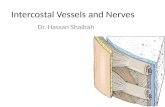
Intercostal Space
-
Upload
drravikumar-bhandari -
Category
Documents
-
view
869 -
download
23
Transcript of Intercostal Space


INTERCOSTAL SPACE
Dr Vandana RAsst prof ,Dept of Anatomy,Navodaya medical college
Raichur

CONTENTS
• DEFINITION• TYPICAL INTERCOSTAL SPACE• BOUNDARIES,PARTS & FEATURE OF SPACE• CONTENTS OF SPACE- MUSCLE,VESSELS &
NERVES.• APPLIED ANATOMY OF SPACE


RIB

Classification of Ribs
• TRUE = Ribs 1 -7– Vertebrosternal
ribs– Connected to
sternum by their costal cartilages

• FALSE = Ribs 8 -12 1. Vertebrochondral - Ribs 8-10
-connected by its costal cart to the cartilage of rib superior to it
2. Floating - Ribs 11-12- Unattached anteriorly

TypicalHave same featuresRibs 3 - 9

Atypical Ribs• Rib 1
– Broadest and most curved– Prominent scalene tubercle
for attachment of scalenus anterior muscle
• Rib 2– Thinner, less curved, longer– Has tuberosity for serratus
anterior• Rib 10
– Articulates w/ T10 vertebra only
• Rib 11 -12– Short, have single facet on
their heads– Have no NECK or TUBERCLE

INTERCOSTAL SPACE

INTERCOSTAL SPACEThe spaces between the ribs are called intercostals spaces. .
11Pairs of spaces,last two open

TYPICAL INTERCOSTAL SPACE
• BETWEEN TYPICAL RIBS AND TRAVERSED BY NERVES & VESSELS WHICH ARE CONFINED TO THORACIC WALL
• 3RD ,4TH ,5TH & 6TH SPACES ARE TYPICAL

BOUNDARIES

PARTS & FEATURES

CONTENTS
• MUSCLES
• VESSELS
• NERVES

INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES

External Intercostal Muscle• Most superficial• Fibers directed downward &
forward• OriginOrigin: from lower border of
the rib above• InsertionInsertion: upper border of
rib below• Extends from the rib
tubercle behind to the costo-chondral junction in front
• Deficient anteriorly & replaced by external external (anterior) intercostal (anterior) intercostal membranemembrane

Internal Intercostal Muscle
• Intermediate layer• Fibers directed
downward & backward• OriginOrigin: from sub7costal
groove of the rib above• InsertionInsertion: upper border
of rib below• Extends from the
sternum in front to the angle of the rib behind
• Deficient posteriorly & replaced by internal internal (posterior) intercostal (posterior) intercostal membranemembrane

S
costochondral junction
CC
V
anterior intercostal membrane &
external intercostal muscle
posterior intercostal membrane &
internal intercostal muscle
Angle of the rib

3. Innermost (Transversus thoracis) muscle
The deepest incomplete layer ,crosses more than one space.. Can be separated into 3 layers sternocostalis , subcostalis intercostalis intima


ACTION
. 1Muscles of respiration.
2. The muscle tone prevents the sucking in or blowing out of the tissues in the intercostals

VESSELS

ARTERIES
• Each intercostal space contains: A single posterior & Two anterior intercostal arteries
• Each artery gives off branches to the muscles, skin, parietal pleura (& breast)

ANTERIOR INTERCOSTAL ARTERIES

POSTERIOR INTERCOSTAL ARTERIES



VENOUS DRAINAGE


NERVES

INTERCOSTAL NERVES
• Twelve pairs• Are the anterior primary rami anterior primary rami of the thoracic thoracic
spinal nerves.spinal nerves.• 1-6 distributed in the intercostal spaces, 7-
11th supply the anterior abdominal wall• Anterior ramus of 1212thth nerve runs forward in
the abdomen as the subcostal nervesubcostal nerve

INTERCOSTAL NERVE

BRANCHES
• COMMUNICATING
• DISTRIBUTING

APPLIED ANATOMY

The Intercostal spaces are important access points for:
Surgical procedures, e.g. resection of (part of) the lung
Percussion and auscultation of underlying structures e.g. heart & lung
To obtain a sample of pleural fluid or drain pus/blood from the pleural cavity. The needle/drain is passed through the intercostal space just above the upper border of the rib to avoid the neurovascular bundle .