Injection moulding technique presentation
-
Upload
umair-khalid -
Category
Engineering
-
view
826 -
download
3
Transcript of Injection moulding technique presentation
INJECTION MOULDING TECHNIQUE
Presented By:
Name Umair Khalid
Roll No E13-311 ( 5th Semester)
Class Polymer & Composites
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
UNIVERSITY OF THE PUNJAB
Introduction: Injection molding involves the manufacturing process of polymeric materials in which
molten plastic material is injected into mold where it is solidified and then released into final product.
A primary manufacturing process which produces different parts ranging from small components to large parts having intricate shape.
Just analogue to die casting for metals. Both Thermoplastic and Thermosetting materials can be used. Various plastic parts are produced having dimensional accuracy and strength. As compared to extrusion which produces continuous parts of fixed cross-section, by
this technique complex and discrete parts having variable cross-section can be produced.
Usually Mold is made of Steel or Aluminum whose designing is much complicated as compared to extrusion die.
Types of Injection Molding Machine:1) Older Type machine2) Modern Type machine
The Basic Difference in both of them is injection units through which molten plastic is injected into mold cavity.
In older type machine, Ram/Plunger and Spreader are used to inject the plastic into mold.
In modern type, reciprocating screw mechanism is used to melt the plastic and inject into the mold.
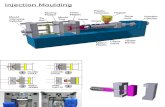
Important Physical Parts: Some of the important parts of Modern mold injection machine are following: Hydraulic Pump Fed Hopper Barrel Screw type plunger Heating Chamber Nozzle Mold Cavity Clamping unit Ejector
The Working Process: Plastic in granular or pelletized form is fed from hopper and fall into barrel through its
throat. Then it is melted through heating by heaters which surrounds the barrel. The material in heating chamber is forced around a spreader to make its better contact
with heated wall and as a result it forms a viscous liquid. This viscous liquid is collected in a pool in a barrel known as injection chamber. Molten plastic is then forced to move forward by the action of plunger (ram). Inside the
barrel, there is a rotating screw which carries the molten plastic along the barrel to the mold.
The reciprocating screw moves back as molten plastic moves forward. Again by the action of ram, this molten plastic is is injected through a nozzle into mold
cavity. Mold is kept warm before plastic injection. To avoid shrinkage or hollows, pressure inside the mold is kept maintained usually
15,000psi until solidification occurs. Finally Solid material is injected by opening the mold and then entire cycle is repeated.
Major Functional Units:1. Injection unit:o Basic purpose: To melt the plastic material and then inject the liquefied material
into the mold.o It consists of Hopper, heated cylinder(Barrel), nozzle and injector.o Injection can be done by reciprocating screw or ram injector which is powered
by (Hydraulic or electric motor).o Plastic resins is melted by mechanical shear and thermal energy from heaters.o Refilling of injection for next shot
2.
2. Molding Section:Generally molds are made from hardened steel or aluminum having fiber glass coating.
It consists of: Stationary plate (Mold cavity)and
movable plate (Mold core). Mold Base (front half and rear half),
runner gate etc.)
Gates (Edge gate, submarine gate, Fan gate) etc.
Mold Functions:1. To give desired shape to material2. To withstand the injection pressure and clamped forces.3. To properly distribute the ejected melt4. Cool and cure the material.
3. Clamping Unit: Before the molten plastic injection into mold, Two halves of
mold must be tightly closed by clamping units. When it is attached to molding machine, each half of it is fixed to large plate called platen.
The clamping mechanism in done with hydraulic clam or toggle.
In a hydraulic clamping, motor activates the clamping bars which pushes the movable pattern towards stationary pattern and make the mold tightly closed.
After required cooling time, mold is opened by clamping motor and solidified material is pushed out from cavity by ejector bar.
Important Points:1. Plastic granules should be melted enough and injected at high temperature. It is important to match heating with resin.2. water is channeled through the mold for Colling purposes and to control the crystallization rate.3. Large shot takes more heat. Typically shot size ranges rom 20g to 20kg. Shot size depends upon density of material.4. Long runner required high temperature of melt.5. For thick part, low molding temperature and high cooling time.
Raw materials:
Incase of thermosets, they are added into mixture form(two chemical components) from hopper into barrel longer cycle time is required as compared thermoplastics due to chemical reactions and curing take place in the mold. They are more abrasives and cant be reuse.
Thermoplastic Thermosetting
PP, PS, PE, Nylon, PVC etc.
Epoxy, Phenolic, Polyurethane etc.
Advantages: Fast production rate (15-30) seconds/cycle. Wide variety of plastics can be manufactured. Design flexibility Relatively low labor cost. Good and smooth surface finish. Low operation cost Low wastage as scrap material can be reused by recycling. Uniform melting Highly automated process
Disadvantages: Highly investment and running costs. Raw material contamination affect the product quality. High pressure involved. Problems in designing molds.
Applications: Aerospace components Automotive components Computer and electronics Engineering prototypes Household equipment's Instrumentation Marketing samples Medical and dental products Toys, Model shops etc. Test Specimens Cable assemblies
And much more.!
Research article (1): Towards Nano-Injection Molding Authors: Nan Zhang, Cormac J. Byrne, David J. Browne, and Michael D. Gilchrist Volume15, Issue15, Date: May 2012, Page:216-221
A Micro-injection molding is cost-effective method for production of a micro polymer components. Plastic components have ranges up to sub-micron (≤ 10-6m) and nanometer scales (≤ 10-7m) size. the need for plastic component with increasingly smaller features are recognized, particularly for information storage and bio-analytical applications.
Most of these devices are fabricated using silicon or glass so as to take advantage of well-developed patterning technologies. These high volume production of polymers having size from mm to cm are of high accuracy and good reproducibility.
Research article(2): Measurement of sink marks on injection molding parts by a new fast processing modelAuthors: Dieter P. Gruber , Johannes Macher , Dietmar Haba , Gerald R. Berger , Gernot Pacher , Walter Friesenbichler , Volume: 33, Page:7-13, Date: October 2013To present the novel methodology in assessing of the visual perceptibility of sink marks on surface of injection molded parts. A new model for the calculation of visibility of sink marks from CCD-images was developed. A new calculated surface model function is used in determining of amplitude second derivatives as a measure of visual perceptibility of sink marks. Injection molding parts were produced using pre-defined processing conditions. Its Influence on visual perceptibility was assessed. The perceptibility of detected sink marks was calculate by using the amplitude of second derivative (ASD) of the molded sink marks.
Fig 1 Shows the Measured ASD value in dependence on the holding pressure as a measure of the visual perceptibility of sink marks. Each point shows the mean ASD value of five specimens produced at the same holding pressure level.
Conclusion
The injection molding is considered as most important process in the production of plastic items, involving intricate shapes and vast production of identical items. Its production services is highly acquired by the defense and aerospace industry due to manufacturing of precision engineering components.
References:
For Slides: Plastic processing technology by Edward A. Muccio,(1999) Ch#6 http://www.custompartnet.com/wu/InjectionMolding http://www.polyplastics.com/en/support/mold/outline/ http://www.technologystudent.com/equip1/inject1.htm web.mit.edu/2.810/www/lecture/Injection Molding
For Articles: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1369702112700925 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142941813002158