Introduction to Microbiology - JU Medicine · Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body") 7. Cytoskeleton 8....
Transcript of Introduction to Microbiology - JU Medicine · Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body") 7. Cytoskeleton 8....

Introduction to
Microbiology
Anas Abu-HumaidanM.D. Ph.D.
Lecture 2

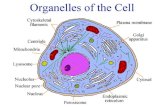
1. Nucleolus2. Nucleus3. Ribosome (80S)4. Vesicle5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum6. Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body")7. Cytoskeleton8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum9. Mitochondrion10. Vacuole11. Cytosol12. Lysosome13. Centriole
Cell structure / Eukaryotes

Cell structure / Eukaryotes / Nucleus
• The nucleus contains the genome, and is surrounded by a porus membrane to traffic proteins.
• The nucleolus is important in ribosome biogenesis.
• DNA wraps around histonesforming nucleosomes, which coil to form fibers called chromatin which coils and loops to form chromosomes.

1. Nucleolus2. Nucleus3. Ribosome (80S)4. Vesicle5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum6. Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body")7. Cytoskeleton8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum9. Mitochondrion10. Vacuole11. Cytosol12. Lysosome13. Centriole
Cell structure / Eukaryotes

1. Nucleolus2. Nucleus3. Ribosome (80S)4. Vesicle5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum6. Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body")7. Cytoskeleton8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum9. Mitochondrion10. Vacuole11. Cytosol12. Lysosome13. Centriole
Cell structure / Eukaryotes

1. Nucleolus2. Nucleus3. Ribosome (80S)4. Vesicle5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum6. Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body")7. Cytoskeleton8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum9. Mitochondrion10. Vacuole11. Cytosol12. Lysosome13. Centriole
Cell structure / Eukaryotes

Cell structure / Eukaryotes / Vesicles
• A lipid bilayer, similar to the cell membrane, that functions in compartmentalizing cellular processes and substances.
• Involved in metabolism, transport and storage of molecules, as well as reaction chambers.
• Include: Vacuoles, lysosomes, transport vesicles and secretory vesicles.

1. Nucleolus2. Nucleus3. Ribosome (80S)4. Vesicle5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum6. Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body")7. Cytoskeleton8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum9. Mitochondrion10. Vacuole11. Cytosol12. Lysosome13. Centriole
Cell structure / Eukaryotes

Cell structure / Eukaryotes / Cytoskeleton
• The cytoskeleton is a scaffold that holds the structure of the cell, and facilitates transport in the cell, as well as motility and migration.
• Microfilaments are polymers of the protein actin.
• Cillia and flagella are made of microtubules (protein cylinders made of tubulin) enclosed in a membrane.
Actin Tubulin

Cell structure / Prokaryotes
• Circular DNA is packaged in nucleoid. More than one nucleoid can be found, but all are similar (haploid).
• Cytoplasm contains smaller ribosomes (70S), and inclusion bodies that function in the storage of energy or as a reservoir of structural building blocks (e.g. Glycogen, PHB, polyphosphate).
• Cell membrane have high protein density, and lacks sterols found in eukaryotes.

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ Cell membrane functions
1. Permeability and transport (active and passive).
2. Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation
3. Excretion of hydrolytic exoenzymes and pathogenicity proteins.
4. Biosynthetic functions
5. Chemotactic systems

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ Gram (+) Cell wall
• High tensile strength owing to Peptidoglycans.
• Plays a role in cell division and its own synthesis. And is an antigenic determinant.
• Teichoic acid is found in Gram(+) bacteria and contributes to tensile strengh, porousity and antiginicity.

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ Gram (-) Cell wall
• Smaller peptidoglycan layer, but an extra outer membrane, with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) outer leaflet.
• Antibiotics pass slowly through the outer membrane contributing to the high antibiotic res. of Gram (-)s.
• Permiplasm contains transporters and detoxifiers (e.g. β-lactamase, important in antibiotic resistance).

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ Cell wall
• Mycoplasmas lack a cell wall, leading to variability in shape, and resistance to antibiotics that attack the cell wall.
• Some bacteria form an external layer of polysaccharides called a capsule when rigid, or a slime layer when loose, which contributes to invasiveness and resistance to phagocytosis.

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ staining

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ staining / Gram staining

Cell structure / Prokaryotes/ staining/ Acid-fast staining

Further reading:
• Jawetz, Melnick & Adelberg's Medical Microbiology, 26th edition-Section 1: Fundamentals of Microbiology-
Chapter 2: Cell Structure