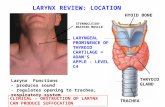
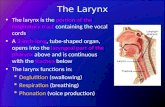
Larynx Imaging 2nd part laryngeal congenital inflammatory traumatic CT MRI Dr Ahmed Esawy
-
Upload
ahmed-esawy -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
54 -
download
0
Transcript of Larynx Imaging 2nd part laryngeal congenital inflammatory traumatic CT MRI Dr Ahmed Esawy

Congenital disorders of the Larynx
Supraglottic Glottic Subglottic
Laryngomalacia Vocal cord paralysis Cong. Subglottic
stenosis
Ductal retention cyst Web and atresia Subglottic hemangioma
Cystic hygroma Interarytenoid web Web & atresia
Bifid epiglottis Posterior laryngeal cleft Cysts
Saccular cyst Cri-du-chat syndrome
Anterior laryngeal cleft
Dr AHMED ESAWY

Subglottic stenosis
• Membranous and cartilaginous types.
• Membranous: fibrous soft-tissue thickening of the subglottic area
• Cartilaginous: thickening or deformity of the cricoid cartilage shelf-like plate
• Grading of laryngeal stenosis – Grade I Less than 70%
– Grade II 70%-90%
– Grade III More than 90%;
– Grade IV Complete obstruction

Subglottic stenosis
Dr AHMED ESAWY

Subglottic Stenosis Laryngeal conditions

( laryngocele)
• diltation of ventricular saccule or appendix
• Usually acquired
• Laryngomucocele Saccular cyst if fluid filled
• Laryngocele if air filled
• pyolaryngocele; is an infected laryngocele, filled with pus, is called a it shows a thickened wall on cross-sectional imaging
• Laryngocele is supragglottic abnormality and the true cord is normal

Laryngocele
• classifications: internal, external, and combined.
• The internal (40%) component is medial to the hyoid
bone,inside larynx
• the external (26%)component lateral to the hyoid.
• Mixed (44%) laryngocele on both side of thyriod
memberane.
• etiology
– transglottic pressure, e.g. in trumpet players,excessive cough
– laryngeal carcinoma partial obstruction
– Congenital
– Search for underlying laryngeal cancer

Laryngocele internal,
external, and combined

• acquired
laryngocele

• Mixed laryngocele. Enhanced CT reveals an air-filled
laryngocele straddling the thyrohyoid membrane. The internal
component (arrowhead) is medial to the hyoid bone (asterisk)
and the external component (arrow) is lateral to the hyoid.

Dr AHMED ESAWY

• Trachea radiograph: At the level of the larynx, on the right side,
a peanut-sized saccular protrusion can be seen (arrow).
• EXTERNAL ONLY THAT APPEAR ON X-RAY

Laryngocele Saccular cyst
fluid filled

• Axial contrast-enhanced CT
image through supraglottic
larynx. Bilateral fluid-filled
internal laryngocele(saccular
cyst) (arrows).
Dr AHMED ESAWY

SACCULAR CYST © LARYNGOCELE
AXIAL POST GADOLINIUM

cysts
• Three types
• 1-saccular cyst ( laryngocele)
• 2-mucosal cyst arise within the larynx
• 3-thyroglossal duct cyst arise just outside
the larynx in close assosciation with the
strape muscles

SACCULAR CYST (LARYNGOCELE) (L)

THYROGLOSSAL DUCT CYST
PARAGLOTTIC FAT (ARROWHEAD)

• Axial CT scan of the neck showing the epiglottic
cyst in the pictures above.

INJURIES OF THE LARYNX
• Results:
• Trauma may result in:
• Cartilage fracture.
• Mucosa lacerations.
• Submucosa Hge.
• Membranes rupture and surgical
emphysema

Overview
• Classification of Trauma
– Blunt
– Penetrating
– Inhalation
– Ingestion
– Iatrogenic

VERTICAL FRACTURE OF THE LARYNX

Laryngeal Fracture
• The above axial CT scan shows a fracture of the thyroid
cartilage lamina. Note the presence of an endotracheal tube

Laryngeal F.B.
Complete Obstruction: Death
Incomplete Obst.: cough, dyspnea, Aphonia
Coin In Larynx

ARYTENIOD DISLOCATION
CRICIOD ARROWHEAD
ARYTENIOD ARROW

inflammatory

Epiglottitis

• Epiglottitis is the inflammation of the
supraglottic structures

Radiographic parameters in adult
epiglottitis
• The measurement differences were significant between the groups only for the width of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds
•
• Width of the epiglottis greater than 8 mm and of the aryepiglottic folds greater than 7 mm seem highly suggestive of epiglottitis in the adult.


Sites of measurement of
aryepiglottic folds and epiglottis
1-width of aryepiglottic folds at
the mid piont of these folds
2- 1-width of aryepiglottic folds
behind epiglottis
3= 1-width of aryepiglottic folds
at the base of these folds


Epiglottis and
aryepiglottic
folds thickened
in epiglottitis

Classic thumprint appearance of a
swollen epiglottis is pathogonomonic
Of epiglottitis (lateral view /erect)

• CT scan in an adult with acute epiglottitis shows a column of air around the epiglottis (E). The right side is more swollen than the left, and the hypoattenuating area (A) is suggestive of fluid or an early abscess formation.

• A, Axial contrast-enhanced CT scan at the level of the hyoid bone shows marked thickening of the aryepiglottic folds (f), posterior pharyngeal wall, and platysma muscle (arrow). B, Edema is seen in the retropharyngeal space extending to the carotid arteries bilaterally (asterisks) and in the subcutaneous fat. There is obliteration of the paraglottic fat planes and thickening of the false vocal cords (V).

CROUP
• SUBGLOTTIC LARYNGITIS

Croup Vs Epiglottitis
Characteristics of Laryngotracheitis and Epiglottitis
Feature Laryngotracheitis Epiglottitis
Age <3 years >3 years
Onset Gradual (days) Acute (hours)
Cough Barky Normal
Posture Supine Sitting
Drooling No Yes
Radiograph Steeple sign, narrowed subglottis Thumb sign, enlarged
epiglottis,dilated hypopharynx
Cause Viral Bacterial
Treatment Supportive (croup tent) Airway management (intubation or
tracheotomy), antibiotics

CROUP is best appreciated on the AP view
And can be distinguished from congenital
Subglottic stenosis and post-intubation
oedema by history
The characteristic church stipple
appearances of croup results
From subglottic oedema obliterating the
normal subglottic shoulder
Of the proximal airway

CROUP is best appreciated on the AP view
And can be distinguished from congenital
Subglottic stenosis and post-intubation
oedema by history
The characteristic church stipple
appearances of croup results
From subglottic oedema obliterating the
normal subglottic shoulder
Of the proximal airway

Epiglottic Enlargement
• NORMAL VARIANT
– Prominent normal epiglottis
– Omega epiglottis
• INFLAMMATION – Acute / chronic epiglottitis
– Angioneurotic edema
– Stevens-Johnson syndrome
– Caustic ingestion
– Radiation therapy
• MASSES – Epiglottic cyst
– Aryepiglottic cyst
– Foreign body

Aryepiglottic Cyst
• Retention cyst
• Lymphangioma
• Cystic hygroma
• Thyroglossal cyst
• may be symptomatic at birth
• well-defined mass in aryepiglottic
fold

• Diphtheria.. The laryngeal cartilages are collapsed and the laryngeal airway occluded. The thyroid (arrowheads) and cricoid (arrow) cartilages are misshapened. The distance between thyroid and cricoid cartilage is diminished.

Chronic Localized Hypertrophic
Laryngitis:
• Vocal (Singer’s) nodules:
• Etiology:
• Prolonged abuse of voice. Occurs commonly in
untrained voice users as singers and teachers.
• Pathology:
• Localized epithelial hyperplasia and/or sub-
epithelial organized haematoma of the vocal
fold.

• Singer’s nodules.
Dr AHMED ESAWY

Vocal cord polyps (papilommas)
• Etiology: usually complicates an
acute violent voice trauma e.g.
shouting.
• Pathology: Localized sub-epithelial
edema (edematous polyp), vascular
engorgement (vascular polyp) or
fibrosis (fibrotic polyp) of the vocal
fold.

Dr AHMED ESAWY