LTBI in Alaska ALASKA...72 year-old Vietnam-born female seen in your clinic for routine primary...
Transcript of LTBI in Alaska ALASKA...72 year-old Vietnam-born female seen in your clinic for routine primary...
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 1
LTBI in Alaska
Lisa Chen MD & Neha Shah MD MPH
Bethel, Alaska, November 2018
ALASKA
Disclosures
None
The findings and conclusions in this presentation are those of the presenter and do not necessarily represent the views of CDC.
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 2
Objectives
At the end of this session, participants will be able to:
1. Identify at least 3 groups who are at risk for tuberculosis and should undergo screening to prevent tuberculosis disease and transmission
2. Discuss pros and cons for the tuberculosis skin tests (TSTs) versus interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) and how they may apply to different risk groups to improve application in clinical practice
3. List four recommended treatment options for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and describe the advantages versus disadvantages to each to inform clinical judgment in choosing the optimum regimen for patient care
Continuing Education Credits
To receive your continuing education hours, you must:
1. Sign-in2. Attend the entire training3. Complete the online evaluation by Thursday Nov. 15th
URL: bit.ly/BethelEvaluation
CME/CEU questions can be directed to [email protected]
Materials available online! URL: bit.ly/BethelTrainingMaterials
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 3
Why are we here?
We want to protect our
patients from developing TB in order for them to
lead happy, healthy lives
Key Points
Who should I test for LTBI?
Birth, travel or residence (>1 month) in a country 1 with an elevated TB rate
Immunosuppression
Close contact to someone with infectious TB disease during lifetime
Alaskan Native
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 4
Key Points
How should I test for LTBI?
IGRA (blood test) preferred for anyone aged 2 or older
Key Points
How should I treat LTBI?
12-dose Isoniazid (INH) +Rifapentine
§ 1 dose per week x 12 weeks
Rifampin (RIF) daily x 4 months
Isoniazid daily x 9 mo.
Safest HIV-infected individuals
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 5
Part 1: What is latent TB infection?
9
How do you explain LTBI?
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 6
What were your key words?
Spectrum of disease
12Dheda K, Lancet, 2016
A – ClearanceB – Latent infectionC – Pulmonary infectionD – Disseminated infection
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 7
Part 2: Why test?
14
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 8
Common patient beliefs about TB testing
I was vaccinated so I will be positive
I do not need to be tested, everyone is positive in my country
ASK: What have you heard about testing?
How do TB Cases Occur in California?
* France et al, Am J Epidemiol. 2015
16
13% RecentTransmission
7.5% Importation
CDC plausible source case method*
79.5% Activation of remote infection
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 9
LTBI Prevalence 2011-2015
M. Hadid, EID 2017
Spectrum of disease
18Dheda K, Lancet, 2016
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 10
10% TB Cases Die
More people die from TB in the world than any other infectious disease
(Global: 1.6 million TB deaths in 2017)
TB elimination
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 11
Part 3: Who to test?
21
What kind of workup would you do?
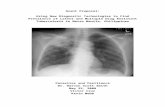
50 year-old Alaskan-born female who has been coughing and was treated with Z-pack for pneumonia without improvement.
72 year-old Filipino female immigrated 10 years ago seen in your clinic for routine primary care. Previous HbA1c = 6.0.
38 year‐old Native American male who is entering a substance treatment program for narcotics and heavy alcohol use.
1 year-old female who brings you a paper saying she needs TB testing for school entrance whose grandfather was just diagnosed with TB
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 12
What is targeted testing?
23
Birth, travel or residence (>1 month) in a country 1 with an elevated TB rate
Immunosuppression
Close contact to someone with infectious TB disease during lifetime
Alaskan Native
Risk Assessment
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 13
Why not test everyone?
Testing populations with low prevalence will result in many false-positive results
25
Prevalence of latent TB infection
Proportion of positive teststhat are false
U.S. born 2.8% 46%
Non-U.S. born 16% 12%
Part 4: When else should I think of TB?
28
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 14
Cases
45 year‐old homeless man with heavy alcohol use was identified as a close contact to a highly infectious TB case
Cough for last 1 week
Bilateral infiltrates
IGRA positive
What would you do?
Clinical history?
CXR
IGRA/TST
What would you do now?
What kind of workup would you do?
50 year-old Alaskan-born female who has been coughing and was treated with Z-pack for pneumonia without improvement.
72 year-old Filipino female immigrated 10 years ago seen in your clinic for routine primary care. Previous HbA1c = 6.0.
38 year‐old Native American male who is entering a substance treatment program for narcotics and heavy alcohol use.
1 year-old female who brings you a paper saying she needs TB testing for school entrance whose grandfather was just diagnosed with TB
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 15
Wait – one more time – what do you do if the TB test (TST or IGRA)
is positive?
Part 5: How to test?
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 16
What would you do in this situation?
72 year-old Vietnam-born female seen in your clinic for routine primary care. On prior diabetes screening was noted to have an HbA1c = 6.0 and was TST+
What would you use to test the following person?
72 year-old Vietnam-born female seen in your clinic for routine primary care. On prior diabetes screening was noted to have an HbA1c = 6.0 and was TST+
45 year-old Alaska-born Native American individual who is HIV positive with CD4 of 200 and has a negative TST
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 17
What would you use to test the following person?
72 year-old Vietnam-born female seen in your clinic for routine primary care. On prior diabetes screening was noted to have an HbA1c = 6.0 and was TST+
45 year-old Alaska-born Native American individual who is HIV positive with CD4 of 200 and has a negative TST
24 year-old health care worker who just moved here from Wyoming with no risk factors but has a TST + test for employment screening
Testing Options
TB skin test
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 18
Testing Options
Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs)➢Measure release of interferon-gamma
following stimulation by antigens unique to TB
Recommended for anyone 2 years of age or older
Testing Options
How to read: ➢ Measure induration (not erythema) at 48-72 hrs
➢ Record millimeters
Positive test:➢ ≥ 5mm for immunosuppressed including HIV,
recent contacts
➢ ≥ 10mm for all others with TB risk
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 19
Advantage of IGRA over TST
Not affected by BCG vaccination
Interpretation is more objective
No return visit needed for interpretation of test
Patients and providers may lack confidence in TST results
39
CDC, MMWR, 2010 | Pai, Clin Micro Rev, 2014
What if I am not confident the test results are correct?
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 20
Repeat Testing
Individual at high risk where missing LTBI has serious consequences
If initial test is negative, REPEAT
Person is considered infected if either test is positive.
Repeat Testing
Unlikely to be infected but testing required.
A second test if the initial is positive ➢Person is considered infected if both tests are positive.
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 21
What would you use to test the following person?
72 year-old Vietnam-born female seen in your clinic for routine primary care. On prior diabetes screening was noted to have an HbA1c = 6.0 and was TST+
45 year-old Alaska-born Native American individual who is HIV positive with CD4 of 200 and has a negative TST
24 year-old health care worker who just moved here from Wyoming with no risk factors but has a TST + test for employment screening
TSTs and IGRAs
19% of all confirmed TB cases have a negative skin test
39% of HIV-positive TB cases are TST negative
Negative IGRA or TST does NOT rule out TB!!!
• CDC, National TB Surveillance System, 2000–2011
• Auld, BMC Infectious Disease, 2013
• Sester, Eur Respir J, 2011
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 22
Summary
IGRA (blood test) preferred for anyone aged 2 years or older
Part 6: How to treat?
46
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 23
Treatment Regimens for Latent TB Infection
Medication(s) Frequency Duration Doses
Rifapentine (RPT) + INH Weekly 3 months 12
Rifampin Daily 4 months 120
Isonizaid (INH) Daily 6–9 months 180 - 270
47
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 24
INH-RPT INH
Administration Directly-observed therapy Self-administered therapy
Frequency/duration 12 weekly doses 9 months daily
Effectiveness 1.9 per 1,000 4.3 per 1,000
Completion rate 82.1% 69.0%
Hepatotoxicity 0.4% 2.7%
INH-RPT by Self-Administered Therapy
Self-Administered
Self-Administered with reminder texts
DOT
Completion rate 77.9% 76.7% 85.4%
Hepatotoxicity 0.9% 1.5% 0.3%
B. Belnap 2017
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 25
Mensies et al, 2018
Rifampin INH
Duration 4 months 9 months daily
Effectiveness 0.05 per 100 0.05 per 100
Completion rate 78.8% 63.2%
Hepatotoxicity 0.3% 1.5%
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 26
Rifampin INH
Duration 4 months 9 months daily
Effectiveness 0 cases of TB 1 case of TB
Completion rate 86.5% 77.1%
Serious Adverse Event
0 0
Isoniazid (INH)
When taken properly, very effective
Completion rates of 50% or less
Hepatotoxicity: Incidence of hepatitis estimated at 1 per 1,000 ➢ Also rash and neuropathies
Can be given to individuals on ARVs
• Nolan, JAMA, 1999
• Smieja, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2000
• Menzies, Ann Int Med, 2008
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 27
LTBI Treatment : INH – Why 9 months?
0 6 12 18 24
Months of Treatment
Cases per
100
5
4
3
2
1
0
Observed values
Calculated curve
Calculated values
Comstock Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 1999;10:847
• 9 months appears optimal
• 6 months less efficacious
• No significant gains if rx
extended to 12 months
Maximize medical benefits
Less hepatotoxicity & better completion
or vs.
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 28
Summary
Medication(s) Frequency Duration Doses
Rifapentine (RPT) + INH Weekly 3 months 12
Rifampin Daily 4 months 120
Isonizaid (INH) Daily 6–9 months 180 - 270
57
Part 6: Case Management
58
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 29
Commonly asked questions from patients
Can I infect my family?
Will I be able to work?
Will I die of this disease?
Will my community shun me?
Why should I bother with treatment if I feel fine?
Case Management
Monthly patient checks
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 30
Date: Dose/Month:
__/__/__0
Baseline
__/__/__1
__/__/__2
__/__/__3
__/__/__4
__/__/__5
__/__/__6
__/__/__7
__/__/__8
__/__/__9
__/__/__10
__/__/__11
__/__/__12
No adverse reaction ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Loss of appetite ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Nausea or vomiting ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Yellow eyes or skin ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Diarrhea ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Rash/hives ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Fever or chills ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Sore muscles or joints ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Numbness or tingling ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Fatigue ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Dizziness/fainting ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Abdominal pain ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
(Other)-________________
☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Treatment stopped or held (complete AE report on last page) ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 31
Summary
Key Points: Who to test?
Use a risk based approach to testing
Patients should be evaluated for TB risk factors regardless of age
64
Birth, travel or residence (>1 month) in a country 1 with an elevated TB rate
Immunosuppression
Close contact to someone with infectious TB disease during lifetime
Alaskan Native
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 32
Key Points: How to Test?
IGRA preferred for everyone over the age of 2 years
Positive test does not rule out active TB disease
How should I test for LTBI?
IGRA (blood test) preferred for anyone 2 years of age or older
Key Points: What to treat with?
Short course regimens have highercompletion rates and are lesshepatotoxic
Treatment of LTBI is key to TB Elimination
How should I treat LTBI?
12-dose Isoniazid (INH) +Rifapentine
§ 1 dose per week x 12 weeks
Rifampin (RIF) daily x 4 months
Isoniazid daily x 9 mo.
Safest HIV-infected individuals
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Basics
Lisa Chen, MDNeha Shah, MD, MPH
LTBI in Alaska: What You Need to KnowNovember 8, 2018 33
Resources
tbfreecalifornia.org
currytbcenter.ucsf.edu
The findings and conclusions in this presentation are those of the presenter and do not necessarily represent the views of CDC.
ALASKA








































![Product Information Report: Rifapentine · rifapentine/INH as an effective alternative regimen for the treatment of LTBI in patients’ ≥12 years old in the US [36]. In November](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5d251abd88c99326698c61a6/product-information-report-rifapentine-rifapentineinh-as-an-effective-alternative.jpg)