list2
description
Transcript of list2
-
Data Structures
jrfTypewritten textList
-
jrfTypewritten textA list or sequence is an abstract data type that represents a sequence of values, where the same value may occur more than once. An instance of a list is a computer representationof the mathematical concept of a finite sequence; the (potentially) infinite analog of a list is astream. Lists are a basic example of containers, as they contain other values. If the same value occurs multiple times, each occurrence is considered a distinct item.
jrfTypewritten textOperations:
Implementation of the list data structure may provide some of the following operations:a constructor for creating an empty list;an operation for testing whether or not a list is empty;an operation for prepending an entity to a listan operation for appending an entity to a listan operation for determining the first component (or the "head") of a listan operation for referring to the list consisting of all the components of a list except for its first (this is called the "tail" of the list.)
jrfTypewritten textLists are typically implemented either as linked lists (either singly or doubly linked) or as arrays, usually variable length or dynamic arrays.
-
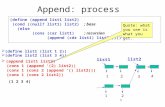
Example: Lists A list is a finite sequence of elements drawn from a set. List operations
Create a list Get the number of items Get the value of item j Set the value of item j Add something to the list before item j Delete item j from the list
Lists have two basic implementation schemes.
-
A List Classclass list { private: // Here is the implementation-dependent code // that defines exactly how the list is stored. public: // Here are the operations to be implemented. // Create and destroy a list list(); ~list(); // Get the number of items in the list int getNumItems() const; // Get the value of item j bool getValue(const int j, int& value) const; // Get the value of item j bool setValue(const int j, const int value); // Add an item before item j bool addItem(const int j, const int value); // Delete item j bool delItem(const int j);}
-
Implementing with ArraysThis source would be put in a file called list.h.
class list { private: // Here is the implementation-dependent code. // Well store the data in this array. int* array_; // Here is the size of the array. int size_; // Here is the number of items in the list. int numItems_; public: list(); ~list(); int getNumItems() const; bool getValue(const int j, int& value) const; bool setValue(const j, const int value); bool addItem(const int j, const int value); bool delItem(const int j);}
-
Constructing and Destructing
This source would be put in a file called list.cpp.
#include "list.h"
list::list() : array_(new int[MAXSIZE]), size_(MAXSIZE), numItems_(0){}
list::~list() { delete array_; size_ = 0;}
-
Implementing List Query Operationsint list::getNumItems() const { return numItems_;}
const bool list::getItem(const int j, int& value) { if (j > 0 && j < size_){ value = array_[j]; return true; }else{ return false; }}
-
List Modification Operationsbool list::addItem(const int j, const int value){ if (numItems_ == size_ || j < 0 || j > size_){ return false; }else{ for (int i = size_; i > j; i--) array_[i] = array_[i-1]; array_[j] = value; size_++; }}
bool list::delItem(const int j){ if (j < 0 || j > size_ - 1){ return false; }else{ for (int i = j; i < size_ - 1; i++); array_[i] = array_[i+1]; size_--; }}
-
Using lists Insertion sort Merge sort/quick sort Binary search Circular lists Doubly linked lists
Slide 3UntitledSlide 6Slide 7Slide 8Slide 9Slide 10Slide 11Slide 13Slide 14Slide 15Slide 16Slide 17Slide 18Slide 19Slide 20Slide 21Slide 22Slide 23Slide 24Slide 25Slide 26Slide 27Slide 28Slide 29Slide 3Slide 6Slide 7Slide 8Slide 9Slide 10Slide 11Slide 12Slide 13Slide 14Slide 15Slide 16Slide 17Slide 18Slide 19Slide 20Slide 21Slide 22Slide 23Slide 24Slide 25Slide 26Slide 27Slide 28Slide 29






![Python Boot Camp · 2020-03-21 · Give it a shot Talk with a ... list2 = [2, 3, 4] Same as list([2, 3, 4])](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5edc7bc8ad6a402d666728ba/python-boot-2020-03-21-give-it-a-shot-talk-with-a-list2-2-3-4-same-as.jpg)