Kidney physiology
-
Upload
julie-stewart -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
203 -
download
1
Transcript of Kidney physiology

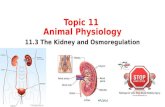
Kidney Physiology (pg 4)

Macroscopic Structure of the Kidney
• Cortex: Outer region

Macroscopic Structure of the Kidney
• Cortex: Outer region • Medulla: Inner region

Macroscopic Structure of the Kidney
• Cortex: Outer region • Medulla: Inner region• Renal pelvis: large cavity that collects the
urine as it is produced. Continuous with ureter

Nephrons• Nephrons are the functional unit of the kidney

Nephrons• Nephrons are the functional unit of the kidney• Over 1 million nephrons per kidney

Nephron Structure
Nephrons have two parts:

Nephron Structure
Nephrons have two parts:1. Renal corpuscle
a. Glomerulus: cluster of capillaries

Nephron Structure
Nephrons have two parts:1. Renal corpuscle
a. Glomerulus: cluster of capillariesb. Glomerular (Bowman’s) Capsule: cup that
surrounds the glomerulus and receives blood filtrate from it

2. Renal tubulea. Proximal convoluted tubule: Highly coiled. Located in cortex

2. Renal tubulea. Proximal convoluted tubule: Highly coiled. Located in cortexb. Loop of Henle: A hairpin loop that dips into the medulla, makes a U-turn, and ascends back to the cortex

2. Renal tubulea. Proximal convoluted tubule: Highly coiled. Located in cortexb. Loop of Henle: A hairpin loop that dips into the medulla, makes a U-turn, and ascends back to the cortexc. Distal convoluted tubule: Coiled, in cortex

Urine Formation• Nephrons form urine in 3 steps
1. Filtration: Water and small solutes enter the nephron (blood cells and proteins do not enter). Filtrate is similar to blood plasma.

Urine Formation• Nephrons form urine in 3 steps
1. Filtration: Water and small solutes enter the nephron (blood cells and proteins do not enter). Filtrate is similar to blood plasma. 2. Reabsorption: Useful substances (water, glucose, amino acids, needed ions) are transported out of the filtrate and back into the blood

Urine Formation• Nephrons form urine in 3 steps
1. Filtration: Water and small solutes enter the nephron (blood cells and proteins do not enter). Filtrate is similar to blood plasma. 2. Reabsorption: Useful substances (water, glucose, amino acids, needed ions) are transported out of the filtrate and back into the blood3. Secretion: Harmful substances (H+, excess K+, some drugs and poisons) are removed from the blood and put into the filtrate