Kaifi new shallow foundation
-
Upload
hamzah-meraj-jamia-millia-islamia-new-delhi -
Category
Education
-
view
256 -
download
7
Transcript of Kaifi new shallow foundation

SHALLOW FOUNDATION
MOINUDDINB.ARCH 3RD YR

•DEFINITION OF FOUNDATION
The lowest part of a structure is generally referred to as foundation.
•FUNCTION OF A FOUNDATION
To transfer load of the superstructure to the soil on which it is resting.
•REQUIREMENTS
A properly designed foundation is one that transfers the structural load throughout the soil without overstressing of soil which can result in either excessive settlement or shear failure, both of which can damage the structure.

LOADS ON FOUNDATION
Dead Load : Refers to the overall weight of the structure. Includes weight of the materials permanently attached to the structure (such as flooring) and fixed service equipment (such as air conditioning)
Live load : Refers to the weight of the applied bodied that are not permanent parts of the structure. Applied to the structure during part of its useful life (e.g. people, warehouse goods). Specified by code.
Wind loads : Acts on all exposed parts of the structure. Calculated using building codes.
Earthquake Forces : Building code is consulted.

CLASSIFICATION NOF FOUNDATIONS
•SHALLOW FOUNDATION
•DEEP FOUNDATION

SHALLOW FOUNDATION
This type of foundation usually refers to those being rested on stratum with adequate bearing capacity and laid less than 3m below ground level. Common examples include pad, strip or raft foundations.The selection of the right type of shallow foundation normally depend on
the magnitude and disposition of the structural loads and the bearing capacity of subsoil. A combination of two or three type of shallow foundation in one single structure is not uncommon.

TYPES OF SHALLOW FOUNDATION

TYPES OF SHALLOW FOUNDATION………..

PAD FOUNDATION / SQUARE SPREAD FOOTING FOUNDATION

•Support a single centrally located column
•Use concrete mix 1:2:4 and reinforcement
•The reinforcement in both axes are to resist/carry tension loads.
PAD FOUNDATION / SQUARE SPREAD FOOTING FOUNDATION……..

Circular Spread Footings
• Are round in plan view
• Most frequently used as foundation
for
• Light standards, flagpoles and
power
• Transmission lines.

CONTINUOUS SPREAD FOOTINGS / STRIP FOUNDATION
•Used to support bearing walls

COMBINED FOOTINGS
• support more than one column
• useful when columns are located too close together for
each to have its own footing

RAFT FOUNDATION
Raft foundation is a large combined thick slab designed to seat
and support the whole or a large part of a structure.
A raft is usually used when subsoil is weak, or columns are closely
located and with deviated loadings. It also serves as a transfer slab to
combine and tie up all the vertical loading elements to the plate-form
foundation. By doing so, differential settlement can be avoided.

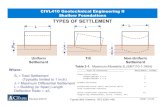
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF SHALLOW FOUNDATION
ADVANTAGES:
•Cost (affordable)
•Construction Procedure
(simple)
•Materials (mostly concrete)
•Labor (does not need
expertise)DISADVANTAGES:
•Settlement
•Limit Capacity Soil Structure
•Irregular ground surface (slope, retaining
wall)
•Foundation subjected to pullout, torsion,
moment.
![[PPT]SHALLOW FOUNDATION - Home - Sri Venkateswara · Web viewSHALLOW FOUNDATION Introduction – Location and depth of foundation – Codal provisions – bearing capacity of shallow](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5aa985c27f8b9a9a188d0876/pptshallow-foundation-home-sri-venkateswara-viewshallow-foundation-introduction.jpg)