Introduction to building wireframes
Transcript of Introduction to building wireframes
Introduction to Building Wireframes
General Assemblyhttp://bit.ly/wireframing_intro
Hong Qu @hqu
My Professional Experience
● Web Developer● UC Berkeley● YouTube● Google● Upworthy
Resources are on in the last slides
http://bit.ly/wireframing_intro
Outline of class
1. Introductions○ What project(s) are you working on?○ What tools do you currently use to build wireframes?
2. What do you want to get out of the class?3. Case studies4. Introduction to User Centered Design5. Workshop
○ design concepts and methods○ hands on demo of software tools
6. Hands on exercise7. Design exercise8. When to build wireframes (in design process)?9. Summary
Big Picture Design Process
● Human Computer Interaction (HCI)● User Centered Design
○ Adaptive Path○ Ideo
@landay professor University of Washington
What is Design Thinking?
As a style of thinking, it is generally considered the ability to combine● empathy for the context of a problem, ● creativity in the generation of insights and solutions, ● and rationality to analyze and fit solutions to the context.
Source: Wikipedia definition of Design Thinking
Source: Bill Buxton's book Sketching User Experiences
Discussion: Goals, Personas, Tasks● Remember that goals:
○ Are what the user wants to do, but not how the user achieves them
○ Do not to make any assumptions about the system interface○ Can be used to compare different interface design alternatives in
a fair way○ Can be personal, practical, or false (don't focus on false goals!)
● Remember that personas:○ Are very specific, although not necessarily accurate○ Are based in large part on the goals.
● Remember that tasks:○ Describe the steps necessary to achieve the goals○ Can vary with the available technology○ Are broken down into steps for task analysis, and are
recombined into sequence of steps for scenario development○ How to do task analysis: Hierarchical Task Analysis○
source: UC Berkeley UI Design Course by Professor Marti Hearst
source: User Interface Design and Developmenthttp://courses.ischool.berkeley.edu/i213/s07/lectures.html
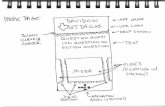
What is a wirefame?
1. Wireframe2. Paper prototype3. Mockup4. Design spec5. Interactive prototype
Presentation on Wireframing using Balsamiqhttp://prezi.com/kbu_fak6srfl/wireframing/
What are the goals for making wireframes?1. concept exploration
○ Parallel Design2. layout content on pages3. brainstorm interactions4. communicate5. storytelling6. build consensus7. documentation8. artifact for user feedback9. minimize risk of the product design turns out to be unusable
Lean startupUser centered design processPaper prototyping
“A blueprint from which designers, developers, architects and project managers will work and
make sure everyone is in sync."
20 Steps to Better Wireframing
"In the early design phase you're more interested in the navigation, workflow, terminology and functionality than in
details of the visual design."
7 myths about paper prototyping
http://divergentmba.wordpress.com/2011/03/14/sketching-user-experiences-by-bill-buxton/
source: http://semanticstudios.com/publications/semantics/000228.php
Rapid Prototyping
Low Fidelity
Scott Klemmerhttp://www.hci-class.org/
Case study: YouTube Playlists
http://www.slideshare.net/hongqu/quicklist-design-process
Where do ideas come from?
Inspiration● Competitive analysis● Design patterns● Metaphors● Existing behavior offline● Mental models● Conceptual diagram● System modeling
Analysis● User goals
○ Personas○ Scenarios
● Tasks○ Primary task○ Secondary task○ Subtasks
● Content inventory● Sitemap● Features● Value to product● User lifecyle
○ Creating engaged and passionate users
http://www.ideo.com/work/method-cards/
Task analysis
Hierarchical task analysis requires a detailed understanding of users’ tasks. You can achieve this understanding by
identifying users’ primary goals detailing the steps users must perform to accomplish their goals optimizing these procedures
source: http://www.uxmatters.com/mt/archives/2010/02/hierarchical-task-analysis.php
Progressive Disclosure
"Progressive disclosure defers advanced or rarely used features to a secondary screen, making applications
easier to learn and less error-prone."
Jakob Nielsen’s Alertbox: December 4, 2006
Discussion: Design patterns● Media/content
○ huffingtonpost.com○ thedailybeast.com
● Branding/advertising○ Nike
● eCommerce○ Gilt Groupe○ Fab.com
● Platform○ Twitter○ bagcheck.com○ Instagr.am○ Pinterest
● Games● Mobile● Hybrids
○ Nowness.com
Inventory of content and data
Meet with your content team and your engineering team to gather a laundry list of all the raw data.
Divide the data into modules.
Layout the modules in a wireframe.
For each module, create variations depending on context, such as if user is logged in or logged out.
Go back to your site map to walk through a task using these data modules.
Verbs
Source: http://glennas.wordpress.com/2009/11/14/defining-requirements-for-social-web-applications-%E2%80%93-part-4-defining-core-user-actions/
Tools for building wireframes
Tools
Software○ PC users - Balsamiq
■ Free web based demo■ mockupstogo.net
○ Mac users - Omnigraffle■ graffletopia.com
○ Skitch (capture screenshots)
Omnigraffle is the industry standard and has advanced features.
Stencils
OmnigraffleKonigiGraffletopiaiPhoneiPad
Balsamiqmockupstogo.net
Hands on wireframe design exercise
Build a wireframe for:
http://www.google.comhttp://www.twitter.com
Finding the stencil shapes may be difficult
Advanced features in omnigraffle Clickable prototypes
Build wireframes
● Install Omnigraffle or Balsamiq● Adding stencils● Create sitemap● Take screenshots of images and "props"● Create concept flow diagram (optional)● Build page wireframes● Walkthrough all the tasks using the wireframes
Are my wireframe designs good (usable)?
Testing Methods○ Paper prototype testing○ 5 Second Test
○ Sketch from memory○ Participatory design
○ Refrigerator magnetics○ Testing Whether Web Page Templates are Helpful
○ Heuristic Evaluation○ 10 Hueristics○ Cognitive Walkthrough
Successful DesignThe user looks through all the wireframe screens and is able to coherently explain:
The user's mental model matchs how the system works.
A mental model is what the user believes about the system at hand.source: http://www.useit.com/alertbox/mental-models.html
"How would you explain how [this product] works to a friend?"
3 Reasons Designs Fail
1. Users are not motivated to achieve this goal - Incentive○ goal and tasks analysis
2. Users don't understand how it works - Learnability ○ mental model
3. Users don't see it - Discoverability○ visibility and affordance
Summary● Define your goals (business metrics, KPI)● Personas and Scenarios● Sitemap● Tasks Analysis● Wireframes are artifacts for
○ exploring concepts○ guiding the developers○ gathering user feedback○ building concensus among the team○ documenting specs○ minimizing risk of unusable UI
● Get inspiration and do analysis from○ metaphors○ competitors○ design patterns○ task analysis○ content inventory○ aligning company goals and with users' goals, tasks, and incentives
● Build wireframes● Test wireframes
Source: Book Design of Everyday Things
Gulf of Execution and Evaluation
Don Norman
The Gulf of execution
●The difference between the intentions and the allowable actions
The Gulf of evaluation
●Reflects the amount of effort that the person must exert to interpret the physical state of the system and to determine how well the the expectations and intentions have been met.
Human Perception PrinciplesProvide a good conceptual model● A conceptual model allows the user to understand the operation of the
device.● A good conceptual model allows the user to predict the effects of their
actions.Make things visible/audiable● By looking,listening,etc, the user can tell the state of the device and the
alternatives for action.The Principle of Mapping● The relationship between two things
○ Natural mapping○ Physical analogies○ Cultural standards
The Principle of Feedback● Sending back information to the user on what has been accomplished.● The user should receive full and continuous feedback about results of
actions.Source: http://www.idc.ul.ie/mikael/CS4358/lecture04.html
ResourcesArticles
● 7 myths about paper prototyping● Using Wireframes to Streamline Your
Development Process● 15 Desktop and Online Wireframing
Tools● 20 Steps to Better Wireframing
UX General● Video Interviews with usability gurus● Jacob Nielsen's Alertbox articles● User Experience Deliverables
Design guidelines● 10 Usability Heuristics● Yahoo! Design Pattern Library● Welie● IDEO method cards● Cognitive science informs design
Tools● PC - Balsamiq
○ mockupstogo.net● Mac - Omnigraffle
○ graffletopia.com● Pop mobile app● Web - Mockingbird● Flash - Balsamiq● Usability test -Silverback Apps
Books● Paper Prototyping: The Fast and Easy
Way to Design and Refine User Interfaces
● Don't Make Me Think● About Face 3● Sketching User Experiences
University Degree Programs
Carnegie Mellon University● human computer
interaction institute
Stanford ● design school
UC Berkeley ● I School
George Tech ● MS in HCI
School of Visual Arts MFA in interaction design
Bentley UniversityHuman Factors Program
NYU ITP
Parsons interaction design program
Professional and Academic organizationsIxDA
UPA
ACM CHI
Don't Make Me Think
About Face 3
Elements of User ExperienceDesign of Everyday Things
Tools
Tools on Mac vs PC vs Web
Omnigraffle - Mac onlyhttps://www.dropbox.com/s/dscujqtdieu2v9o/OmniGraffle_tutorial.graffle.ziphttp://zurb.com/playground/foundation-stencil-sets
keynotopia.com - PC and Mac
Balsamiq - PC and Mac and Webgomockingbird.com - Web
Balsamiq
Turn Balsamiq wireframes into clickable prototypeshttp://support.balsamiq.com/customer/portal/articles/111742
Omnigraffle shortcuts
http://www.nickfinck.com/blog/entry/omnigraffle_5_keyboard_shortcuts_cheat_sheet/
When to build wireframes (in design process)?
1. Who are the users?2. Identify user goals
○ Look at competitors in the same category3. Break down goals into tasks
○ Prioritize tasks into primary and secondary tasks4. Take an inventory of content and functionality
○ Static content○ Dynamic content
5. Create sitemap and flow diagrams6. Create navigation paths for each task7. Sketch at least 5 different design concepts8. Build wireframe in Omnigraffle (or other software tool)9. Test wireframe with real users
10. Update wireframe based on user feedback
source: http://semanticstudios.com/publications/semantics/000228.php
UX Best Practices
http://bitly.com/UX_research_best_practicehttp://bitly.com/UX_design_best_practice
http://bitly.com/UX_process_stages
Omnigraffle Tutorial
● Jackson Fox's Tutorial on slideshare● The Right Way to Wireframe music video● Build attractive site maps in minutes using OmniGraffle● Use Omnigraffle to sketch apple web site● Creating your first diagram in OmniGraffle● Shared Layers in OmniGraffle Pro