Iptv
-
Upload
asmaa-maher -
Category
Technology
-
view
360 -
download
1
Transcript of Iptv

IPTVماهر اسماء
مصطفىخليفة علي سريه
محمد
رويدا / د

AgendaIntroduction.Architecture.IPTV Services.Underlying Protocols.Contact between User and IPTV.Privacy and Security.Transport models.

Introduction
IPTV
IPTV and Internet TV
Why IPTV?

IPTV Internet Protocol Television(TV + IP). is a system through which television services are
delivered using the Internet protocol suite over a packet-switched network such as the Internet.
is defined as multimedia services delivered over IP based networks managed to provide the required level of quality of service and experience, security, interactivity and reliability.

IPTV and Internet TV.IPTV : delivered to TV set, not PC A set-top box (STB) or set-top unit (STU)
Internet TV (ITV): anyone can create an endpoint and publish
that on a global basis. (YouTube)

Why IPTV? Consumers want more and higher quality
service. IPTV has the potential to offer an interactive,
customized experience. Network infrastructure today has become
highly evolved and is required to support converged IP applications.

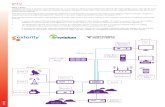
Architecture
Depending on the network architecture of the service provider
there are two main types of video server architecture that can be considered for IPTV deployment centralized and distributed.

IPTV serviceslive TV
with or without interactivity related to the current TV show.
Time-shifted TVCatch-up TV (replays a TV show that was broadcast hours or days ago)Start-over TV (replays the current TV show from its beginning).
Video On Demand(VOD)browse a catalog of videos, not related to TV programming.

IPTV ProtocolsThe primary underlying protocols: Internet group management protocol (IGMP):
live multicast stream. changing from one live multicast stream to another.
real time streaming protocol (RTSP):based unicast only live and VoD streaming.
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol(HTTP)

Contact between User and IPTV
How to subscribe to IPTV?
Constraints to subscribe IPTV
How to send from IPTV to User?
How can I get IPTV?

How to subscribe to IPTVUser can subscribe to it over broadband local networks
(LAN).
Broadband support QOS.Multicast , Separation of end user traffic. Differentiate between services.Must support Secure and Robust.

Constraints to subscribe IPTVDigital TV.High speed internet connection.Bandwidth.Set-top-box

How to send from IPTV to User ??
Sending ways
One-to-one (Unicast)One-to-many (Multicast)

One-to-one (Unicast)A Model required to deliver unique content
to a single user.Point-to-Point connection between user and
the media in the network.

One-to-many (Multicast)BeginningAs a single stream that is transported
through the network .Then duplicated for hundreds or even
thousands of end-users .
Ending Receiving same data at same time without
overloading the network or video server .

One-to-many (Multicast)Multicast 1. Efficiently Controls network traffic 2. Reduces server and CPU loads3. Eliminates traffic redundancy4. Makes Multipoint applications possible

Now, How can I get IPTV ???
Distribution Models
LIVE content Stored content

LIVE and Stored ContentLIVE contentMulticast stream.Start from where it is. No control.
Stored contentUnicast stream.Start from beginning.Control it (play, pause, stop).

Privacy and SecurityIPTV
The home network must be a closed one.Users
It should be a secure network where access is limited only to users and concerned devices within the home.

Transport Model
Transport Model
Centralized Distributed

Centralized Model
From one broadcast center.Easy and simple to manage.Cheaper.Bandwidth limitation.

Distributed ModelSeveral systems.Synchronization.More maintenance.Very reliable.No limit on usage.