INTERNAL CONTROLS for IT [email protected]. Internal Controls: An Overview Internal Controls: An...
-
Upload
charlene-palmer -
Category
Documents
-
view
238 -
download
0
Transcript of INTERNAL CONTROLS for IT [email protected]. Internal Controls: An Overview Internal Controls: An...

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Objectives Define what internal controls are Describe the five components of the
internal control framework Discuss the limitations of internal controls Determine who is responsible for internal
controls and the categories of responsibility
Internal controls from an auditor’s perspective
Practical elements of IT internal controls

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
What are internal controls? A coordinated set of policies and
procedures that help to ensure that management’s objectives are achieved.
Practical techniques employed by management to accomplish its objectives and meet its responsibilities.
Management techniques, an inextricable part of how management conducts its business.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
All governments exist to serve some purpose.
Management provides leadership for the government to fulfill its purposes. Management has limitations in
achieving goals.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Management’s fundamental responsibilities should address: Effectiveness
Are activities actually achieving their intended purposes?
Efficiency Is management making the best use of
scarce resources?

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Management’s fundamental responsibilities should address: Compliance
Is management using resources according to federal/state and local laws?
Financial reporting Do managers have a system of accounting
and financial reporting in place to make good decisions?
Are managers accountable for their actions to individuals and groups outside the government for their management of resources?

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Management’s responsibilities or objectives: Effectiveness and efficiency of
OPERATIONS COMPLIANCE FINANCIAL REPORTING
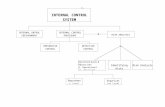
Internal Control: Framework that management
establishes to ensure that it meets those responsibilities or objectives.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Five Components of Internal Control Framework: Provides a favorable CONTROL
ENVIRONMENT Management is knowledgeable about
controls. Management is committed to
establishing and maintaining controls. Management communicates its support
for internal controls to staff at all levels.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Five Components of Internal Control Framework: Continually ASSESSES RISK
The risk here is that management’s objectives will not be fulfilled.
Causes might include: Changes within the government – new
personnel Changes outside the government – population
increase or decrease Sound internal control framework helps
management to anticipate, identify and assess potential risks.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Five Components of Internal Control Framework: Establish and maintain effective
control-related POLICIES AND PROCEDURES
Preventive controls Prior authorization and approval of transactions Segregation of duties
Detective controls Account reconciliations Timely preparation of financial statements

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Five Components of Internal Control Framework: Effective COMMUNICATION
Ensures that RIGHT information is provided to RIGHT individuals at the RIGHT time and in the RIGHT format.
Provides for communication between levels and activities within the organization.
Provides for communication with parties outside the government.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Five Components of Internal Control Framework:
MONITORS effectiveness of control policies and procedures/resolution of problems identifies by controls.
Ensures that controls continue to function properly
Control system could undergo a self-assessment
Also includes follow-up on potential problems

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview

Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud
Survey$660 billion in annual fraud losses

Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud
SurveySmall business hit the hardest

Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud
SurveyFraudulent statements – least #, highest $Asset misappropriation – highest #, least $

Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud
SurveyTips were the most common means of detection – all industries (39.6%)

Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?Why Have an Anti-Fraud Program?ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud
SurveyTips were the most common means of detection – government agencies (48.5%)

Common Elements of FraudCommon Elements of Fraud
False statement, representation, or document
Made intentionally or recklessly
About a material fact
Upon which a victim relies

Who Commits Fraud? Who Commits Fraud? Based on ACFE 2002 Occupational Fraud Survey
The majority of frauds (64%) are committed by employees. Frauds committed by managers or executives are three-and-a-half times more costly than frauds committed by employees.
Males accounted for losses that were three times greater than those of females.
Most fraudsters were first-time offenders. Only about 7% of fraud perpetrators had been convicted of a previous crime.
Approximately 33% of reported frauds involved collusion (two or more individuals).
The oldest perpetrators (over 60) caused median losses 27 times greater than those of the youngest fraudsters (below 25)—older employees generally occupy more senior positions with greater access to assets.

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Executives commit the frauds with the largest losses

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
51% make less than $50,000 a year

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
56% have worked 6 or more years with the same employer

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Men have a slight majority over women

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Men commit frauds with three times the losses by women

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Persons 41-50 commit 32% of the frauds

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Persons over 51 commit the largest frauds

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Persons those with some college or less commit most of the frauds

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Despite low frequency, those with advanced degrees commit the most costly frauds

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
Two-thirds of the frauds are committed by one person

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
When there is collusion, the losses quadruple

Who Commits Fraud?Who Commits Fraud? From ACFE 2004 Occupational Fraud Survey
83% have never been charged or convicted

Fraud TriangleFraud Triangle
Opportunity
Pressures / Incentives
Rationalization / Attitude

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Limitations of Internal Controls Cost may exceed benefit Management can override controls Risk of collusion

Types of Fraud
Skimming
Corruption
Invoice Kickbacks
Conflicts of
Interest
Economic
Extortion
Illegal Gratuities
Write-offs
Understatement
Lapping
Misuse
of Property
ForgeryFalse shipping
False in
voices

Fraud CategoriesFraud Categories
Fraud
Corruption
Asset Misappropriation
Fraudulent Statements
Cash Non-Cash

Corruption CategoriesCorruption Categories
Corruption
Conflicts of Interest
BriberyIllegal
Gratuity
Purchasing Schemes
Sales Schemes
Invoice Kickbacks
Bid Rigging
Extortion

Cash Misappropriation CategoriesCash Misappropriation CategoriesAsset
Misappropriation
Cash
Theft Skimming
Cash on hand
From deposit
Sales
Receivables
Refunds
Unrecorded
Understated
Write-offs
Lapping
Unconcealed

Non-Cash Misappropriation Non-Cash Misappropriation CategoriesCategories
Asset Misappropriation
Non-Cash
Theft Misuse
Requisitions
Transfers
False Sales
False Shipping
Purchasing
Receiving
Unconcealed

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Responsibility for Internal Controls Management is primarily
responsible for internal controls. Governing board is ultimately
responsible for internal controls. Auditors can help management, but
must never assume primary or ultimate responsibility.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Categories of Management Responsibility for Internal Controls: Design
Use the five interrelated components of I/C to design policies and procedures.
Implementation Controls are actually installed as
designed and placed in operation.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Categories of Management Responsibility for Internal Controls: Monitoring
Controls continue to function or changed as needed.
Reporting Governing board should be kept
apprised of how I/C are functioning or changes that need to be implemented.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Management’s Methods of Monitoring I/C Internal Auditors Self-Assessment External Auditors
Management’s misconception that external auditor’s monitor.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Internal Controls from an Auditor’s View Auditors render opinion that financial
statements are in accordance with GAAP. Auditors must
Gain an understanding of internal controls Document that understanding in audit workpapers Determine planned risk assessment based on
understanding Perform tests of controls Determine if controls can be relied upon to
achieve audit efficiency.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Internal controls are techniques – policies and procedures that are incorporated into the way day-to-day business is handled– to accomplish management’s objectives.
Five interrelated components are essential for a comprehensive internal control framework.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
These five components include: CONTROL ENVIRONMENT
Create and maintain an environment conducive to control RISK ASSESSMENT
Ensure that risks from both inside and outside the government are assessed and managed on an ongoing basis
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES Result in the design and implementation of appropriate
control-related policies and procedures Provide for appropriate communication both inside and
outside the government Monitor the effectiveness of control-related policies and
procedures

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
These five components include: COMMUNICATION
Provide for appropriate communication both inside and outside the government
MONITORING Monitor the effectiveness of control-related
policies and procedures

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Internal controls have limitations. Not cost beneficial Subject to management override Risk of collusion
Management is primarily responsible for internal controls
Governing board is ultimately responsible for internal controls.

Internal Controls: An Internal Controls: An OverviewOverview
Auditors must gain an understanding of internal controls and test those controls looking for weaknesses that could have a significant impact on financial reporting.
Auditors are not a substitute for management monitoring of internal controls.

YOUR RISK YOUR RISK ASSESSMENTASSESSMENT
What could go wrong? How could we fail? What must go right for us to succeed? Where are we vulnerable? What assets do we need to protect? How could someone steal from the
department? How could someone disrupt our operations? How do we know whether we are achieving
our objectives?

YOUR RISK YOUR RISK ASSESSMENTASSESSMENT
On what information do we most rely? On what do we spend the most money? How do we bill and collect our revenue? What decisions require the most
judgment? What activities are most complex? What activities are regulated? What is our greatest legal exposure? What is our greatest political exposure?

The Control Environment The Control Environment Component of Internal ControlComponent of Internal Control
1. Does management adequately convey the message that integrity cannot be compromised?
2. Is the competence of the entity’s people commensurate with their responsibilities?
3. Are financial statements submitted to and reviewed by management, the governing board, or the audit committee at regular intervals?
4. Does management demonstrate concern about and willingness to correct important weakness in the system of internal control?
5. Does the entity maintain an up-to-date accounting policies and a procedures manual?

The Control Environment The Control Environment Component of Internal ControlComponent of Internal Control
6. Is there a low turnover of accounting, IT, and key management positions?
7. Are key operating positions adequately staffed, therefore avoiding constant crisis?
8. Is there adequate coordination between accounting and information technology departments, resulting in timely reports and closings?
9. Are there formal job descriptions that clearly set out duties and responsibilities?
10. Are backgrounds and references of applicants for financial, IT, and key management positions investigated?

The Control Environment The Control Environment Component of Internal ControlComponent of Internal Control
11. Are personnel policies and employee benefit plans documented and communicated to employees?
12. Is a formal conflict of interest policy or code of conduct in effect?
13. Are employees who handle cash, securities, and other valuable assets bonded?
14. Are employees adequately trained to meet their assigned responsibilities?
15. Is the job performance periodically evaluated and reviewed with employees?

The The RiskRisk Assessment Component Of Assessment Component Of Internal ControlInternal Control
1. Does management consult with its legal counsel regarding the implications of any new legislation?
2. Are new employees in key positions adequately supervised to ensure that they understand and perform in accordance with the entity’s policies and procedures?
3. Are procedures in place to assess the effects of new or redesigned information systems and to monitor new technologies?
4. Is management aware of the existence of new accounting or reporting pronouncements and how they may affect the entity’s financial reporting practices?

The Control Activities Component of The Control Activities Component of Internal ControlInternal Control
1. Does management have clear objectives in terms of budget, profit, and other financial and operating goals? If yes, are these objectives:
Clearly written? Activity communicated throughout the entity? Activity monitored? Has management established procedures to prevent
unauthorized access to, or destruction of documents, records, and assets?
2. Has management established policies for controlling access to programs and data files?
3. Does management adequately monitor such policies?

The Control Activities Component of The Control Activities Component of Internal ControlInternal Control
4. Are control and subsidiary accounts reconciled regularly and discrepancies reported to appropriate personnel?
Are signatures required as evidence of the performance of critical control functions, such as reconciling accounts?
Are general journal entries, other than standard entries, required to be approved by a responsible official not involved with their origination?
Are accounting estimates and judgment made by knowledgeable and responsible personnel?
Are financial statements and related disclosures prepared and reviewed by competent personnel who are knowledgeable of the factors affecting the entity’s financial reporting requirements?

The Information and The Information and Communication Component of Communication Component of
Internal ControlInternal Control 1. Is the development or revision of information systems over
financial reporting based on a strategic plan and interrelated with the entity’s overall information systems and its responsiveness to achieving the entity-wide and activity-level objectives?
2. Does management commit the human and financial resources to develop the necessary financial reporting information systems?
3. Does management communicate employees’ duties and control responsibilities in an effective manner?
4. Are communication channels established for people to report suspected improprieties?
5. Does communication flow across the organization adequately to enable people to discharge their responsibilities effectively?

The Monitoring Component of The Monitoring Component of Internal ControlInternal Control
1. Are customer complaints about billings investigated and any internal control deficiencies corrected?
2. Are communications from vendors and monthly statements of accounts payable used as control monitoring techniques?
3. Are internal control recommendations made by external auditors (and internal auditors, if applicable) implemented?
4. Does management receive feedback from training seminars, planning sessions, and other meetings on whether controls operate effectively?
5. Does the organization take a fresh look at the internal control system from time to time and evaluate its effectiveness?

The Monitoring Component of The Monitoring Component of Internal ControlInternal Control
6. Does the entity have an adequate internal audit function? If yes, do the internal auditors:
Possess adequate training and experience?
Adhere to applicable professional standards?
Have an adequate documentation of the organization’s internal control?
Perform test of controls and substantive tests?
Have adequate documentation of their work?
Submit reports on their findings to the board of directors or audit committee in a timely manner?
Follow up on corrective actions taken by management?
Have direct access to the board of directors or audit committee?
Have direct access to records and the scope of their activities is not limited?

IT Controls-General ControlsIT Controls-General Controls
1) IT Control Environment
2) Program Development and Implementation
3) Program ChangesSoftware changes can impact segregation of duties
4) Access to Program and DataTraceability of who, when and what/how

ITIT Controls-Application ControlsControls-Application Controls
1) Input Controls
2) Processing Controls
3) Output Controls
4) Security1) Segregation of Duties2) Traceability3) Exceptions4) Overrides

Strategies for SuccessStrategies for Success
Ask your auditor for format desired in documenting the understanding of IT.
Delegate the parts to various professionals inside your organization that can help. If you are a one person shop carve the project
into pieces with deadlines to give to an accountability partner to review like possibly your finance director or another auditor.
Reward yourself and/or your department when complete.