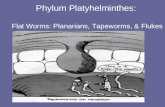
Schistosoma Schistosoma (Blood Flukes) TREMATODES -1- Doç.Dr.Hrisi BAHAR.
Intestinal Flukes Questions
-
Upload
cherryl-surigao -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Intestinal Flukes Questions

7/26/2019 Intestinal Flukes Questions
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/intestinal-flukes-questions 1/4
1. The egg of Fasciolopsis buski is said to be undistinguishable to the egg of what other
trematode?
a. Schistosoma japonicum
b. Fasciola hepatica
c. Paragonimus westermani
d.
Echinostoma Ilocanum
2. Which of the following serves as a second intermediate host for Fasciolopsis buski?
a. Pila luzonica
b. Trapa bicornis
c. Melania juncea
d. Nasturtium officinale
3. All of the following are characteristics of Fasciolopsis buski, except:
a.
Testes arranged in tandem in posterior half of body b. Vitellaria situated throughout the lateral margin of the body
c. With cephalic cone
d. Elongated, oval in shape
4. What is the infective stage of Fasciolopsis buski?
a.
Embryonated egg
b. Miracidium
c. Cercaria
d. Metacercaria
5. Which of the following can prevent the transmission of Fasciolopsis buski?
a. Avoid soaking aquatic plants in water
b. Not using pig or human feces as fertilizers in agriculture
c. Boiling and filtering of water
d. All of the above
6. Which of the following is 20 to 75 mm in length, 8 to 20 mm in width, and has
unbranched intestinal ceca?
a. Schistosoma japonicum
b.
Artyfechinostomum malayanum
c. Paragonimus westermani
d. Fasciolopsis buski

7/26/2019 Intestinal Flukes Questions
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/intestinal-flukes-questions 2/4
7. Which of the following is not a reason for the worldwide distribution of heterophyid flukeinfection?
a. Heterophyid have adapted to snails belonging to various families
b. Freshwater, brackish water and salt water fish can serve as their second intermediate host
c. Reservoir hosts such as dogs, cats, birds, etc. are additional sources of this infectiond. Freshwater, brackish water, salt water and marine mammals can serve as their second
intermediate host
8. How do you distinguish Heterophyid from Clonorchis and Opisthorcis eggs?
a. Clonorchis and Opisthorcis eggs are ovoid while Heterophyid eggs are peanut shaped
b. A fully developed miracidium is present in Heterophyid eggs but not in Clonorchis and
Opisthorcis
c. presence of prominent shoulder at the operculum of Clonorchis and Opisthorcis eggsd. It is easy to distinguish based on their size
9. Which of the following is not a control and prevention technique from infection withHeterophyid flukes?
a. Encouraging people to eat pickled and smoked fish instead of raw fish b. Educating people on the dangers of eating raw fish
c. Treating reservoir hosts of Heterophyid
d. Sanitary disposal of human feces by construction of toilets and their proper use
10. What is the treatment for Heterophyid infection?
a. Albendazole 25mg/kg, 3 doses for one day b. Pyrantel Pamoate 25mg/kg, 3 doses for one day
c. Praziquantel 25mg/kg, 3 doses for one dayd. Bithionol 25mg/kg, 3 doses for one day
11. Which is not true regarding Heterophyid infection?
a. It can be acquired via ingestion of fish harbouring infective larva b. Autoinfection is common
c. It is underdiagnosed in the Philippines
d. Heterophyid adult worm inhabits the small intestine of humans
12. Which is the infective stage of Heterophyid flukes?
a. Eggs
b. Metacercaria
c. Sporocystd. Both A and B

7/26/2019 Intestinal Flukes Questions
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/intestinal-flukes-questions 3/4
13. Which is not a reason for the low prevalence of Heterophyid infection in the Philippines?
a. It is misdiagnosed as peptic ulcer disease b. light infection easily missed because of low number of eggs in the feces
c. Its second intermediate host is not common in a tropical area like the Philippines
d. Local health units have insufficient capacity to diagnose and treat this infection
14) What is the reservoir host of echinostomids?
a) Birds
b) Pigs
c) Sheep
d) Fish eating mammal
15) How are echinostomids transmitted?
a)
Inhalation
b)
Ingestion of improperly cooked fishc) Ingestion of raw snail
d) Skin penetration
16) What are the first and second intermediate hosts of echinostomids?
a) Rats and leafy vegetables
b) Snailsc) snails and rats
d) fish and crab
17) What factor greatly contributes to the endemicity of the disease?
a) Eating habits of the population
b) Climatec) Geography
d) Age and Gender
18) What diagnostic method can be used for Echinostomids?
a) serological testing
b) biopsy
c) endoscopy
d) Detection of characteristic eggs in the stool
19) What are the infective stage of echinostomids?
a) filariform b) cercaria
c) metacercaria
d) encysted larva

7/26/2019 Intestinal Flukes Questions
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/intestinal-flukes-questions 4/4
20) What are echinostomids?
a) Blood nematodes
b) Intestinal flukes
c) Lung flukes
d) Intestinal cestodes














![[PPT]OBSTRUCCION INTESTINAL - semio2013 | This … · Web viewOBSTRUCCION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCCION INTESTINAL OBSTACULO AL TRANSITO DEL CONTENIDO INTESTINAL Adinámico o paralítico](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5b36ceb57f8b9a4a728b5103/pptobstruccion-intestinal-semio2013-this-web-viewobstruccion-intestinal.jpg)