Joints. Classification of Joints Structural Classification – Presence or absence of a space...
-
Upload
joy-joyce-daunt -
Category
Documents
-
view
247 -
download
3
Transcript of Joints. Classification of Joints Structural Classification – Presence or absence of a space...

Joints

Classification of Joints
• Structural Classification– Presence or absence of a space (synovial cavity)/– Type of Connective Tisssue/
• Functional Classification– Relates to the degree of movement they permit.

Structural Classification of Joints
• Fibrous Joints– Fibrous CT– Lack a synovial cavity
• Cartilaginous Joints– Cartilage– Lack a synovial cavity
• Synovial Joints– Have a synovial cavity– Dense irregular CT– Often associated with accessory ligaments

Functional Classification of Joints
• Synarthrosis (syn = together)– Immovable joint
• Amphiarthrosis (amphi = on both sides)– A slightly moveable joint
• Diarthrosis (moveable joint)– A freely moveable joint– Synovial joints

Fibrous Joints
• Lacks a synovial cavity• Little or no movement

Fibrous Joints
• Sutures– Immovable– Synostosis – suture that is replaced by bone in the adult
• Syndesmoses– Slightly moveable (amphiarthrosis)– Ligament– Interosseous membrane
• Gomphoses– Dentoalveolar joint

Cartilaginous Joints
• Lacks a synovial cavity• Allows little or no movement• Synchondroses– Epiphyseal plate
• Symphyses– Pubic symphisis– Intervertebral discs

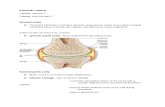
Synovial Joints
• Synovial (Joint) Cavity – space btwn. Bones• Freely moveable• The bones are covered by hyaline cartilage• Contains the following:– Articular capsule– Synovial fluid– Accsessory ligaments and articular discs

Arthroscopy
• Observaion of the interior of a joint• Utilizes a lighted, pencil-thin instrument• Assists in surgery and assessment of the joint
space

Sprain & Strain
• Sprain – a forcible wrenching or twisting of the joint that stretches or tears its ligaments, but does not dislocate the bones.– The ankle joint is the most often sprained.– The lumbar spine is another prominent location of
sprain.
• Strain – a stretched or partially torn muscle.

Bursae & Tendon Sheaths
• Bursae– Saclike structures– Reduce friction in some synovial joints
• Tendon sheaths– Tubelike bursae that wrap around tendons– Occurs where tendons pass through synovial
cavities– Reduce friction

Bursitis
• An acute or chronic inflammation of a bursa• Caused by trauma or infection• Repeated excessive exertion• Symptoms– Pain, swelling, inflammation & limited movement
• Treatment– Oral anti-inflammatory agents (herbal, O.T.C. And
prescription), corticosteroid injections

Types of Synovial Joints
• Plantar Joints• Hinge Joints• Pivot Joints• Condyloid Joints• Saddle Joints• Ball & Socket Joints


Types of Movements at Synovial Joints
• Gliding– Simple back and forth movement, limited in range, planar
joints
• Angular Movements– Increase or decrease in the angle btwn. bones
• Rotation– Bone revolves around a longitudinal axis
• Special Movements

Angular Movements
• Flexion, extension, lateral flexion, hyperextension
• Abduction, adduction, and circumduction

Rotation
• Medial (internal) rotation• Lateral (external) rotation

Special Movements
• Elevation• Depression• Protraction• Retraction• Inversion

Special Movements
• Eversion• Dorsiflexion• Plantar flexion• Supination• Pronation• Opposition

Dislocation
• Luxation – displacement of a bone from a joint– Causes tearing or ligaments, tendons, and
articular capsules
• Subluxation– Incomplete dislocation







Rotator Cuff Injury
• Supraspinatous• Infraspinatous• Teres Minor• Subscapularis• Common injury among pitchers and volleyball
players due to excessive circumduction

Separated Shoulder
• Injury of the acromioclavicular joint• Due to forceful trauma such as when the
shoulder strikes the ground in a fall

Tennis Elbow
• Lateral epicondylitis• Little-league elbow

Golfer’s Elbow
• Medial Epicondylitis

Dislocation of the Radial Head
• The most common upper limb dislocation in children
• Occurs with a strong pull to the forearm while it is extended and supinated
• Swinging a child around with outstretched arms

Swollen Knee
• Immediate swelling is due to blood loss• Delayed swelling is due to excessive
production of synovial fluid “water on the knee”

Dislocated Knee
• Displacement of the tibia relative to the femur• Most commonly dislocates anteriorly

Rheumatism
• Any painful disorder of the supporting structures of the body – bones, ligaments, tendons, or muscles – that is not caused by infection or injury.

Arthritis
• A form of rheumatism in which the joints are swollen, stiff, and painful.

Types of Arthritis
• Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)– Autoimmune disease – the body attacks its own
tissues• Osteoarthritis (OA)– Degenerative joint disease
• Gouty arthritis– A person with gout produces excessive uric acid or
is unable to excrete it properly

Lyme Disease
• First reported in Lyme, CT• Bacteria transported by deer ticks• The rash often resembles a bull’s eye target,
although some people never develop a rash• Symptoms– Joint stiffness, fever, chills, headache, stiff neck,
nausea

Terminology
• Arthralgia – pain in a joint• Bursectomy – removal of a bursa• Chondritis – inflammation of cartilage• Synovitis – inflammation of a synovial
membrane in a joint