Intestinal Obstruction
-
Upload
sophia-parsons -
Category
Documents
-
view
16 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Intestinal Obstruction

Intestinal Obstruction
Presented By:Sahar Bannani
Supervised By:Dr. Fatmah AlThubaity

ClassificationsIntestinal Obstruction
Dynamic/ Mechanical
Small Bowel
Large Bowel
Adynamic/ Ileus
- Paralytic- PseusoObs

Etiology
Small Bowel: Adhesions: 60-80 % Hernia: 15-20 % Neoplasms: 10-15 %, extramural >
intramural
Large Bowel: Malignancy: 60% Diverticulitis: 15% Volvulus “esp. elderly”: Sigmoid > Cecal

Adynamic: Metabolic: K+, Mg++, Na+, Ketoacidosis,
Uremia, Porphyria, Metal posioning.Inflammation: Appendicitis, Abscess.Drugs: Narcotics, Antipsychotics,
Anticholinergics.Neuropathy: DM, MS, SD, SLE,
Hirschsprung’s. Post-Op. Ogilvie’s Syndrome.

pathophysiology Bowel distal to the obstruction: collapsed. Bowel proximal to the obstruction:
Distends: Gas Fluids:
– Intralumenal: secretion, absorption net secretion– Intramural– Peritoneal cavity
Altered Motility. Vomiting
Hypovolemia, Shock, Death. Perforation, Sepsis, Shock, Death.

Clinical picture
Partial vs. Complete Subacute, Acute, Chronic, Acute on
Chronic Small Bowel: high vs. low Strangulated Perforated

How to diagnose
History: Age Nausea, Vomiting, Obstipation, Pain,
Distention Past Surgical Hx Past Medical Hx Medications Systemic Review

Cont’ how to diagnose Physical Exam:
Vitals Abdomen Rectum
Labs: CBC: WBC, Hct, Hb U&E, creatinine ABG Amylase Urine Output

Cont’ how to diagnose
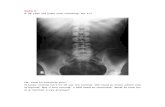
Radiology: Abdominal X-Ray: erect and supine.Erect CXR CT abdomen Upper GI series / small bowel series Contrast enema

How to manage
Resuscitation. NGT Conservative/Medical vs. Surgical

Paralytic ileus
LBO SBO
+ Late, ± feculent
Early, ± bilious Nausea, Vomiting
Minimal or absent
Colicky Colicky Pain
+ ++ + (proximal),++ (distal)
Distention
+ + + Con-/Ob-stipation
±visible peristalsis
± visible peristalsis
Others
or absent Or Or Bowel Sounds
Air throughout small bowel and colon
Air-fluid levels, picture-frame appearance, haustral markings, proximal distention
Air-fluid levels, Ladder pattern, valvulae conniventes, proximal distention + no colonic gas
AXR Findings

THANK YOU ALL