.12 Segment Two Practice Test 1608.13 Segment Two Exam
COMPLETION
Leraning Goals:
Module 5:
Module 6:
It is understood that students may choose not to submit during OCPS Thanksgiving, Winter, and Spring Breaks, which may change their completion date according to this
pace chart.
Students will be able to use ratios, compute lengths and areas, and solve problems involving scale drawings, identify and recognize types of angles, solve algebraic equations to determine unknown angles, use formulas for circumference and area, find the surface area and volume of two and three dimensional objects. To identify translations, corresponding sides and angles, center of rotation, direction and degree of rotation, and line of reflection , describe the effects of dilations, translations, and reflections on 2-D figures and whether two figures are similar and identify angles created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal and identify corresponding angles.
Students will be able to understand how to describe the likelihood of an event occurring, predict the approximate relative frequency, given the probability, use modeling to determine the probability of an event, observe frequencies, apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths, to real-world scenarios, and right triangles in two – and three – dimensional figures, and fixed points on a coordinate plane, and can describe and apply formulas for calculating volume of cones, cylinders, and spheres.

Module 7:
Module 8:
Students will be able to use and create organized lists, tables, and tree diagrams to identify the outcomes in a sample space, identify the probability of a compound event, design and use a simulation to generate data for compound events, define a function, read input and outputs, determine whether a relation is a function, and compare properties of functions represented algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables of verbal descriptions. In addition to describing a linear function and comparing characteristics of linear and non-linear functions.
Students will be able to understand how to recognize valid inferences from a random sample, compare and contrast estimates and predictions, measure the difference between the centers, draw informal comparative inferences about two populations, interpret and construct scatter plots, lines of best fit, interpret lines, and construct frequency tables, and draw conclusions and make predictions about dat

angles.