K15b Dermatitis Atopic
-
Upload
zikri-putra-l-lubis -
Category
Documents
-
view
239 -
download
1
description
Transcript of K15b Dermatitis Atopic
-
Chairiyah TanjungDepartment of Dermato-venereologyMedical Faculty, North Sumatera University
-
Atopic dermatitis (AD) = Atopic eczemaA chronically relapsing skin diseaseOccurs most commonly during early infancy and childhoodFrequently associate with elevated serum IgE levelsA personal/family history of atopy(+)
-
epidemiologyPrevalence 3x than 1960sIndustrialized countries > agricultural countriesFemale : male = 1,3:1 AD, associated with :- small family size- increased income and education- migration rural urban- use of antibiotic
-
Etiology and PathogenesisHereditary(genetic)
Psychological effectAllergy (hypersensitivity)FoodaeroalergenCellularImmunity defectIrritantInfectionClimateXerosisDecreaseSkin barierDermatitis Atopic
-
Genetic FactorStrong maternal influenceChromosome 5q31-33, contains a clustered family of functionally related cytokine genes :- IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 expressed- GM-CSF by Th2 cell- Differences in transciptional activity of the IL-4 gene influence AD predisposition- A significant association between a specific polymorphism in the mast cell chymase gene and AD
-
Immune Response in AD SkinKey cell types in AD skin :Langerhans cellsLymphocyte cellsEosinophilsMast cells
-
Immunopatogenesis of DA
-
Systemic Immune Abnormalities in ADIncreased synthesis of IgEIncreased specific IgE to multiple allergens, including foods, aeroallergens, microorganism, bacterial toxins, autoallergensIncreased expression of of CD23 (affinity IgE receptor) on B cells and monocytesIncreased basophil histamine release
-
Systemic Immune Abnormalities in ADImpaired delayed-type hypersensitivity responseEosinophiliaIncreased secretion of IL-4, IL-5 dan IL-13 by Th2 cellsDecreased secretion of IFN- by Th1 cellsIncreased soluble IL-2 receptor levelsElevated levels of monocyte CAMP-phosphodiesterase with increased IL-10 and prostaglandin E2
-
Skin barrierDermatitis atopic skin
Epidermal lipid TEWL Skin capacitance Soap &detergenDecrease skin barrier functionAllergen absorption Microbial colonization Treshold of pruritus
-
Environment factorFood infant and children :milk and eggs adult :seafood and nutsAeroallergens : dust mites,animal danders,molds,pollens.Temperature &humidityIntens perspirationEmotional stressor
-
CLINICAL FINDINGSinfantile phase (0-2 years)
-
Childhood phase(2-12 years)
-
Adolescent phase(12-18 years)
-
diagnosisDiagnostic criteria of AD : SomeThe UK working partys :proposed alternative system,the criteria of Hanifin &Rajka (1994)Diagnose of AD:-Three or more of the major criteria-three or more of the minor criteria
-
Major criteriaPruritusTypical morphology &distribution :facial & ekstensorInvolvement during infancy &early childhood flexuralFlexural dermatitis in adultChronic or Chronically relapsing dermatitisPersonal or family histrory of atopy
-
Minor CriteriaXerosisSkin infectionHand/foot dermatitisIchthyosis/palmar hyperlinearity/keratosis piliarisPityriasis albaNipple eczemaWhite dermatografism&delayed blanched response
-
Minor criteriaCheilitisInfra orbital foldAnterior subcapsular catarractsOrbirtal darkeningFacial pallorIchiness when sweating
-
Minor criteriaPerifollicular accentuationFood hypersensitivityDuration of AD influecenced by environment and phychis factorsImmediate skin test reactivityElevated serum IgEEarly age of AD
-
Xerosis
-
Keratosis piliaris
-
Hiperlinear palmaris and dennei morgan
-
White dermographism & pitriasis alba
-
Skin infection
-
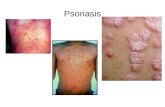
Differential diagnosisSeborrhoic dermatitisContact dermatitisNumular dermatitisScabiesIchthyosisPsoriasis Dermatitis herpetiformisSezary syndromeLeterrer-Siwe disease
-
In infantWiskott-Aldrich syndromeHyper- Ig E syndrome
-
General skin care measureEducationAppropriate skin hydration & use of emolient skin barier repair measureAvoidance of irritansIdentification & treatment of complication bacterial, viral of fungal infectionTreatment of psychosocial aspect of diseaseAntipruritic intervention
-
Treatment Topical therapySystemic therapy
-
Topical therapyCutaneus hydrationTopical glucocorticoidTopical calcineurine inhibitor ( tacrolimus & pimocrolimus)Tar preparationTopical anti histamin : not recommended except : doxepine cream 5%
-
Systemic therapySystemic glucocorticoidAnti histaminInfection agentInterferoneCycloporinePhototherapy (UVB, UVA+UVB,PUVA)
-
Prognosis Many factor correlate with AD difficult to predict prognosisThe predictive factors correlate with a poor prognosis of AD :Widespread AD in childhoodAssociated allergenic rhinitis & asthmaFamily history of AD in parents or siblingEarly age at onset of ADBeing an only childrenVery high serum IgE levels
-
30-35% infatile AD asthma / hay feverOften develop non specific irritant hand dermatitis
********************************