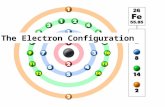
Last lecture Introduction to materials science and engineering Atoms / electron configuration.
-
Upload
patience-lloyd -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
1
Transcript of Last lecture Introduction to materials science and engineering Atoms / electron configuration.

last lecturelast lecture
Introduction to materials science and engineering
Atoms / electron configuration

todaytoday
Bonding in solids
Structure of crystal solids

Bonding Forces and EnergiesBonding Forces and Energies
re p u ls iv e
a ttra c tiv e
n e t e n e rg y
e n e rg y /fo rc e
r 0
in te ra to m ic fo rc e
distance r

The Periodic TableThe Periodic Table
METALS NONMETALS
INTERMEDIATE
increasing electronegativity

Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding
e.g. sodium chloride e.g. methane

Metallic BondingMetallic Bonding
+
d isc re te e n e rg y le v e ls o f e le c tro n sE
1
23
4
rn u c le u s+ +
1
2
n u c le u s
e n e rg y b a n d s = > fre e e le c tro n s
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
io n c o re s se a o f e le c tro n s

Bonding EnergiesBonding Energies
low
high

Crystalline StructuresCrystalline Structures

Crystalline StructuresCrystalline Structures
amorphous crystalline

Example: GlassExample: Glass
quartz(crystalline)
quartz glass(amorphous)
Si4+O2-
glass(amorphous)

Crystalline StructuresCrystalline Structures
simple cubicbody-centered cubic (bcc)
bcc
fcc

Hexagonal Crystal StructuresHexagonal Crystal Structures
hcp unit cell

Stacking Sequence of Stacking Sequence of Close-Packed StructuresClose-Packed Structures
first plane Afirst plane A and second plane Bfirst plane A, second plane B and third plane C: fccfirst plane A, second plane B and third plane A: hcp

FCC and BCC Solid Sphere ModelFCC and BCC Solid Sphere Model
fcc unit cell bcc unit cell
R
R = atomic radiusa = unit cell length / lattice constant
a a

Crystalline Structures of MaterialsCrystalline Structures of Materials

Lattice ParametersLattice Parameters
a
b
c
x
y
z

Crystal SystemsCrystal Systems

Crystal SystemsCrystal Systems

How to define a directionHow to define a direction
Vector of convenient length (pass through origin)
Project the vector to the axes (and measure in a, b, and c)
Multiply or divide these numbers by common factor to get smallest set of integers
Write them down as [uvw]

Miller Indices: Miller Indices: Crystallographic DirectionsCrystallographic Directions
a
b
c
x
y
z
a
b
c
x
y
z

Miller Indices: Crystallographic Miller Indices: Crystallographic Directions (Miller Bravais)Directions (Miller Bravais)
a 1
a 2
a 3
z
[0 001 ]
[111 0 ]

How to define a planeHow to define a plane
Plane may not include origin!
Determine the intercepts with appropriate axes as a, b, and c
Take reciprocals (no intercept means infinity reciprocal of infinity = 0)
Multiply or divide these numbers by common factor to get smallest set of integers
Write them down as (hkl)

Miller Indices: Miller Indices: Lattice PlanesLattice Planes
x
z
y
(0 11 )
x
z
y
= > (111 )
x
z
y
intersection points: 1/2 a, 1/2b, 1/2creciprocal values: (222)

DefectsDefects
Point defects
Linear defects
2-dimensional defects

Point DefectsPoint Defects
self-interstitial vacancy

Impurity AtomsImpurity Atoms
interstitial substitutional

Dislocations: Edge DislocationDislocations: Edge Dislocation
Burgers vectorinserted half plane
dislocation line

Dislocations: Screw DislocationDislocations: Screw Dislocation
Burgers vector
dislocationline

Grain BoundariesGrain Boundaries
Ni-Base Superalloy Waspalloy
50µm
high-angle grain boundary (>15°)
low-anglegrain boundary

nextnext
Properties of materials