Ionic bonds
Transcript of Ionic bonds

Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds

LecturePLUS Timberlake 2
Chapter 4
Compounds and Their Bonds
4.1 Valence Electrons
4.2 Octet Rule and Ions

LecturePLUS Timberlake 3
Chemical Bonds
Attraction between two or more atoms
Interaction between valence electrons
Ionic bonds
Covalent bonds

4
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the highest (outer) electron level
Have most contact with other atoms
Known as valence electrons
Outer shells of noble gases contain 8 valence electrons (except He = 2)
Example: Ne 2, 8
Ar 2, 8, 8LecturePLUS Timberlake

5
Electron Dot Structures
Symbols of atoms with dots to represent the valence-shell electrons
1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A
H He:
Li Be B C N O : F :Ne :
Na Mg Al Si P S :Cl :Ar :

LecturePLUS Timberlake 6
Learning Check
A. X would be the electron dot formula for
1) Na 2) K 3) Al
B. X would be the electron dot formula
1) B 2) N3) P

LecturePLUS Timberlake 7
Solution
A. X would be the electron dot formula for
1) Na 2) K
B. X would be the electron dot formula
2) N 3) P

LecturePLUS Timberlake 8
Octet Rule
An octet in the outer shell makes atoms stable
Electrons are lost, gained or shared to form an octet
Unpaired valence electrons strongly influence
bonding

LecturePLUS Timberlake 9
Formation of Ions from Metals
Ionic compounds result when metals react with nonmetals
Metals lose electrons to match the number of valence electrons of their nearest noble gas
Positive ions form when the number of electrons are less than the number of protons
Group 1A metals ion 1+
Group 2A metals ion 2+
• Group 3A metals ion 3+

10
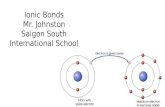
Formation of Sodium Ion
Sodium atom Sodium ion
Na – e Na +
2-8-1 2-8 ( = Ne)
11 p+ 11 p+
11 e- 10 e-
0 1+

11
Formation of Magnesium Ion
Magnesium atom Magnesium ion
Mg – 2e Mg2+
2-8-2 2-8 (=Ne)
12 p+ 12 p+
12 e- 10 e-
0 2+

12
Some Typical Ions with Positive Charges (Cations)
Group 1A Group 2AGroup 3A
H+ Mg2+ Al3+
Li+ Ca2+
Na+ Sr2+
K+ Ba2+

13
Learning Check
A. Number of valence electrons in aluminum
1) 1 e- 2) 2 e- 3) 3 e-
B. Change in electrons for octet
1) lose 3e- 2) gain 3 e- 3) gain 5 e-
C. Ionic charge of aluminum
1) 3- 2) 5- 3) 3+

14
Solution
A. Number of valence electrons in aluminum
3) 3 e-
B. Change in electrons for octet
1) lose 3e-
C. Ionic charge of aluminum
3) 3+

LecturePLUS Timberlake 15
Learning Check
Give the ionic charge for each of the following:
A. 12 p+ and 10 e-
1) 0 2) 2+ 3) 2-
B. 50p+ and 46 e-
1) 2+ 2) 4+ 3) 4-
C. 15 p+ and 18e-
2) 3+ 2) 3- 3) 5-

LecturePLUS Timberlake 16
Solution
Give the ionic charge for each of the following:
A. 12 p+ and 10 e-
2) 2+
B. 50p+ and 46 e-
2) 4+
C. 15 p+ and 18e-
2) 3-

LecturePLUS Timberlake 17
Learning Check
A. Why does Ca form a Ca2+ ion?
B. Why does O form O2- ion?

LecturePLUS Timberlake 18
Solution
A. Why does Ca form a Ca2+ ion?
Loses 2 electrons to give octet
2-8-8-2 2-8-8 (like Ar)
B. Why does O form O2- ion?
Gains 2 electrons to give octet
2-6 + 2e- 2-8 (like Ne)

19
Ions from Nonmetal Ions
In ionic compounds, nonmetals in
5A, 6A, and 7A gain electrons from
metals
Nonmetal add electrons to achieve
the octet arrangement
Nonmetal ionic charge:
3-, 2-, or 1-

LecturePLUS Timberlake 20
Fluoride Ion
unpaired electron octet
1 -
: F + e : F :
2-7 2-8 (= Ne)
9 p+ 9 p+
9 e- 10 e- 0 1 -
ionic charge

LecturePLUS Timberlake 21
Learning CheckComplete the names of the following ions:
5A 6A 7A N3 O2 F
nitride __________ fluoride
P3 S2 Cl
___________ __________ _________
Br
_________

LecturePLUS Timberlake 22
Solution
5A 6A 7A
N3 O2 F
nitride oxide fluoride
P3 S2 Cl
phosphide sulfide chloride
Br
bromide