Lecture 5 Thoery
Transcript of Lecture 5 Thoery
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
1/13
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
2/13
Normality analysis of data in
Minitaby P-Value > 0.05 Null hypothesis accepted
y P-Value
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
3/13
Normality analysis of data in
Minitaby P value 0.035 means 3.5% probability that data is
normally distributed.
y P value 1 means there is 100 percent probability thatdata is normally distributed
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
4/13
Correlation of data variablesy Q. What is correlation analysis?
A. Correlation analysis looks at the indirectrelationships in survey data
y Q. When would you use it?A. To objectively establish which variables are mostclosely associated with a given action or mindset
y Q. What are the advantages?A. It can provide a more discriminatory analysis thanasking a direct question
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
5/13
Correlation of data variablesy In statistics, correlation and dependence are any of a
broad class of statistical relationships between two or
more random variables or observed data values.
y General examples are
y Correlation between physical properties and offspring
y Correlation between product demand and supply
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
6/13
Correlation of data variablesy Formally, dependence refers to any situation in which
random variables do not satisfy a mathematical
condition of probabilistic independence
y P value for variables dependencies and concept ofsignificant correlation between two variables.
y Correlation between two variables represented by 1and no correlation is represented by 0.
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
7/13
Different outputs of correlation
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
8/13
The concept of modeling
yWhat is meant by modeling?
y Types of modeling
y Advantages of modeling
y Mathematical modeling
y Statistical modeling
y AI based Modeling
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
9/13
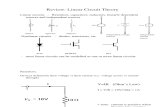
Regression analysisy The concept of dependent and independent variables
y The relationship of dependent and independentvariables in form of an equation.
y The concept of linearity and non linearity.
y The concept of confidence level or accuracy percentage
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
10/13
Regression analysisY
Y = mX + b
b = Y-intercept
X
Change
in Y
Change in X
m = Slope
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
11/13
Regression analysis
YY XXii ii ii!! FF FF II00 11
y 1. Relationship Between Variables Is a LinearFunction
DependentDependent(Response)(Response)VariableVariable(e.g., income)(e.g., income)
IndependentIndependent(Explanatory)(Explanatory)VariableVariable(e.g., education)(e.g., education)
PopulationPopulationSlopeSlope
PopulationPopulationYY--InterceptIntercept
RandomRandomErrorError
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
12/13
Regression analysisPath Diagram of A Linear Regression
i iY k b x b x b x e!
1 1 2 2 3 3
-
8/8/2019 Lecture 5 Thoery
13/13
Regression analysis
UnknownRelationship
PopulatioPopulationn
Random SampleRandom Sample
Y Xi i i! F F I0 1
$ $$
$
$
$$
$$
$$