Liver ANATOMY,LFT,LIVER IMAGING
-
Upload
nri-medical-college -
Category
Education
-
view
823 -
download
5
Transcript of Liver ANATOMY,LFT,LIVER IMAGING

LIVER ANATOMY,FUNCTION TESTS ,IMAGING
G.NARENDRA MS general surgery NRI HOSPITAL GUNTUR

2
embryology• Liver develops from endodermal bud from
ventral aspect of gut• Between junction of foregut and midgut• Bud grows into ventral mesogastrium and
passes through it into septum transversum• Enlarges and divides into large cranial part-
pars hepatica• Small caudal part- pars cystica

3
• Pars hepatica divides into right & left parts• Pars hepatica enlarges & extend into septum
transversum• Umbilical & vitelline veins which lie in septum
transversum break up to form sinusoids of liver• Hepatic bud endoderm- parenchyma of liver ,
bile capillaries• Mesoderm of septum transversum-capsule of
liver

4

5
ANATOMY
• Largest organ in body • 1500 gm• In right upper abdomen ,beneath
diaphragm ,protected by rib cartilage• surrounded by a fibrous sheath known as
Glisson’s capsule.

6
• Liver is held in place by several ligaments• ROUND LIGAMENT – a remnant of obliterated umbilical vein – enters the left liver hilum at the front edge of the
falciform ligament• FALCIFORM LIGAMENT – separates the left lateral and left medial segments along
the umbilical Fissure – anchors the liver to the anterior abdominal wall
• LEFT & RIGHT TRIANGULAR LIGAMENTS– ,secure two sides of liver to diapragm
• CORONARY LIGAMENTS .– Extensions of triangular ligament anteriorly on liver

7
• The right coronary ligament also extends from the right undersurface of the liver to the peritoneum overlying the right kidney, thereby anchoring the liver to the right retroperitoneum.
• Surgical importance -These ligaments (round, falciform, triangular,and coronary) can be divided in a bloodless plane to fully mobilize the liver to facilitate hepatic resection.

8
diaphragm
Triangular ligament
Lt triangular ligament
Round ligament
Falciform ligament

9
• just to the left of the gallbladder fossa, the liver attaches via hepatoduodenal and the gastrohepatic ligaments .
• The HEPATODODENAL LIGAMENT – is known as the porta hepatis – contains the common bile duct, the hepatic artery, and the portal
vein.,nerves & lymphatics– From the right side and deep (dorsal) to the porta hepatis is the
foramen of Winslow, also known as the epiploic foramen.
– anatomical relationship of thesestructures is for the bile duct to be within the free edge, the hepatic artery to be above and medial, and the portal vein to lie posteriorly.
– This passage connects directly to the lesser sac and allows complete vascular inflow control to the liver when the hepatoduodenal ligament is clamped using the Pringle maneuver.

10
GASTROHEPATIC LIGAMENT
HEPATODUODENAL LIGAMENT
FORAMEN OF WINSLOW

11
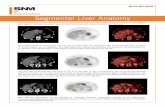
SEGMENTAL ANATOMY
• Liver is grossly seperated into right & left lobes by cantlie line
• REX-CANTLIE’S line – plane from gall bladder fossa anteriorly to IVC posteriorly passing through middle hepatic vein
• Also known as scissura or portal fissure

12
Couinaud functional classification• Based on hepatic vein & portal vein
liver
Cantlie line
Caudate lobe Left lobe
II,III,IV
Right lobe
V,VI,VII,VIII

13
• The caudate lobe lies to the left and anterior of the IVC • contains 3 subsegments:
– the Spiegel lobe,– the paracaval portion,– the caudate process
• Blood supply- independently from left & right portal veins,hepatic arteries
• Drainage- independendtly into IVC • Biliary drainage into both right & left hepatic duct at
their confluence

14
• Left hepatic vein divides left lobe into medial & lateral sectors
• Left lateral- superior-II inferior- III• Left medial- superior -IV a inferior- IV b• Supplied by-left hepatic artery ,left portal vein• Drainage-left hepatic duct,left hepatic vein
(II,III), middle hepatic vein (IV)

15
• Right hepatic vein divides right lobe into anterior & posterior sectors
• Right anterior -inferior- V• - superior- VIII• Right posterior-inferior-VI• - superior-VII• Supplied by right hepatic artery,right portal
vein,• Drainage- right hepatic duct,right hepatic
vein(V,VI,VII,VIII), middle hepatic vein(V,VIII)

16
II
III
IVb
IV aVIII
VVI
VII

17
II
III
I
IV b
v
VI
VII

18
PORTAL VEIN
HEPATIC VEIN

19
AT HEPATIC VEIN LEVEL
IIIVa
VIII
VII
LHV
MHV
RHV

20
AT PORTAL BIFURCATION
IIIIV b
V
VI

21
BELOW PORTAL BIFURCATION
IIIIVB
V
VI

22
BLOOD SUPPLY
• dual blood supply consisting of the hepatic artery and the portal vein
• Portal vein- 75 %• Hepatic artery -25 %

23
Celiac trunk
Left gastric
splenic
Common hepatic
gastroduodenal
hepatic

24
Replaced RHA from SMA (10-15%)

25
Replaced LHA from left gastric (3-10%)

26
Portal vein• formed by the confluence of the splenic vein
and the superior mesenteric vein.• Traverses through porta hepatis • Then left portal vein branches from main
vein ,consists of transverse portion ,followed by 90 degree turn at umbilical fissure base,to become umbilical portion
• Supplies II,III,IV and dominant supply to I lobe

27
• Right portal vein branches near to liver parenchyma,
• Supplies V,VI,VII,VIII lobes• Other branches- coronary/left gastric vein• -superior pancreaticoduodenal
vein

28
SPLENIC
CORONARY
IMV
SMV

29
TRANSVERSE PORTION
UMBILICAL PORTION
I
II
III
IV a
IV b
V
VIIIVIII
VI
VII

30
• The portal vein drains the splanchnic blood from the stomach,pancreas, spleen, small intestine, and majority of the colon to the liver before returning to the systemic circulation.
• The portal vein pressure in normal individual is 3 to 5 mmHg.
• The portal vein is valveless, • in the setting of portal hypertension, the pressure can
be quite high (20 to 30 mmHg). • This results in decompression of the systemic circulation
through portocaval anastomoses, most commonly via the coronary (left gastric) vein, which produces esophageal and gastric varices with a propensity for major hemorrhage

31
Hepatic Veins and Inferior Vena Cava
• venous drain of liver is by 3 hepatic veins• Right, middle & left hepatic veins & drain into
suprahepatic IVC• RHV drains V,VI,VII,VIII segments• MHV drains IV,V,VIII segments• LHV drains II,III segments• Segment I / caudate drains directly into IVC

32
• In 95 % Persons, LHV , RHV together forms a common trunk & drain into IVC
• In 20 % people , accessory RHV may be present in hepatocaval ligament
• This can be source of torrential bleed during right hepatectomy
• umbilical vein is additional vein that runs under the falciform ligament, between the left and middle veins,and empties into the left hepatic vein

33
• Hepatic vein bisects the portal branches in liver parenchyma
• RHV runs between right anterior & posterior portal veins
• MHV runs between right anterior & left portal vein
• LHV runs between branches of left portal vein supplying II,III segments

34
Bile ducts & hepatic ducts
• Intrahepatic bile ducts along with respective portal vein & hepatic artery is known as portal pedicle
• the bile duct branches are usually superior to the portal vein, whereas the hepatic artery branches run inferiorly
• Left hepatic duct –present at base of umbilical fissure -drains II,III,IV segments,
• Right hepatic duct formed by anterior & posterior branches- drains V,VI,VII,VIII segments

35
• Caudate lobe has its own biliary drainage both into left & right hepatic ducts
• Longer left hepatic duct joins with right hepatic duct to form confluence anterior to right portal vein
• This forms common hepatic duct- 4mm diameter• Below cystic duct ,it is common bile duct-6mm
diameter

36
Nerve supply
• Parasympathetic innervation – by vagus– Left vagus- anterior hepatic branch– Right vagus- posterior hepatic branch
• Sympathetic innervation is by – greater thoracic sphlanchnic nerves, – celiac ganglion
• Source of reffered pain to right shoulder & scapula is phrenic nerve stimulation due to glisson capsule stretch or diaphragm irritation

37
Lymphatic drainage
• Lymph produced in liver• Drains via perisinusoidal space of disse &
periportal clefts of mall to• Cystic duct lymph node,CBD,hepatic
artery,retropancreatic & celiac lymph nodes(along hepatic arteries)
• Also drains superiorly into cardiophrenic lymph nodes(along hepatic veins)

38
Plate system of liver
• On the ventral surface of liver connective tissue condenses & forms system of fibrous plates & sheaths
• They extend into liver along with biliovascular structures
• consists of a sheath which surrounds the bile duct and blood vessels (hepatic artery and portal vein)
• continuous with the Glisson’s capsule intra-hepatically
• the hepatoduodenal ligament extra-hepatically.

39
• system also contains a large number of lymphatics, nerves and a small vascular network.
• Three plates are found in the hilar area: – the hilar plate, – the cystic plate and– the umbilical plate.

40

42
• upper curved edge of the hilar plate is dissected free from the undersurface of the liver to expose the left hepatic duct, the biliary ductal confluence and the right hepatic duct when repairing a biliary stricture

43
• during cholecystectomy, the cystic plate is left behind
• severe inflammation and fibrosis—– , the cystic plate may become short and thick and– the distance between the cystic plate and right portal
pedicle may be markedly reduced.– the plane between the gallbladder and the cystic plate
may be obliterated– may enter the plane behind the cystic plate.
• Continued dissection in this plane will eventually reach the right portal pedicle and if the sheath of the pedicle is breached, there is a very high risk of injury to the right hepatic artery and right portal vein

44
Microscopic anatomy
• Hepatic parenchyma organised into microscopic functional units – acinus/lobule
• Lobule is formed bya central terminal hepatic venule surrounded by 4 – 6 portal traids
• In between central venule and portal triad hepatocytes are arranged in single layer surrounded by sinusoids
• Blood flows from • portal triad sinusoids central venule

45
• Bile flows from • Hepatocyte terminal canaliculi bile ducts portal
triad• Between portal triad & central venule there are 3
zones• Zone 1 – periportal zone- rich in oxygen,nutrients• Zone 2-intermediate zone• Zone 3- perivenular zone-poor in oxygen,nutrients• Hence zone 3 more prone to ischemia & zone 1 to
toxic injury

46

47
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
• SYNTHESIS FUNCTION• Serum albumin• Synthesized exclusively by hepatocyte 10 gm/day• Half life – 20 days,hence not a marker for acute
dysfunction• Low albumin-– chronic liver disease– neprotic syndrome– protein malnutrition– chronic infections

48
• Acute liver damage• PT/INR• All clotting factors except viii –syntesized in hepatocyte• hAlf life 6hrs to 4 days• 2,7,9,10 factors – collectively measured by serum
prothrombin time• Elevated – hepatitis,cirrhosis,obstuctive jaundice, fat
malabsorption• PT not correctable with parenteral vit k-
hepatitis,DIC,portal vein obstruction

49
• Serum enzymes that reflect damage to hepatocytes
• Aminotransferases- within cytoplasm of hepatocyte
• Aspartate aminotransferase AST / SGOT• Alanine aminotransferase ALT / SGPT• Normal levels < 20 u/L• Upto 300 - nonspecific

50
• These enzymes are elevated in serum in great amounts when there is damage to liver cell membrane resulting in increased permeability
• > 1000 u/L - 1) viral hepatitis• 2) ischemic liver injury• 3)toxic / drug induced liver injury• Also a sensitive indicator of transplant rejection• AST/ALT > 2:1 – Alcohol liver disease

51
• Enzymes reflecting cholestasis• Alkaline phosphatase • 5 nucleotidase• Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase• ALP & 5 nucleotidase found in bile canalicular
membrane of hepatocytes• GGT in bile duct epithelium & endoplasmi
reticulum of hepatocyte

52
• ALP – greater than a four fold rise of normal value indicates cholestasis,liver infiltration,amyloidosis,pagets disease
• Also present in bone and placenta• Cannot differentiate intra or extrahepatic
biliary obstruction

53
• Serum bilurubin- produced in reticulo endothelial system , breakdown product of eme containing protein
• Conjugated in in hepatocyte• Excreted through bile• Hepatocellular damage – both direct and indirect
bilurubin level increases• Impaired excretion – increase in direct & total bilurubin
levels• NORMAL serum bilurubin < 1mg/dl• Direct – 30 % of normal

54
• DETOXIFICATION FUNCTION– Liver converts ammonia to urea– Normal < 60 mmol/L – Raised levels – hepatic encephalopathy
• Serum ceruloplasmin– Copper binding protein secreted by liver– Decreased – wilson disease• Alpha feto protein• Pathognomonic for primary liver malignancy

55
IMAGING OF LIVER

56
ULTRASOUND
• Based on pulse- echo principle• The ultrasound transducer converts electrical energy to
high-frequency sound energy that is transmitted into tissue.
• waves are transmitted through the tissue, some are reflected back,
• ultrasound image is produced when the receiver detects those reflected waves.
• augmented by Doppler flow imaging.• can detect the presence of blood vessels but also can
determine the direction and velocity of blood flow

57
advantages• inexpensive,• widely available,• no radiation exposure,
disadvantages• Incomplete imaging ( at dome,beneath ribs,lesion
boundaries)• Obesity & bowel gas reduce quality• lower sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound
compared with CT and MRI

58
uses
• Liver size• Detects lesions in liver• Detects gall stones• Detects biliary dilatation• Differentiates solid from cystic masses• Determines flow in vessels• As a guide in percutaneous biopsy• As a guide in aspiration of liver abscess

59
GALL STONES
HYPER ECHOIC LESION, POST ACOUSTIC SHADOW

60
SIMPLE CYST
HYPOECHOIC LESION WITH NO SEPTATIONS/DEBRIS,POST ACOUSTIC ENHANCEMENT

61
HYDATID CYST
HYPOECHOIC LESION WITH HYDATID SAND FLOATING

62
METASTASIS
HYPERECHOIC LESION WITH SURROUNDING HALO,NO SHADOW OR ENHANCEMENT

63
HEMANGIOMA
HOMOGENOUSLY HYPERECHOIC

64
Normal pv flow – continuous ,hepatopetalHepatofugal- portal hypertension

65
Hepatic vein flow - phasic

66
Contrast enhanced ultrasound• Improved ability to differentiate among benign
and malignant lesions• Contrast- gas microbubble agents• Microbubbles are <10 μm• improves delineation of liver lesions through
identification of dynamic enhancement patterns and the vascular morphology of the lesion.
• some agents exhibit a late liver-specific phase and accumulate in normal liver parenchyma after the vascular enhancement has faded

67
Intra-operative ultrasound
• gold standard for detecting liver lesions• tumor staging,• visualization of intrahepatic vascular
structures ,• guidance of resection plane by assessment of
the relationship of a mass to the vessels.• biopsy of lesions and• ablation of tumors

68
Ultrasound elastography
• used to assess the degree of fibrosis or cirrhosis in the liver.
• Low-frequency vibrations transmitted through the liver induce an elastic shear wave that is detected by ultrasonography
• The velocity of the wave correlates with the stiffness of the organ
• wave travels faster through fibrotic or cirrhotic tissues.• Advantage over biopsy is that , it is non
invasive,rapid,aquires information from large surface

69
Computerised tomography
• Increased accuracy of diagnosis & staging• CECT is widely used & best validated for liver
imaging• Most of liver pathologies have similiar density to
liver parenchyma• Liver has dual supply ,portal vein 75 % & hepatic
artery 25 %• Many liver tumours recieve major supply from
hepatic artery

70
Arterial phase Portal/venous phase
Time since contrast delivery
20 – 30 sec 60 – 70 sec
Tumours enhancement
Hypervascular conditions enhancement
Liver parenchyma enhanced
Hypervascular conditions like HCC,FNH,adenoma, metastasis from colorectal,RCC ,islet cell tumour,carcinoid best seen in arterial phaseMets from breast lung,hypovascular conditions, best seen in venous phase

71
MRI
• AS effective as CT• Useful in case of allergy to iodinated contrast• Biliary pathology

72
THANK YOU