ITNE3008 Advanced Switching · the diagram. By default, VLAN 1 is used as the management VLAN....
Transcript of ITNE3008 Advanced Switching · the diagram. By default, VLAN 1 is used as the management VLAN....

ITNE3008 Advanced Switching
Lab Tutorial - 1 of Lesson - 3
July 2019

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 2
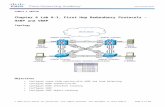
Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology
Objectives
• Set up a VTP domain.
• Create and maintain VLANs.
• Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background
VLANs logically segment a network by function, team, or application, regardless of the physical location of the
users. End stations in a particular IP subnet are often associated with a specific VLAN. VLAN membership on
a switch that is assigned manually for each interface is known as static VLAN membership.
Trunking, or connecting switches, and the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) are technologies that support
VLANs. VTP manages the addition, deletion, and renaming of VLANs on the entire network from a
single central switch.
Note: This lab uses Cisco WS-C2960-24TT- L switches with the Cisco IOS image c2960-lanbasek9-
mz.122-46.SE.bin, and Catalyst 3560-24PS with the Cisco IOS image c3560-advipservicesk9-mz.122-
46.SE.bin. You can use other switches (such as a 2950 or 3550) and Cisco IOS Software versions if they
have comparable capabilities and features. Depending on the switch model and Cisco IOS Software
version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab.

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 3
Required Resources
• 2 switches (Cisco 2960 with the Cisco IOS Release 12.2(46)SE C2960-LANBASEK9-M image or
comparable)
• 2 switches (Cisco 3560 with the Cisco IOS Release 12.2(46)SE C3560-ADVIPSERVICESK9-M
image or comparable)
• 4 PCs (optional)
• Ethernet and console cables
Step 1: Prepare the switches for the lab.
Power up the switches and use the standard process for establishing a HyperTerminal console
connection from a workstation to each switch in your pod. If you are connecting remotely to the switches,
follow the instructions that have been supplied by your instructor.
Remove all VLAN information and configurations that may have been previously entered into the switches.
Refer to Lab 1-1, “Clearing a Switch,” and Lab 1-2, “Clearing a Switch Connected to a Larger Network.”
Step 2: Configure basic switch parameters.
Assign each switch a hostname and configure an IP address on the management VLAN according to
the diagram. By default, VLAN 1 is used as the management VLAN.
Enter basic configuration commands on each switch according to the diagram.
DLS1 example: Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# hostname DLS1
DLS1(config)# interface vlan 1
DLS1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.101 255.255.255.0
DLS1(config-if)# no shutdown
(Optional) On each switch, create an enable secret password and configure the vty lines to allow remote
access from other network devices.
DLS1 example:
DLS1(config)# enable secret cisco
DLS1(config)# line vty 0 15
DLS1(config-line)# password cisco DLS1(config-line)# login
Step 3: Display the switch default VLAN information.
Use the show vlan command in privileged mode on any switch. The following output is for a 2960 switch.

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 4
ALS1# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
Gi0/1, Gi0/2
1002 fddi-default act/unsup 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
Remote SPAN VLANs ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
The following output is for a 3560 switch:
DLS1# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
1002 fddi-default
act/unsup Gi0/1, Gi0/2
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 5
Remote SPAN VLANs ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
Note the default VLAN numbers, names, and associated types, and that all switch ports are automatically
assigned to VLAN 1.
You can use the show vlan command to determine the mode of a port. Ports configured for a particular VLAN
are shown in that VLAN. Ports configured for trunk mode are not associated with a specific VLAN, and so are
not included in the output.
Step 4: Examine VTP information.
A VTP domain, also called a VLAN management domain, consists of trunked switches that are under the
administrative responsibility of a switch or switches in server VTP mode. A switch can be in only one VTP
domain with the same VTP domain name. The default VTP mode for the 2960 and 3560 switches is server
mode. VLAN information is not propagated until a domain name is specified and trunks are set up between
the devices.
The following table describes the three VTP modes.
VTP Mode Description
VTP server You can create, modify, and delete VLANs and specify other
configuration parameters, such as VTP version and VTP
pruning, for the entire VTP domain. VTP servers advertise their
VLAN configuration to other switches in the same VTP domain
and synchronize their VLAN configuration with other switches
based on advertisements received over trunk links.
VTP server is the default mode.
VTP client VTP clients behave the same way as VTP servers, but you
cannot create, change, or delete VLANs on a VTP client.
VTP transparent VTP transparent switches do not participate in VTP. A VTP
transparent switch does not advertise its VLAN configuration nor
synchronize its VLAN configuration based on received
advertisements. Transparent switches do forward VTP
advertisements that they receive out their trunk ports in VTP
Version 2.
Use the show vtp status command on any switch. The output should be similar to the following sample for
DLS1. DLS1# show vtp status
: running VTP1 (VTP2 capable) VTP Version
Revision Configuration : 0
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005
Number of existing VLANs : 5

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 6
VTP Operating Mode : Server
VTP Domain Name : VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP V2 Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
MD5 digest : 0x57 0xCD 0x40 0x65 0x63 0x59 0x47 0xBD
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 0-0-00 00:00:00
Local updater ID is 10.1.1.101 on interface Vl1 (lowest numbered VLAN interface
found)
Because no VLAN configurations were made, all settings are the defaults. Notice that the VTP mode is
server mode. The number of existing VLANs is the five built-in VLANs. The 3560 switch supports 1,005
maximum VLANs locally. The 2960 switch supports 255 VLANs. The configuration revision is 0, and the
default VTP version is 1. All switches in the VTP domain must run the same VTP version.
The importance of the configuration revision number is that the switch with the highest revision number in
VTP server mode propagates VLAN information over trunked ports. Every time VLAN information is
modified and saved in the VLAN database or vlan.dat file, the revision number is increased by one when
the user exits from VLAN configuration mode.
Multiple switches in the VTP domain can be in VTP server mode. These switches can be used to manage
all other switches in the VTP domain. This is suitable for small-scale networks where the VLAN information
is small and easily stored in all switches. In a large network, the administrator must determine which
switches make the best VTP servers. The network administrator should select switches to function as VTP
servers. The other switches in the VTP domain can be configured as clients. The number of VTP servers
should be consistent based on the amount of redundancy desired in the network.
Step 5: Configure VTP on the switches.
Change the VTP domain name on DLS1 to SWLAB using the vtp domain command. If the VTP
version defaults to 1, set it manually to version 2 using the vtp version command.
DLS1(config)# vtp domain SWLAB
Changing VTP domain name from NULL to SWLAB
DLS1(config)# vtp version 2
Note: The newest VTP version, VTPv3, is not supported by the IOS used on the switches in this lab.
However, it is supported in IOS versions 12.2(52)SE and newer on all platforms eligible for this IOS
(2960, 3560, 3750, etc.). VTPv3 has improvements in three major areas.
Better administrative control over which device is allowed to update other devices’ view of the VLAN topology. The chance of unintended and disruptive changes is significantly reduced, and availability is increased.
Functionality for the VLAN environment has been significantly expanded. In addition to supporting the earlier
ISL VLAN range from 1 to 1001, the new version supports the whole IEEE 802.1Q VLAN range up to 4095.
In addition to supporting the concept of normal VLANs, VTP version 3 can transfer information regarding
Private VLAN (PVLAN) structures.
The third area of major improvement is support for databases other than VLAN (for example, MST).
Set up the switches so that the distribution layer switches are in VTP server mode, and the access layer
switches are in VTP client mode. Set the version number to 2 on the DL switches.

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 7
DLS1(config)# vtp mode server
Device mode already VTP SERVER.
Because the default mode is server, you receive a message on DLS1 stating that the device mode
is already VTP server. ALS1(config)# vtp mode client
Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode.
Note: You cannot modify the version in VTP client mode
Use the show vtp status command on either of the AL switches. The output should be similar to the
following sample for ALS1.
ALS1# show vtp status
: running VTP1 (VTP2 capable) VTP Version
Configuration Revision : 0
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 255
Number of existing VLANs : 5
VTP Operating Mode : Client
VTP Domain Name :
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP V2 Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
MD5 digest : 0x57 0xCD 0x40 0x65 0x63 0x59 0x47 0xBD
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 0-0-00 00:00:00
Notice that you do not see the VTP domain name that you set up on DLS1. Because no trunks are set
up between the switches, they have not started to distribute any VLAN information. There is no IP
address (0.0.0.0) or time listed for the last configuration modification.
Step 6: Configure trunking.
The show interfaces switchport command lists the configured mode of each port in detail. The
following partial sample output is for a 2960 switch on Fa0/7.
ALS1# show interfaces fastEthernet 0/7 switchport
Name: Fa0/7
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: dynamic auto Operational Mode: static access
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q
Operational Trunking Encapsulation: native Negotiation of Trunking: On
Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default)
Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled
Voice VLAN: none Administrative private-vlan host-association: none
Administrative private-vlan mapping: none Administrative private-vlan trunk native VLAN: none
Administrative private-vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled
Administrative private-vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private-vlan trunk normal VLANs: none
Administrative private-vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private-vlan: none
Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 8
Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001 Capture Mode Disabled
Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL
Protected: false
Unknown unicast blocked: disabled Unknown multicast blocked: disabled
Appliance trust: none
Ports on the 2960 and 3560 switches are set to dynamic auto by default. This means that they are willing to
negotiate a trunk with the neighbor; however, if both sides are set to dynamic auto, the link will remain in access
mode. This can be done by configuring one end of the trunk using the switchport mode trunk command. On
the 3560 switches, you also need to configure the trunk encapsulation with the switchport trunk
encapsulation command. The 3560 switch can use either Inter-Switch Link (ISL) or 802.1Q
encapsulation, whereas the 2960 switch only supports 802.1Q.
Refer to the lab diagram for which ports to set up as trunks and the type of encapsulation to use.
Configure only the interfaces on DLS1 and ALS1 with the switchport mode trunk command, and leave
DLS2 and ALS2 as the default port types for Fast Ethernet interfaces 0/9–0/12. Fast Ethernet 0/7 and 0/8
of DLS2 also need to be configured with the switchport mode trunk command for the trunks connecting
DLS2 and ALS2.
The 2960 and 3560 switches have a range command that you can use to designate multiple individual ports
or a continuous range of ports for an operation. Use the interface range command to configure all trunk
ports at once for trunking.
The following is a sample configuration for the 802.1Q trunk ports on DLS1. DLS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 - 10
DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk DLS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/11 - 12 DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk
The following is a sample configuration for the trunk ports on ALS1.
ALS1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 – 12
ALS1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
The following is a sample configuration for the trunk ports on DLS2.
DLS2(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 - 8 DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk
Note: This lab uses dynamic trunking protocol (DTP) to negotiate trunking, which can lead to security issues.
In general, when configuring trunks, it is a good practice to deactivate DTP using the switchport
nonegotiate command and configure all trunks statically.

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 9
Step 7: Verify trunk configuration.
Use the show interfaces fastEthernet 0/7 switchport command on ALS2. ALS2# show interfaces fastEthernet 0/7 switchport
Name: Fa0/7
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: dynamic auto
Operational Mode: trunk
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q
Negotiation of Trunking: On
Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default)
Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default)
Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none
Administrative private-vlan host-association: none Administrative private-vlan mapping: none
Administrative private-vlan trunk native VLAN: none
Administrative private-vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private-vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q
Administrative private-vlan trunk normal VLANs: none
Administrative private-vlan trunk private VLANs: none
Operational private-vlan: none
Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001
Capture Mode Disabled
Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL
Protected: false Unknown unicast blocked: disabled
Unknown multicast blocked: disabled
Appliance trust: none
Notice that administrative mode on Fa0/7 is still the default dynamic auto. Fa0/7 on ALS2 is operating as a
trunk, because port Fa0/7 of DLS2 was configured using the switchport mode trunk command. Once this
command was issued, trunking was negotiated between the two switch ports.
Use the show interfaces trunk command on DLS1.
DLS1# show interfaces trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa0/7 on 802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/8 on 802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/9 on 802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/10 on 802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/11 on 802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/12 on 802.1q trunking 1
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Fa0/7 1-4094 Fa0/8 1-4094
Fa0/9 1-4094 Fa0/10 1-4094 Fa0/11 1-4094
Fa0/12 1-4094
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/7 1

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 10
Fa0/8 1 Fa0/9 1 Fa0/10 1
Fa0/11 1
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/12 1
Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
Fa0/7 1 Fa0/8 1 Fa0/9 1 Fa0/10 1 Fa0/11 1
Fa0/12 none
Note: By default, all VLANs are allowed on all trunks. You can explicitly control which VLANs are allowed
on a trunk by using the switchport trunk allowed vlan vlan-id command on the interface at each end of
the trunk. In addition, you can specify a native VLAN other than the default VLAN 1, using the switchport
trunk native vlan vlan-id command. These two measures can help reduce the possibility of VLAN attacks.
Use the show interfaces trunk command on DLS2.
DLS2# show interfaces trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa0/7 on 802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/8 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/9 auto n-802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/10 auto n-802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/11 auto n-802.1q trunking 1
Fa0/12 auto n-802.1q trunking 1
Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/7 1-4094 Fa0/8 1-4094 Fa0/9 1-4094 Fa0/10 1-4094 Fa0/11 1-4094
Fa0/12 1-4094
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/7 1 Fa0/8 1 Fa0/9 1 Fa0/10 1
Fa0/11 1
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/12 1
Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
Fa0/7 1 Fa0/8 1 Fa0/9 1 Fa0/10 1 Fa0/11 1
Fa0/12 1

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 11
Notice the highlighted portion of the above output from DLS2 where it indicates that these ports became
trunks by negotiation. For example, port Fa0/9 mode is Auto and encapsulation is n-802.1q. The “n”
indicates the 802.1q encapsulation was negotiated. The connected ports of the respective switches
were configured using the switchport mode trunk command.
Step 8: Configure access ports.
A port on the 2960 switch can operate in one of three modes, and a port on the 3560 switch can operate in
one of five modes. Use the switchport mode ? command for interface Fast Ethernet 0/6 in interface
configuration mode to view the modes.
The following command output is for a 2960 switch. ALS1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6
ALS1#(config-if)# switchport mode ?
access Set trunking mode to ACCESS unconditionally
dynamic Set trunking mode to dynamically negotiate access or trunk mode
trunk Set trunking mode to TRUNK unconditionally
The following command output is for a 3560 switch.
DLS1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6
DLS1(config-if)# switchport mode ?
access Set trunking mode to ACCESS unconditionally
dot1q-tunnel set trunking mode to TUNNEL unconditionally
dynamic Set trunking mode to dynamically negotiate access or trunk
mode
Set the mode to private-vlan host or promiscuous private-vlan
trunk Set trunking mode to TRUNK unconditionally
The Fast Ethernet ports connected to the hosts on the network can be set up as static access because they
are not to be used as trunk ports. Use the switchport mode access command to set the access mode on
the Fast Ethernet 0/6 port on all four switches in the pod.
The following is a sample configuration for the access port on ALS1.
ALS1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6
ALS1(config-if)# switchport mode access
Use the show interfaces command for Fast Ethernet 0/6 to verify the configuration.
The following command is for a 3560 switch. DLS1# show interfaces fastEthernet 0/6 switchport
Name: Fa0/6
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: static access Operational Mode: down
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate
Negotiation of Trunking: Off
Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default)
Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled
Voice VLAN: none Administrative private-vlan host-association: none
Administrative private-vlan mapping: none

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 12
Administrative private-vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private-vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled
Administrative private-vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private-vlan trunk normal VLANs: none
Administrative private-vlan trunk private VLANs: none
Operational private-vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL
Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001 Capture Mode Disabled
Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL
Protected: false
Unknown unicast blocked: disabled Unknown multicast blocked: disabled
Appliance trust: none
Note that administrative mode has now changed to static access and that trunking negotiation is off.
The Fast Ethernet 0/6 ports on all four switches are now statically set to connect to a host device.
Step 9: Verify VTP configuration.
Before configuring the VLANs, verify the VTP configuration within the domain by using the show vtp status
command on ALS1 and ALS2.
The following sample output is from ALS1. ALS1# show vtp status
: running VTP2 VTP Version
Configuration Revision : 1
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 255
Number of existing VLANs : 5
VTP Operating Mode : Client
VTP Domain Name : SWLAB
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP V2 Mode : Enabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
MD5 digest : 0xD1 0xC0 0x36 0xF9 0xC4 0x3E 0x73 0xA0
Configuration last modified by 10.1.1.101 at 3-1-93
00:12:43 The following sample output is from ALS2.
ALS2# show vtp status
: running VTP2 VTP Version
Configuration Revision : 1
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 255
Number of existing VLANs : 5
VTP Operating Mode : Client
VTP Domain Name : SWLAB
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP V2 Mode : Enabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
MD5 digest : 0xD1 0xC0 0x36 0xF9 0xC4 0x3E 0x73 0xA0
Configuration last modified by 10.1.1.101 at 3-1-93 00:12:43
At this point, all switches in the lab are in VTP domain SWLAB and have five existing VLANs. All are
running VTP version 2. DLS1 and DLS2 are configured as VTP servers, and ALS1 and ALS2 are configured
as clients.
Note: You can limit the VLAN traffic passed between switches using VTP pruning. Pruning increases
available bandwidth by restricting flooded traffic to those trunk links that the traffic must use to access the

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 13
destination devices. You can enable VTP pruning on a switch in VTP server mode using the vtp pruning
command. For example, if a VLAN is not defined on access switch ALS1 but is defined on distribution
switches DLS1 and DLS2, the VLAN will be pruned from the trunk links between ALS1 and the
distribution switches but not from the link between the two distribution switches.
Step 10: Configure VLANs by assigning port membership.
VLANs can be configured on a switch in different ways, depending on the type of switch used and the Cisco
IOS version.
An older way to configure VLANs is to use the VLAN database. This method is being deprecated and is no
longer recommended. However, the VLAN database is still accessible for those who choose to use it. For
example, the following command is for a 3560 switch.
DLS1# vlan database
% Warning: It is recommended to configure VLAN from config mode, as
VLAN database mode is being deprecated. Please consult user
documentation for configuring VTP/VLAN in config mode.
A more current method to create a VLAN is to assign a port to a VLAN that does not yet exist. If the switch
is in VTP Server or Transparent mode, it automatically creates the VLAN to the port that it has been
assigned to.
VLAN 1 is the management VLAN by default. By default, all ports are set to dynamic mode and their access
VLAN is set to 1. There is no need to create a VLAN 1, assign ports to it, or to set the mode of each port.
According to the lab diagram, VLANs 100, 110, and 120 must be created, and port 6 must be assigned to
each VLAN. You will create VLANs 100 and 110 on the distribution switches using the port assignment
method. You will create VLAN 120 for the access switches using global configuration commands and
then assign ports to those VLANs.
Use the switchport access vlan command to assign port 6 on DLS1 and DLS2, according to the diagram.
Port Fast Ethernet 0/6 of DLS1 will be assigned to VLAN 100, and Fast Ethernet 0/6 on DLS2 will be
assigned to VLAN 110.
The following command is for the 3560 switches.
DLS1(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/6 DLS1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 100
% Access VLAN does not exist. Creating vlan 100
VLAN 100 was created at the same time port 6 was assigned to it.
Configure DLS2 in the manner similar to DLS1, but this time use VLAN 110.
DLS2(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/6 DLS2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 110
% Access VLAN does not exist. Creating vlan 110
Issue the show vlan command on DLS1 to verify that VLANs 100 and 110 have been created. The
output should be similar to the following output.
DLS1# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- -----------------------------

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 14
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
Fa0/18
Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17,
Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21,
Fa0/22
Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
100 VLAN0100
active Fa0/6 110 VLAN0110 active 1002 fddi-default act/unsup 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
-------- ------ ----- ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ----
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
100 enet 100100 1500 - - - - - 0 0
110 enet 100110 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ----- ---- -----
1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
Remote SPAN VLANs
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- ----------------- -----------------------------------------
Because VLAN 100 and 110 were not named, the switch automatically assigns default names, which are
VLAN0100 and VLAN0110.
Note that on DLS1, port Fa0/6 is active in VLAN 100. A show vlan command issued on DLS2 should
show port Fa0/6 active in VLAN 110.
Step 11: Configure VLANs in configuration mode.
Another way of creating VLANs is to create them in configuration mode without assigning port membership.
You can create a VLAN in global configuration mode using the vlan command. Because ALS1 and ALS2 are
configured for VTP client mode and it is not possible to create a VLAN when a switch is in client mode, you
must create the VLAN on the switch that is acting as a server for the network. The VLAN then propagates to
the other switches that are in client mode.
Issue the vlan command in global configuration mode on DLS1.
DLS1(config)# vlan 120
Ports still need to be assigned to VLAN 120. Port assignment to a VLAN is an interface configuration
operation. Use the switchport access vlan command on Fast Ethernet 0/6 of ALS1 and ALS2 to configure
ports for VLAN 120.

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 15
ALS1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6
ALS1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 120
ALS2(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/6
ALS2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 120
Use the show vlan command to verify the creation of VLAN 120, with port Fa0/6 assigned to it. The output
should be similar to the following.
ALS1# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports ---- ------------------------------ --------- -----------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15
Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19
Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
100 VLAN0100 active Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
110 VLAN0110 active
Fa0/6
120 VLAN0120 active 1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ----- ---- -----
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
100 enet 100100 1500 - - - - - 0 0
110 enet 100110 1500 - - - - - 0 0
120 enet 100120 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ----- ---- -----
1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - srb 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
Remote SPAN VLANs
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports ------- --------- ----------------- -----------------------------------------
Step 12: Change the VLAN names.
The VLANs have not been named yet. Naming VLANs can help network administrators identify the
functionality of those VLANs. To add names, use the name command in VLAN configuration mode.
The following is a sample configuration for naming the three VLANs created in the domain.

ITNE3008 Lab Tutorial 3
Copyright © 2015-2018 VIT, All Rights Reserved. 16
DLS1(config)# vlan 100 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Server-Farm-1 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit
DLS1(config)# vlan 110 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Server-Farm-2 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit
DLS1(config)# vlan 120 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Net-Eng
DLS1(config-vlan)# exit
Use the show vlan command on DLS1 to verify that the new names have been added.
DLS1# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13
Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17
Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21
Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1
Gi0/2
Fa0/6
100 Server-Farm-1 active
110 Server-Farm-2 active
120 Net-Eng active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
100 enet 100100 1500 - - - - - 0 0
110 enet 100110 1500 - - - - - 0 0
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
120 enet 100120 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
Remote SPAN VLANs
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports ------- --------- ----------------- ---------------------------------------