Macromolecules. Organic Chemistry Isomers S = Difference in covalent bonds G = Difference in...
-
Upload
ethan-burke -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of Macromolecules. Organic Chemistry Isomers S = Difference in covalent bonds G = Difference in...

Macromolecules

Organic Chemistry

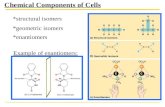
Isomers
S = Difference in covalent bonds
G = Difference in arrangement around double bond
E = Different in spatial arrangement

Pharmacological Enantiomers


Awakenings

Thalidomide

Chemical Groups

Functional Groups

Monomers and Polymers
Monomers to Polymers (build larger molecules) – Dehydration synthesis
Polymers to Monomers (break down molecules) - Hydrolysis

Monomers and Polymers

Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Nucleic Acids

Monosaccharides

Carbohydrates

Simple Sugars
Monosaccharaides – One subunit
Ex. Glucose, Fructose
Disaccharides – two subunits
Ex. Maltose, Sucrose

Complex Carbohydrates Polysaccharides (Storage)
Starch - Plants Glycogen - Animals

Complex Carbohydrates Polysaccharides (Structure)
Cellulose - Plants Chitin - Animals

Buyer’s Beware

Why can’t we eat grass?

Lipids
TriglyceridesGlycerol
Three fatty acids

Saturated vs. Unsaturated

Partially Hydrogenated Fats (Trans)

Phospholipids

Steroids
Cholesterol
Testosterone
Estrogen

Anabolic Steroids

Lipid Functions
Energy storage
Cushions internal organs
Insulation
Membrane Structure
Water storage
Toxic storage
Chemical Messengers

Proteins

Peptide Bonds

Primary Structure
Straight Chain
Peptide Bonds

Secondary Structure
Hydrogen Bonds
Alpha Helix, Beta Pleats, Random Coils

Tertiary Structure
All Bonds
Usually Globular

Quaternary Structure
Two or more subunits together
All bonds


Hemoglobin

Protein Functions
Structure
Storage
Transport
Coordination of body activities (Hormones)
Communication
Contractile (Movement)
Protection
Enzymes

Nucleic Acids
Made up of nucleotides
Pentose Sugar
Nitrogenous Base
Phosphate Group
Ex. DNA, RNA, ATP

Nucleic Acids Functions
Genetic Information
Energy Movement