Introduction to differential equation
-
Upload
islamic-university-kushtia -
Category
Education
-
view
1.727 -
download
104
Transcript of Introduction to differential equation

Introduction to Differential Introduction to Differential EquationsEquations
CSE:108
Bappa SarkarLecturerCSE, IU, Kushtia

Definition:
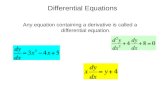
A differential equation is an equation containing an unknown function and its derivatives.
32 xdxdy
032
2
aydxdy
dxyd
364
3
3
ydxdy
dxyd
Examples:.
y is dependent variable and x is independent variable, and these are ordinary differential equations
1.
2.
3.
Ordinary differential equations

Partial Differential EquationExamples:
02
2
2
2
yu
xu
04
4
4
4
tu
xu
tu
tu
xu
2
2
2
2
u is dependent variable and x and y are independent variables, and is partial differential equation.
u is dependent variable and x and t are independent variables
1.
2.
3.

Order of Differential Equation The order of the differential equation is order of the highest derivative in the differential equation.
Differential Equation ORDER
32 x
dxdy
0932
2
ydxdy
dxyd
364
3
3
ydxdy
dxyd
1
2
3

Degree of Differential Equation
Differential Equation Degree
032
2
aydxdy
dxyd
364
3
3
ydxdy
dxyd
0353
2
2
dxdy
dxyd
1
1
3
The degree of a differential equation is power of the highest order derivative term in the differential equation.

Linear Differential Equation A differential equation is linear, if
1. Dependent variable and its derivatives are of degree one,2. Coefficients of a term does not depend upon dependent
variable.
Example:
364
3
3
ydxdy
dxyd
is non - linear because in 2nd term is not of degree one.
.0932
2
ydxdy
dxydExample:
is linear.
1.
2.

Example:3
2
22 x
dxdyy
dxydx
is non - linear because in 2nd term coefficient depends on y.
3.
Example:
is non - linear because
ydxdy sin
!3
sin3yyy is non – linear
4.

First Order Ordinary Differential equation
8

Second order Ordinary Differential Equation
9

nth – order linear differential equation
1. nth – order linear differential equation with constant coefficients.
xgyadxdya
dxyda
dxyda
dxyda n
n
nn
n
n
012
2
21
1
1 ....
2. nth – order linear differential equation with variable coefficients
xgyxadxdyxa
dxydxa
dxydxa
dxdyxa n
n
nn
012
2
2
1
1 ......
10