LUMBAR SPINE SACRUM COCCYX SI JOINTS SCOLIOSIS
description
Transcript of LUMBAR SPINE SACRUM COCCYX SI JOINTS SCOLIOSIS
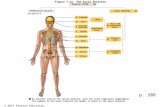
32• A body• E transverse process • D pedicle• O superior articular
facet, left• P pars
interarticularis, left• R inferior articular
facet, left• I apophyseal
(interfacetal) joint, left• V disk space
38• The AP and PA oblique projections are helpful in demonstrating spondylolysis. What is the definition of this condition?
• Spondylolysis is defined as the breaking down of the vertebra, usually at the pars interarticularis of the lumbar vertebrae. It is an acquired bony defect that may affect one or both sides of the lamina between the articular processes of the vertebrae.
39• Critique?• The positioning error
suggested is over-obliquity or excessive rotation of the patient.
40
• Zygapophyseal joints and pedicles are posterior to the vertebral body and indicate over-obliquity
41 • AP OBIQUE – CRITIQUE
• The positioning error suggested is insufficient obliquity or rotation of the patient
62
ankylosing spondylitis
• Ankylosing spondylitis is a rheumatoid arthritis involving the SI joints and spine,
• It is characterized radiographically by ossification of the outer portion of the annulus fibrosus and osteophyte formation between the vertebrae (bone spurring).
66
• What are the major differences between spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis?
• Spondylolisthesis is the forward displacement of one vertebra on another vertebra. It is a degenerative or congenital condition predominantly seen at the L5–S1 level. This condition almost exclusively involves the lumbar spine
67• The AP and PA oblique projections are helpful in demonstrating spondylolysis. What is the definition of this condition?
• Spondylolysis is defined as the breaking down of the vertebra, usually at the pars interarticularis of the lumbar vertebrae. It is an acquired bony defect that may affect one or both sides of the lamina between the articular processes of the vertebrae.
68• A body• E transverse process • D pedicle• O superior articular
facet, left• P pars
interarticularis, left• R inferior articular
facet, left• I apophyseal
(interfacetal) joint, left• V disk space
113 SPINE – POSITIONS FOR BEST SEEN?
• INTERVERTEBRAL FORAMEN
• ZYGOAPOPHYSEAL ARTICUALTIONS
• C.SP
• T.SP
• L.SP
• SI joints
133
• Scoliosis cassette
• 14x 36”
• Different speed screens
• Top to bottom
135 OTHER POSTIONSLECTURE ONLY
• What projections can be taken to determine the range of motion of the spine at the level of the spinal fusion?
• FLEXION / EXTENSION
• BENDING (LATERAL)
136
bending
•These projections are functional studies of the lumbar spine to determine the range of motion of the spine at the point of spinal fusion.• Following spinal fusion surgery, the orthopedic physician or neurosurgeon may order a study to evaluate the flexibility of the spine.•These projections will require the patient to assume different positions to determine how much flexibility of the spine has returned.•Early signs of scoliosis and herniated intervertebral disk or HNP can be evaluated with these projections.
140
What is HNP ?
• HNP refers to Herniated Nucleus Pulposus
• a situation in which the nucleus pulposus extrudes through an aspect of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disk.
141
laminectomy
• The term laminectomy is defined as the surgical removal of the bony arch of one or more vertebrae. Laminectomy is performed to remove a portion of the intervertebral disk to relieve compression of the spinal cord or one of the spinal nerves due to HNP. An aspect of the bony arch must be removed to provide access to the herniated disk.