Juvenile Justice Chapter 4 - Kean Universityjdrylie/docs/Microsoft... · Choice Theory In the 1970s...
Transcript of Juvenile Justice Chapter 4 - Kean Universityjdrylie/docs/Microsoft... · Choice Theory In the 1970s...
Juvenile Justice Juvenile Justice
CJ3650 CJ3650
Professor James DrylieProfessor James Drylie
Chapter 4 Chapter 4
Theories of Delinquency Theories of Delinquency
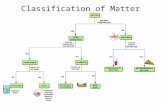
�� There are several theories related to the There are several theories related to the
causation of crime and delinquency causation of crime and delinquency
�� A A theorytheory is a principle or an idea that is a principle or an idea that
attempts to define and explain a attempts to define and explain a
phenomenon. phenomenon.
Classical & Positivistic TheoryClassical & Positivistic Theory
�� Two major schools of criminological Two major schools of criminological
thoughtthought
�� ClassicalClassical
�� People choose to commit crime People choose to commit crime
�� Positive Positive
�� The environment influences behavior The environment influences behavior
The Classical School The Classical School
�� Behavior is rationalBehavior is rational
�� Product of Product of free willfree will�� Juveniles choose to commit delinquent Juveniles choose to commit delinquent acts/crimeacts/crime
�� Decisions in this regard are rationalDecisions in this regard are rational�� Based the pleasure/pain related to the actBased the pleasure/pain related to the act
�� Strongly influenced early American Strongly influenced early American thought through the 1800sthought through the 1800s
CesareCesare BeccariaBeccaria (1738(1738--1794)1794)
�� Italian nobleman Italian nobleman
�� Believed that people Believed that people
are are hedonistic hedonistic
�� Maximize pleasureMaximize pleasure
�� Minimize pain Minimize pain
�� Often referred to as Often referred to as
the the pleasurepleasure--pain pain principle principle
�� Focuses on the Focuses on the
offense committedoffense committed
�� Not the offender Not the offender
�� Concerned with how Concerned with how
punishment is appliedpunishment is applied
�� Must fit the crimeMust fit the crime
�� Pain vs. pleasure Pain vs. pleasure
Positive SchoolPositive School
�� Influenced juvenile justice practices by the Influenced juvenile justice practices by the
late 1800slate 1800s
�� Grounded in the belief that behavior is Grounded in the belief that behavior is
beyond individual controlbeyond individual control
�� Factors other than free will influence behaviorFactors other than free will influence behavior
�� Emerging thought Emerging thought
�� The emergence of the scientific method as a The emergence of the scientific method as a
means to study phenomenonmeans to study phenomenon
�� The classical approach toward punishment The classical approach toward punishment
was proving ineffective was proving ineffective
Early positivist thoughtEarly positivist thought
�� CesareCesare LombrosoLombroso
�� Early criminologists looked to biological Early criminologists looked to biological
factors as a cause of crime factors as a cause of crime
�� Over time there was more of an emphasis on Over time there was more of an emphasis on
isolating psychological and social factorsisolating psychological and social factors
�� FamilyFamily
�� SchoolSchool
�� Peer relationships Peer relationships
Choice TheoryChoice Theory
�� In the 1970s the classical school of In the 1970s the classical school of
thought reemerged asthought reemerged as
�� Rational ChoiceRational Choice
�� Choice TheoryChoice Theory
�� The renewed interest in the classical The renewed interest in the classical
school based onschool based on
�� Questioning the premise of positivismQuestioning the premise of positivism
�� An increased crime rateAn increased crime rate
�� Questioning if rehabilitation was workingQuestioning if rehabilitation was working
Routine ActivitiesRoutine Activities
�� Based on rational choiceBased on rational choice
�� Contends that the motivation to commit Contends that the motivation to commit crime and the number of offenders are crime and the number of offenders are constantconstant
�� Some would argue that the change in Some would argue that the change in crime rates are due to fluctuations in the crime rates are due to fluctuations in the number of available offendersnumber of available offenders
�� Cohen & Cohen & FelsonFelson believe that there is a believe that there is a steady stream of offenders willing and steady stream of offenders willing and capable of offending capable of offending
�� Additionally, Cohen and Additionally, Cohen and FelsonFelson posit that posit that
crime rates fluctuate due to the following:crime rates fluctuate due to the following:
�� Motivated offenderMotivated offender
�� Suitable target (victim)Suitable target (victim)
�� Absence of capable guardianAbsence of capable guardian
�� ParentParent
�� NeighborsNeighbors
�� PolicePolice
�� Teachers, etc. Teachers, etc.
�� All three factors must be present for a crime All three factors must be present for a crime
to occur to occur
Deterrence Theory Deterrence Theory
�� Follows from choice theoryFollows from choice theory
�� Juveniles commit crime because they Juveniles commit crime because they choose to do sochoose to do so
�� The choice is based in perceived risks and The choice is based in perceived risks and benefitsbenefits
�� If the risk outweighs the benefit they will If the risk outweighs the benefit they will most likely not commit the actmost likely not commit the act
�� Two types of deterrence:Two types of deterrence:�� GeneralGeneral
�� Specific Specific
General deterrence General deterrence
�� Discourages wouldDiscourages would--be delinquents from be delinquents from
committing delinquent acts because the committing delinquent acts because the
threat of punishment is realthreat of punishment is real
�� The fear of punishment outweighs the The fear of punishment outweighs the
benefits of the actsbenefits of the acts
Specific deterrence Specific deterrence
�� Is designed to impose a sanction on an Is designed to impose a sanction on an
adjudicated delinquent to prevent them adjudicated delinquent to prevent them
from committing additional delinquent actsfrom committing additional delinquent acts
�� Imposing stiff sanctions on a juvenile for Imposing stiff sanctions on a juvenile for
committing an offense or delinquent actcommitting an offense or delinquent act
�� Do six months of community service every Do six months of community service every
weekend and you may think twice before you weekend and you may think twice before you
do something to get in trouble againdo something to get in trouble again
The Assumptions of DeterrenceThe Assumptions of Deterrence
�� Individuals are rational actorsIndividuals are rational actors
�� Weigh potential risk against benefits Weigh potential risk against benefits
�� Juveniles are aware of sanction/penaltyJuveniles are aware of sanction/penalty
�� The risks associated with punishment are The risks associated with punishment are
unpleasant unpleasant
�� The sanction is swift, certain, and severeThe sanction is swift, certain, and severe
Biological theoryBiological theory
�� The oldest approach in the biological The oldest approach in the biological
theories of crime are theories of crime are morphological morphological
�� Criminals are viewed as biologically inferior Criminals are viewed as biologically inferior
�� Biological inferiority produces certain physical Biological inferiority produces certain physical
characteristics that make the appearance of characteristics that make the appearance of
criminals and criminals and noncriminalsnoncriminals different different
�� Two particular theories are:Two particular theories are:
�� LombrosoLombroso’’ss atavism theoryatavism theory
�� SheldonSheldon’’s s somatypesomatype theorytheory
AtivismAtivism�� CesareCesare LombrosoLombroso (1835(1835--1909) considered 1909) considered
the father of the positive schoolthe father of the positive school
�� He identified several factors that he felt He identified several factors that he felt
influenced crimeinfluenced crime
�� Population densityPopulation density
�� EducationEducation
�� Unemployment Unemployment
�� News coverage News coverage –– Contagion Contagion
�� The The born criminalborn criminal
Atavistic anomaliesAtavistic anomalies
�� Large skullsLarge skulls
�� Large protruding jawsLarge protruding jaws
�� Canine teethCanine teeth
�� High foreheads High foreheads
�� Flattened nosesFlattened noses
�� Deep, closeDeep, close--set eyesset eyes
�� Especially large or small earsEspecially large or small ears
�� Very long arms or legsVery long arms or legs
SomatotypeSomatotype
�� Sheldon focused on body typeSheldon focused on body type
�� EndomorphEndomorph
�� Soft, round, and fat body typeSoft, round, and fat body type
�� Seeks comfort and are extrovertedSeeks comfort and are extroverted
�� EctomorphEctomorph
�� Thin, frailThin, frail
�� Introverted and strong ability for selfIntroverted and strong ability for self--controlcontrol
�� MesomorphMesomorph
�� Muscular, firm, and strongMuscular, firm, and strong
�� Assertive and aggressive Assertive and aggressive
Refer to chart on page 101
Genetics Genetics
�� Criminal activity tends to run in familiesCriminal activity tends to run in families
�� Agree or disagree?Agree or disagree?
�� Twin studies (Denmark)Twin studies (Denmark)
�� MonzygoticMonzygotic –– identical identical
�� If one twin has a conviction, 35% of the cases the If one twin has a conviction, 35% of the cases the
other twin also has a conviction other twin also has a conviction
�� Concordance rate is 35%Concordance rate is 35%
�� DizygoticDizygotic –– fraternal fraternal �� Concordance rate was 12%Concordance rate was 12%
Adoption studies Adoption studies
�� Better than twin studies in that they can Better than twin studies in that they can
isolate biological influences on isolate biological influences on
delinquency because the environmental delinquency because the environmental
influence of the biological parent is absent influence of the biological parent is absent
Chemical & Neurological Chemical & Neurological
�� Biochemical explanations suggest that Biochemical explanations suggest that
chemical deficiencies or abnormalities in chemical deficiencies or abnormalities in
the body can affect behaviorthe body can affect behavior
�� DietaryDietary
�� Sugar, vitamins B/CSugar, vitamins B/C
�� Fetal alcohol syndrome & prenatal drug useFetal alcohol syndrome & prenatal drug use
�� One study of FAS found that 60% of males and One study of FAS found that 60% of males and
40% of females reported trouble with the law40% of females reported trouble with the law
�� 45% of youth between 12 45% of youth between 12 –– 20 with FAS had 20 with FAS had
committed a violent offense committed a violent offense
�� Hormones Hormones
�� Autonomic nervous systemAutonomic nervous system�� Controls involuntary body functionsControls involuntary body functions
�� Blood pressureBlood pressure
�� BreathingBreathing
�� Heart rateHeart rate
�� Produces the Produces the ““fight or flightfight or flight”” responseresponse�� Adrenal glandsAdrenal glands
�� Anxiety increases involuntary body functionsAnxiety increases involuntary body functions�� These experiences are unpleasant and people These experiences are unpleasant and people generally avoid anxiety producing behaviorgenerally avoid anxiety producing behavior
�� Psychopaths or sociopaths do not develop Psychopaths or sociopaths do not develop adequate consciences and may be incapable adequate consciences and may be incapable of feeling fear or anxiety of feeling fear or anxiety
�� Learning disabilities Learning disabilities
�� School failure has been linked to drop out School failure has been linked to drop out
rates and delinquency rates and delinquency
�� LDs are biologically determined factors that LDs are biologically determined factors that
impose difficulties to learningimpose difficulties to learning
�� Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
�� Symptoms areSymptoms are
�� InattentionInattention
�� ImpulsivityImpulsivity
�� Hyperactivity Hyperactivity
�� ADHD children are more likely to have contact with ADHD children are more likely to have contact with
the system the system
Psychological theory Psychological theory
�� Freud believed that personality is formed early in Freud believed that personality is formed early in childhood and develops into a threechildhood and develops into a three--part part personality structure personality structure �� IdId
�� Collection of unconscious desires and instinctsCollection of unconscious desires and instincts
�� Sex and aggressionSex and aggression
�� EgoEgo�� The identity and actual behaviorThe identity and actual behavior
�� Superego Superego �� Conscience and moral character Conscience and moral character
�� Freud argued that juveniles have Freud argued that juveniles have underdeveloped superegos that are unable to underdeveloped superegos that are unable to regulate the Idregulate the Id
Personality disorders Personality disorders
�� Personality refers to the emotional and Personality refers to the emotional and
behavioral attributes of an individual behavioral attributes of an individual
�� Delinquents characteristically areDelinquents characteristically are
�� ExtrovertedExtroverted
�� ImpulsiveImpulsive
�� Lack selfLack self--controlcontrol
�� HostilityHostility
�� ResentmentResentment
�� Destructiveness Destructiveness
�� Ambivalence toward authority Ambivalence toward authority
Antisocial Personality Disorder Antisocial Personality Disorder
�� APD is pervasive pattern of disregard for APD is pervasive pattern of disregard for and the violation of rights of others that and the violation of rights of others that begins in childhood or adolescence and begins in childhood or adolescence and continues into adulthood. Diagnosis is for continues into adulthood. Diagnosis is for adults, 18yoa.adults, 18yoa.�� DeceitfulnessDeceitfulness
�� Impulsivity Impulsivity
�� Lack of remorseLack of remorse
�� Consistent irresponsibility Consistent irresponsibility
�� Reckless disregard for safety of self or others Reckless disregard for safety of self or others
Learning theoryLearning theory
�� Some believe that delinquency is learned Some believe that delinquency is learned
behaviorbehavior
�� Learning is both psychological as well as a Learning is both psychological as well as a
social processsocial process
�� Classical conditioning Classical conditioning
�� We learn by connecting a stimulus with a We learn by connecting a stimulus with a
responseresponse
�� PavlovPavlov’’s dogss dogs
�� Modeling Modeling
�� We model or imitate behaviorWe model or imitate behavior
�� BF SkinnerBF Skinner
�� Operant conditioning is controlled by the Operant conditioning is controlled by the
consequences of the behaviorconsequences of the behavior
�� Consequences that increase the behavior are Consequences that increase the behavior are
reinforcersreinforcers
�� PraisePraise
�� MoneyMoney
�� Consequences that decrease behavior are Consequences that decrease behavior are
punisherspunishers
�� Parental or peer disapprovalParental or peer disapproval
�� ArrestArrest
�� Punishment Punishment