Mammalian Heart(2)
-
Upload
nickmirad2 -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Mammalian Heart(2)
-
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
1/7
Chapter 9
The Mamalian
Heart
-
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
2/7
Structure
Shape: Cone (apex pointed left)
Size: Fist
Mass: 300-500g
Location: Thoracic cavity (left) *except Dextrocardia
Enveloped in pericardium
Muscle: Myocardium (Cardiac muscle) joined by intercalated discs
for rapid nerve Impulse transmission. Mamalian heart Notes.doc
MyogenicSelf-excitable (Contract and relax naturally
without nerve stimulation)
http://c/Documents%20and%20Settings/kfsharon/My%20Documents/Personal/CV/KBU%20College/Mamalian%20heart%20Notes.dochttp://c/Documents%20and%20Settings/kfsharon/My%20Documents/Personal/CV/KBU%20College/Mamalian%20heart%20Notes.dochttp://beakstreetblog.com/2011/09/glassworks-map-of-the-human-heart/ -
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
3/7
Structure
Right atrium
Left atrium
Right ventricle
Left
ventricle
Atria wall Ventricle wall Reason
Thinner Thicker Ventricle pumps blood out of heart to lungs
and whole body.
Atria pumps to ventricles.
Right ventricle
Thinner
Left
ventricle
Thicker
Left ventricle- pumps to whole body
Right ventriclepumps to lungs only
Chambers:
2 atrium - receives blood from vein
2 ventricles - pumps blood out of the
heart into arteries
Septum
-
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
4/7
Structure Valves:
Atrio-ventricular valve-i) Tricuspid
ii) Bicuspid
(Mitral)
Semilunar valves- i) at Aorta entrance(Aortic valve)
ii) at Pulmonary
artery entrance
(Pulmonary valve)
Function: One direction flow from..to,
prevent backflow
Vessels:
Vena Cava
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary veinAorta
Carotid arteries:
- surface
- nutrients for myocardium
Aorta Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Semilunar
valve
Semilunar
valveTricuspid
valve
Bicuspid
valve
Vena Cava
(Superior)
Vena Cava
(Inferior)
Circulations:
i) Pulmonary circulation
ii) Systemic circulation
-
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
5/7
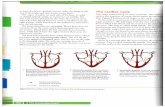
1: AV valve close 3: SL valve close
2: SL valve open 4: AV valve open
Cardiac Cycle
1) Atrial systole
- Atria wall contract
- Atrial pressure high, forces blood
through AV valves into ventricles
- SL valve closes dub
2) Ventricular systole
- After 0.1 second, last for 0.3seconds
- Ventricles contract
- Ventricular pressure muchhigher, forces blood through SL valves
out of the ventricles
-AV valves close lup
3) Ventricular diastole
- Atria and ventricles relax
- Heart pressure drops
- SL valves close- Blood from vena cava fills atrium
Sequence of events that makes one heart beat
http://www.karenmcarthur.com/samples/medIll/heart_fills.html -
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
6/7
Control of the Heart BeatPacemakers:
Specialized cardiac muscle cells that initiate
and coordinates rhythmic heart beat.
i) SAN (Sinoatrial Node)ii) AVN (atrioventricular Node)
iii) Purkyne Tissues (Bundle of Hiss,branches)
Heart beat rate: 70 times per minute
(average) =>pulse
Non-conductive fibres between AV
Purkyne tissues
-rapid transmission between septum
outwards upwards ventricle walls
- Ventricles contract bottom up
Heart sound
http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Military_OBGYN/Textbook/GynecologicExam/HeartExam/Heart3.jpg -
7/26/2019 Mammalian Heart(2)
7/7
Electrocardiogram
Electrodes10
Graph of electrical potential generated and
recorded against time
P: Atria contraction (depolarization)
Q, R, S: Ventricular contraction
Atria relaxation (repolarization)
T: Ventricular relaxation
Electrocardiograph
http://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/En/HowTheBodyWorks/IntroductiontotheHeart/TheHeartbeat/Pages/ElectrocardiogramECG.aspx
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/animate/flash-electrical.swf
http://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-lesson.aspx?coursecaseorder=6&courseid=301
http://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-lesson.aspx?coursecaseorder=6&courseid=301http://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-lesson.aspx?coursecaseorder=6&courseid=301http://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-lesson.aspx?coursecaseorder=6&courseid=301http://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-lesson.aspx?coursecaseorder=6&courseid=301http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-2oQ1lmN-n9A/T6fujYeq4LI/AAAAAAAAApc/XI35K4E0BXs/s1600/ECG_Placement_EMSWorld.tiffhttp://www.karenmcarthur.com/samples/EKG_cbt/index.html