M2 Electric Circuit - KMUTTwebstaff.kmutt.ac.th/~werapon.chi/M2_1/1_2013/M2_1_Class...1 M2 Electric...
Transcript of M2 Electric Circuit - KMUTTwebstaff.kmutt.ac.th/~werapon.chi/M2_1/1_2013/M2_1_Class...1 M2 Electric...
1
M2Electric Circuit
LECTURE 7
1
LECTURE 7
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
Outline
Introduction
Circuit elements
2
Circuit elements
Circuit terminologies
Basic laws
Time response
Responses: sinusoidal vs. non-sinusoidal excitations
Complex impedance and frequency response
Phasors and AC powers Three-phase systems
2
Electricity: How they work?3
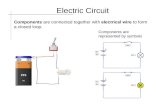
Electric Circuit4
• The battery, places a net positive charge at net positive charge at one terminal and a net negative charge on the other
• The free electrons (of negative charge) will drift toward the will drift toward the positive terminal
• The negative terminal is a “supply” of electrons
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
3
Circuit Elements
5Active Elements Passive Elements
• A dependent source is an active
Independentsources
Dependentsources
pelement in which the source quantity is controlled by another voltage or current.
• There are four different types: VCVS, CCVS, VCCS, CCCS
C.K. Alexander and M.N.O. Sadiku, Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, 5th edition, McGraw Hill
A Voltage Source6
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
4
A Current Source7
http://www.olympusmicro.com/primer/java/solarcell/
A Power Supply8
http://www.glentestco.com/product/product_pwrsupply01.htm
5
9
Resistors
http://www.macnn.com/articles/12/05/24/well.designed.adapter.protects.phone.from.damage.malfunction/http://www.resistorguide.com/metal-film-resistor/http://www.colourbox.com/image/the-printed-circuit-board-with-computer-chips-resistors-and-condensers-image-2350532
Inductors & Capacitors10
http://www.splung.com/content/sid/3/page/capacitorshttp://www.area51esg.com/inductors-coils-chokes.htmlA.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
6
Circuit Terminologies11
• A branch represents a single element such as a voltage source or a resistor
• A node is the point of connection between two or more branches
• A loop is a closed path (same beginning and end nodes) with no node passed more than once
• A mesh is a loop which does not contain any other loops within it
C.K. Alexander and M.N.O. Sadiku, Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, 5th edition, McGraw Hill
The Almighty Laws: Ohm’s Law12
• George Simon Ohm
• German (Erlangen, Cologne) (1789–1854)Ge a ( a ge , Co og e) ( 789 854)
• Physicist and Mathematician
• Professor of Physics,
• University of Cologne http://www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk/Mathematicians/Ohm.html
• v-i relationship of a resistor
Note: the negative current and voltage result in the graph extended in the 3rd quadrant
C.K. Alexander and M.N.O. Sadiku, Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, 5th edition, McGraw Hill
7
Kirchhoff’s Laws: KCL13
• Kirchhoff’s current law
• German (Königsberg
http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/k/kirchhoff.htm
• German (Königsberg, Berlin) (1824-87)
• Physicist• Professor of Physics,• University of
Heidelberg
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
Kirchhoff’s Laws: KVL14
Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL): the algebraic sum of thepotential rises and drops around a closed loop (or p p ppath) is zero.
These laws will be important bases of circuit theorems and analysis techniques
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
8
Time Response: Resistor15
There is no limitation on the rate
Purely resistive circuit
There is no limitation on the rate of change imposed on the resistor voltage and current
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
Time Response: R-L16
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
9
An Inductor and a Fluorescent Lamp17
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z55566ep0Hg
18
Breaking an Inductive Circuit
When the inductor current is interrupted the field begins to collapse causing a large induced voltage across the coil.
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
10
19
Breaking an Inductive Circuit
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=INbS-71KSz0
Charging a Capacitor20
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IvFVu7Jxa2I
11
Discharging a Capacitor21
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5D2cLj28Pc8
Time Response: RC22
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
12
Time Response: RC23
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
A Sinusoidal Waveform24
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
13
Periodic Functions25
Squarewave signal
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hallhttps://www.projectrhea.org/rhea/index.php/HW1.4_Ben_Laskowski_-_Periodic_and_Non-Periodic_Functions_ECE301Fall2008mboutin
Sawtooth signalTriangular signal
Full-wave signal
Fourier Series26
French (Auxerre, Grenoble, Paris) (1768–1830)Mathematician, Egyptologist, and AdministratorProfessor of Mathematics, École Polytechnique, y q
http://www2.math.umd.edu/~dlevy/photos2/photos/mathematical_lineage/jean-baptiste_fourier.html
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
14
27
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
Phasor28
A phasor is a rotating line whose projection on a vertical axis can be used torepresent sinusoidally varying quantitiesaxis can be used torepresent sinusoidally varying quantities
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
15
Phasor Illustration29
http://www.ceb.cam.ac.uk/pages/impedance-analysis-basics.html
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
Resistance and Sinusoidal Excitation30
• Response in time domain
• Phasor (frequency) domain
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
16
Inductance and Sinusoidal Excitation31
• Response in time domain
• Phasor domain
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
Capacitance and Sinusoidal Excitation32
• Response in time domain
• Phasor domain
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
17
Resonance33
Resonant condition
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
Resonance34
Practical implication: Capacitor and inductor voltages can be much larger than the supplied voltage
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
18
An Application of a Resonant Circuit35
• Induction heating
f = 15 kHz
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
One-Port vs. Two-Port Networks36
One-port networkTwo-port network
R.L. Boylestad, Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11th Ed, Prentice Hall
19
37
Power38
• Instantaneous power
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
20
Power39
• Inductor
• Observation1) Average power is zero2) The power alternately flows into and out of the inductor
(also known as reactive power: Q)
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
Power40
• Capacitor
• Observation (similar to the inductor)1) Average power is zero2) The power alternately flows into and out of the inductor
(also known as reactive power: Q)
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning
21
Complex Power41
iv θθIVIVS
• Power triangle
iv
)θ (θsin I V j )θ (θ cos I VS iviv
S = P + j Q
C.K. Alexander and M.N.O. Sadiku, Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, 5th edition, McGraw Hill
Why Rated VA?42
• Using only active power • Reactive power is in the picturepicture
A.H. Robbins, W.C. Miller, Circuit Analysis with Devices: Theory and Practice, 3rd edition, Cengage Learning