Injection Moulding Basics
-
Upload
mrriassaty -
Category
Documents
-
view
247 -
download
0
Transcript of Injection Moulding Basics
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
1/27
InjectionInjectionMouldingMoulding
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
2/27
2
Moulding machineMoulding machine
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
3/27
3
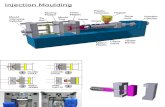
Basics of InjectionBasics of Injection
MouldingMouldingHopper
Screw & Barrel
Nozzle
Clamping unit
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
4/27
4
Calculated by multiplyingtheprojected area of the cavity
(cavities), including runner system by the maximum internalpressure (hold pressure).
Clamping pressureClamping pressure
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
5/27
5
Clamping pressureClamping pressure
POMPOM
PAPA
LCPLCP
PETPPETP
PCPC
PMMAPMMA
PPPP
PEPE
ABSABS
PSPS
3 - 4 T/inch3 - 4 T/inch22
3 - 5 T/inch3 - 5 T/inch22
4 - 6 T/inch4 - 6 T/inch22
4 - 6 T/inch4 - 6 T/inch22
3 - 5 T/inch3 - 5 T/inch22
2 - 4 T/inch2 - 4 T/inch22
1 - 4 T/inch1 - 4 T/inch22
1 - 4 T/inch1 - 4 T/inch22
3 - 4 T/inch3 - 4 T/inch22
2 - 3 T/inch2 - 3 T/inch
22
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
6/27
6
Drying PrinciplesDrying Principles
Non-hygroscopic Polymers :e.g. P/S, P/E, P/P, POM
Drying require only to remove surface moisture.Hygroscopic Polymers :
e.g. P.A., P/C, PBTP, PETP, PET-G
Use Dehumidified air drier or Vacuum oven
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
7/27
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
8/27
8
Water content & lowering of molecular weight:
0
10
20
30
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25
Water content of pellet (wt%)
Loweringofm
olecular
weight(%)
Moulding temp.300 cMoulding temp.300 c
PolycarbonatePolycarbonate
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
9/27
9
30% GR PET30% GR PET
Influence of Moisture on impact strength
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
10/27
10
Drying time &Drying time &
temperaturestemperaturesMaterial Moisture level Temp (
oC) Time (Hrs)
PA 0.2 80 2 4
PBTP 0.04 120 3 4
PETP 0.02 130 3 4
P/C 0.02 120 4 6
POM 0.2 80 1 2
LCP 0.01 135 2 4PPS 0.04 150 4 6
ABS 0.1 80 2 4
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
11/27
11
Moulding temp. & lowering of molecularMoulding temp. & lowering of molecular
weight:weight:
100
1000
10000
350 340 320 300 280
Moulding temp (deg.C)
L
oweringofm
ol.wt.(Mv)
35 min35 min
20 min20 min
5 min5 minResidencetime
Residencetime
PolycarbonatePolycarbonate
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
12/27
12
Hold-up-timeHold-up-time
Toughened Nylon 6.6
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
13/27
13
Temperature profileTemperature profile
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
14/27
14
Injection and HoldInjection and Hold
PressurePressure
Injection pressureInjection pressure - Dynamic filling phase (under velocity- Dynamic filling phase (under velocitycontrol), moves the screw and push the material intocontrol), moves the screw and push the material into
the mould, (around 95% of the part volume).the mould, (around 95% of the part volume).
Hold pressureHold pressure - Quasi-static feeding phase (under- Quasi-static feeding phase (underpressure control), packing the part to compensate forpressure control), packing the part to compensate for
the change in volume from a liquid to a solid.the change in volume from a liquid to a solid.
V-P switch pointV-P switch point
- In crystalline material, use distance- In crystalline material, use distance
rather than with pressure, as would typically be donerather than with pressure, as would typically be done
for an amorphous materialfor an amorphous material..
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
15/27
15
Hold pressure time Vs
part weight and shrinkageDelrin* 500
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
16/27
16
Hold-on-timeHold-on-time
POMPOM
PAPA GR-PAGR-PA
MR-PAMR-PA
PBTPBT
GR-PBTGR-PBT
PETPET LCPLCP
TEEETEEE
88 secssecs/mm/mm
55 secssecs/mm/mm 33 secssecs/mm/mm
33 secssecs/mm/mm
44 secssecs/mm/mm
33 secssecs/mm/mm
44 secssecs/mm/mm 0.50.5 secssecs/mm/mm
4-84-8 secssecs/mm/mm
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
17/27
17
Tool at 400C Tool at 900C
Influence of ToolInfluence of Tool
TemperatureTemperature
Outer layer insufficientlycrystallised
Optimum structure
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
18/27
18
Shrinkage behaviourShrinkage behaviour
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
19/27
19
Gate PositionsGate Positions
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
20/27
20
Gate Size and DesignGate Size and Design
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
21/27
21
Effect of Gate diameterEffect of Gate diameter
on the qualityon the qualityNylon 6.6
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
22/27
22
Runner Size and Design
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
23/27
23
Venting designVenting design
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
24/27
24
Moulding tolerancesMoulding tolerances
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
25/27
25
RegrindRegrind
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
26/27
26
Forcrystalline materials. (With amorphous materials, the
main differences are shorter hold on time, but much longer
cooling time.)
Moulding cycle-TimeMoulding cycle-Time
-
8/8/2019 Injection Moulding Basics
27/27
A Polymer for Every ApplicationA Polymer for Every Application