Lecture 16 Allergy Hay fever 20% Asthma ~5%. Figure 10-1.
-
Upload
regina-tucker -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of Lecture 16 Allergy Hay fever 20% Asthma ~5%. Figure 10-1.

Lecture 16 Allergy
•Hay fever 20%•Asthma ~5%

Figure 10-1

(hives)
Allergies
4 types of hypersensitivity reactions

Delayed-type hypersensitivityImmune complex disease

Type I hypersensitivity-
mediated by mast-cell degranulation.
Preformed granules contain histamine,
heparin, TNF, chondroitin sulfate, neutral proteases,
and other.
Mucosal mast cell/Connective tissue mast cell

Figure 10-4

Figure 10-5Ingranules
Produced after
activation

Histamine
Binds to histamine receptors: H1, H2, H3-cell-type specific
Binding to H1 on: endothelial cells (increased permeability); smooth muscle (contraction); mucosal epithelium (mucus secretion)

Mediators
Neutral proteases activate Metalloproteases - remodeling of the extracellular matrix
TNF- inflammation
Lipid Mediators (PGD2, LTC4) - inflammation
Chemokines (MIP-1) - chemotaxis of leukocytes
Cytokines - Production of eosinophils, Th2 cells
Proteoglycans, heparin and chondroitin - sequester mediators, and effect a timed release

Prostaglandins and leukotrienes
PGD2- vessel dilation and permeability and chemoattractant for neutrophils
LTC4- same as histamine, but 100x more potent - late response. Leukotrienes used to be called Slow Reacting Substance of Anaphylaxis - SRS-A

Biologic effects of mediators

Biological effects of Eosinophil mediatorsLate stage of an allergic response includes the
recruitment of eosinophils and Th2 cells contrast with
a DTH (type IV) response which includes infiltration of macrophages and Th1 cells

Eosinophils

Figure 10-9 part 1 of 2
Products released by eosinophils

Figure 10-10

Figure 10-12

Figure 10-14

Figure 10-16
FEV1 - the forced expiratory volume of air in one second

Figure 10-18

Systemic anaphylaxis

Use of adrenaline to counteract the effects of
system anaphylaxisIn anaphylactic shock, blood vessels leak, bronchial tissues swell and blood pressure drops, causing choking and collapse. Adrenaline (epinephrine) acts quickly to constrict blood vessels, relax smooth muscles in the lungs to improve breathing, stimulate the heartbeat and help to stop swelling around the face and lips (angioedema).

Asthma

Figure 10-22 part 1 of 2

Figure 10-22 part 2 of 2

Histopathology of bronchial asthma

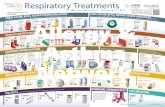
Treatment of asthma

New therapy for asthma and allergy: blocking the Fc portion of IgE from binding to the FcR on mast cells

Ragweed
Control
Histamine
Skin test for allergy

Food allergies

Type II hypersensitivityis caused by antibodies to
altered cell-surface components

Figure 10-27

Type III hypersensitivity reactions (Arthus Reaction)
Antibody-Antigen Complexes
Critical mediators appear to be C5a-receptor and FcRIII--probably present on mast cells

Figure 10-31

Figure 10-29

Figure 10-32

Type IV hypersensitivity - Delayed-type hypersensitivity

Figure 10-34
Also, note time scaleWhat is missing from this scheme?

Figure 10-35

Figure 10-36


Figure 10-23