Lecture: Trusts & Government Corruption The American Industrial Revolution.
-
Upload
ronald-gibbs -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Lecture: Trusts & Government Corruption The American Industrial Revolution.

Lecture: Trusts & Government Corruption
The American Industrial Revolution

Bell Ringer
• Complete RSG 6.3 “Big Business & Labor”– Highlight important words and phrases– Complete the graphic organizer– Answer the questions
– Reminder: • Please get started immediately!!!• No talking after the bell!!!• If you forgot your RSG then work on your packet…

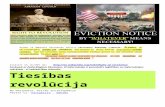
Trusts and Government CorruptionWhat do you see here? What to the men wearing
top hats represent?
Who are the men at the desks?
What is the intended message of the cartoonist?

Standard 11.2.5.
• Discuss corporate mergers that produced trusts and cartels and the economic and political policies of industrial leaders.

Objective
Students will be able to discuss the economic and political policies of industrial leaders by creating a sensory figure.

• Rise of Industrial Trusts
– Corporation:• A form of business organization that enables a
group of individuals to operate as a single “artificial legal person” It can sue and be sued, hire and fire, buy and sell, manufacture and trade.
• Advantages:– Securing of Capital: Can buy stocks and bonds – Limited liability– One can easily transfer out of corporation buy selling
shares– Perpetual life

• Merger: the consolidation of two companies into a single corporation
– Horizontal Integration: Companies producing similar products merge
– Vertical Integration: Companies producing different products merge

• Monopoly– The elimination of competition. – Combined corporations in order to
control prices, production, and sales of territory• Pool: a secret agreement among
competing companies to fix prices and output, or to divide sales territory.
–By the Interstate Commerce Act (1887) railroad pools were declared illegal

• Monopoly• Trust: Stockholders of competing
companies turned their stock over to a board of trustees and in exchange received trust certificates. In this way, the board of trustees gained full control and managed the member companies in such a way as to eliminate competition.
–The Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) made trusts illegal

• Examples of Business Consolidations– OIL: John D. Rockefeller: Standard Oil
Company• By 1879 controlled 90% of the countries oil
refineries

Film Clip: Oil Industry

• Examples of Business Consolidations– STEEL: Andrew Carnegie: Carnegie Steel
Company• 1900 – producing ¼ of countries steel• J.P. Morgan: formed a steel monopoly: The U.S.
Steel Corporation

Film Clip: The Steel Industry

• Examples of Business Consolidations– RAILROAD: Cornelius Vanderbilt: Merged
Eastern RR’s.

Film Clip: Railroad Industry

• Examples of Business Consolidations– OIL: John D. Rockefeller: Standard Oil
Comany• By 1879 controlled 90% of the countries oil
refineries
– STEEL: Andrew Carnegie: Carnegie Steel Company
• 1900 – producing ¼ of countries steel• J.P. Morgan: formed a steel monopoly: The U.S.
Steel Corporation
– RAILROAD: Cornelius Vanderbilt: Merged Eastern RR’s.

• http://www.bing.com/images/search?q=political+cartoon+trusts#focal=e7e13f5b053c039846a8bcbb27b1020a&furl=http://www.usdoj.gov/atr/public/hearings/single_firm/docs/219389_6.gif
1. Who is this man?2. What is he doing?3.What type of merger does this cartoon represent?

Advantages of Big Business
• Mass Production– Ex. assembly line, division of labor,
standardization of parts
• Wide Distribution: Used advertising and sold products across nation
• Efficient Management– Able to hire best executives, maintain costly
research laboratories and raise capital for expansion

Abuses of Big Business
• Elimination of competition–Large corporations drove out
small businesses• Power over the consumer
–Could force consumer to pay high prices and accept inferior quality

Abuses of Big Business• Exploitation of workers
– Pay low wages, long working hours, prevented them from forming unions
• Influence over the government– Manipulated government at federal, state and
local levels– Industrial giants ran for government offices,
made generous contributions to political candidates, and bribes legislatures
– Political “Machines” and “bosses” – political favors given in exchange for votes

Pair-Share
• Describe the corporate mergers that were produced by trusts and cartels and the policies of the industrial leaders.