Intro to-anatomy-powerpoint-1227697925069712-8
-
Upload
rofel-shri-g-m-bilakhia-college-of-pharmacy -
Category
Documents
-
view
570 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Intro to-anatomy-powerpoint-1227697925069712-8

Human Anatomy
Introduction

Anatomical position – a common visual reference point Person stands erect with feet together and eyes
forward Palms face anteriorly with the thumbs pointed away
from the body

Regional terms – names of specific body areas Axial region – the main axis of the body Appendicular region – the limbs
Directional terminology Refers to the body in anatomical position Standardized terms of directions are paired terms

Orientation and Directional Terms

Orientation and Directional Terms

Orientation and Directional Terms

Regional Terms

Regional Terms

Body Planes and Sections

Body Planes and Sections Coronal (frontal) plane - Lies vertically
and divides body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts
Sagittal plane – lies vertically and divides the body into left and right sides.Median (midsagittal) plane - Specific sagittal
plane that lies vertically in the midline Transverse plane - runs horizontally and
divides body into superior (up) and inferior (down) parts

Figure 1.6
Body Planes and Sections Oblique section through the trunk

Body Cavities and Membranes Dorsal body cavity Cavity subdivided
into the cranial cavity and the vertebral cavity. Cranial cavity
houses the brain. Vertebral cavity
runs through the vertebral column and encloses the spinal cord

Body Cavities and Membranes Ventral body cavity
– subdivided into: Thoracic cavity –
divided into three parts
Two lateral parts each containing a lung surrounded by a pleural cavity
Mediastinum – contains the heart surrounded by the pericardial sac

Body Cavities and Membranes Ventral body cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity – divided into two parts
Abdominal cavity – contains the liver, stomach, kidneys, and other organs
Pelvic cavity – contains the bladder, some reproductive organs, and rectum

Body Cavities and Membranes Serous cavities – a slit-like space lined by a
serous membrane Pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum
Parietal serosa – outer wall of the cavity Visceral serosa covers the visceral organs

Body Cavities and Membranes

Other Body Cavities Oral cavity Nasal cavity Orbital cavities Middle ear cavities Synovial cavities

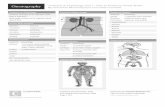
Abdominal Regions and Quadrants Abdominal regions divide the abdomen into
nine regions

Abdominal Quadrants Abdominal quadrants divide the abdomen into four
quadrants Right upper and left upper quadrants Right lower and left lower quadrants

FOUR TYPES OF FOUR TYPES OF ANIMAL TISSUESANIMAL TISSUES

EPITHELIAL TISSUEEPITHELIAL TISSUE(COVERING)(COVERING)
Tightly-joined closely-packed cells One side of epithelium exposed to air
or internal fluid, other side attached to a basement membrane, a dense mat of extracellular matrix (connective tissue)
Covers the outside of the body and lines the internal organs and cavities
Barrier against mechanical injury, invasive microorganisms, and fluid loss
Provides surface for absorption, excretion and transport of molecules

TYPES OF TYPES OF EPITHELIAL EPITHELIAL TISSUETISSUE Cell shape
Squamous (flat & thin) Cuboidal (box or square) Columnar (rectangular)
Number of cell layers Simple (one) Stratified (two or more) Pseudostratified (one but
appears to be two) RELATE STRUCTURE TO
FUNCTION!

CONNECTIVE TISSUE(FRAMEWORK) Main function: binding
and support other tissues
Large amount of extra-cellular matrix with fewer cells
Connective tissue cells secrete the extra-cellular matrix
Extracellular matrix consists of network of fibers in liquid, jelly-like or solid matrix


MUSCLE TISSUEMUSCLE TISSUE(MOVEMENT)(MOVEMENT) Composed of long cells
called muscle fibers Contraction movement

NERVOUS TISSUENERVOUS TISSUE(CONTROL)(CONTROL)
Senses stimuli and transmits signals called nerve impulses from one part of an animal to another
Consists of a cell body and long extensions called dendrites (towards cell body) and axons (towards another cell or an effector)
Axon
Dendrite
Cell body

Tissue Type Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve
Cell Shape Flattened, cuboidal, columnar
Irregular or round Elongated Cell appendages branched
Cell Arrangement
Single multilayered
Scattered in matrix
In sheets or bundles
Isolated or networked
Location Body covering or lining organs or
cavities
Supports other organs
Lining internal organs, make
skeletal muscles
Concentrated in brain and spinal cord + all over
the body
Surface Feature of Cells
Cilia, microvilli - - -
Matrix Type Basement membrane
Varied – protein fibers + liquid, gelatinous, firm
to calcified
- -
Matrix Amount Minimal Extensive Absent Absent
Unique Feature No direct blood supply, except for
glands
Cartilage has no blood supply
Can generate electrical signals,
force and movement
Can generate electrical signal