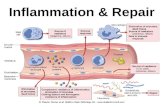
Inflammation
-
Upload
gopisankar-mg -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
106 -
download
2
Transcript of Inflammation
Vascular eventsVascular events
Hemodynamic changes Hemodynamic changes Permeability changesPermeability changes
Hemodynamic changesHemodynamic changes
1.1. Transient vasoconstriction of ArteriolesTransient vasoconstriction of Arterioles
2.2. Persistant progressive vasodilatationPersistant progressive vasodilatation
3.3. Elevated local Hydrostatic pressureElevated local Hydrostatic pressure
4.4. Stasis of microcirculationStasis of microcirculation
5.5. WBC migrationWBC migration
Lewis experimentLewis experiment
1.1. Red line Red line vasodilatation vasodilatation
2.2. Flare Flare vasodilatation of surrounding vasodilatation of surrounding vesselsvessels
3.3. Wheal Wheal traqnsudation of fluid into the traqnsudation of fluid into the extra vascular space..extra vascular space..
Vascular permeability changeVascular permeability change
1.1. Endothelial contraction Endothelial contraction immediate immediate transienttransient
2.2. Endothelial retraction Endothelial retraction delayed and delayed and prolongedprolonged
3.3. Direct endothelial injury Direct endothelial injury immediate and immediate and prolonged / delayed and prolongedprolonged / delayed and prolonged
4.4. Injury by WBCInjury by WBC
5.5. NeovascularisationNeovascularisation
Exudation of WBCExudation of WBC
1.1. Margination( formed elements widen ) and Margination( formed elements widen ) and pavementing( PMN comes in contact woth pavementing( PMN comes in contact woth vessel wall )vessel wall )
2.2. Rolling and adhesionRolling and adhesion
3.3. EmigrationEmigration
4.4. ChemotaxisChemotaxis
RollingRolling
SelectinsSelectins Three typesThree types
1.1. E selectin E selectin in Endothelium in Endothelium
2.2. P selectin P selectin Endo + Platlets Endo + Platlets
3.3. L selectin L selectin WBC WBC
AdhesionAdhesion
ICAM1 ICAM1 LFA 1 ,Mac -1LFA 1 ,Mac -1 Adhesion and Adhesion and TransmigrationTransmigration
VCAM 1 VCAM 1 VLA 4 VLA 4 Adhesion Adhesion PECAM 1 PECAM 1 CD31 CD31 Transmigration Transmigration
ChemotaxisChemotaxis
1.1. Bacterial Products Bacterial Products esp. with N formyl esp. with N formyl methionine terminalsmethionine terminals
2.2. Cytokines of Chemokine family IL 8Cytokines of Chemokine family IL 8
3.3. Complements –C 3a ,C5aComplements –C 3a ,C5a
4.4. LT B4LT B4
Leukocyte activationLeukocyte activation
PhagocytosisPhagocytosis Production of substances that destroys Production of substances that destroys
phagocytosed microbes phagocytosed microbes lysosomal lysosomal enzynes , reactive oxygen and nitrogen speciesenzynes , reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
Production of mediaters that amplify Production of mediaters that amplify inflemmatory reaction inflemmatory reaction AA metabolites and AA metabolites and cytokinescytokines
PhagocytosisPhagocytosis
1.1. Recognition and attachment of particles to Recognition and attachment of particles to WBCWBC
2.2. Formation of phagocytic vacouleFormation of phagocytic vacoule
3.3. Killing and degradation of ingested Killing and degradation of ingested substancesubstance
HealingHealing
Regeneration Regeneration proliferation of parenchymal proliferation of parenchymal cellscells
RepairRepair proliferation of connective tissue proliferation of connective tissue results in fibrosis and scarringresults in fibrosis and scarring
RegenerationRegeneration
Proliferation of the original cells from the Proliferation of the original cells from the margin of the injurymargin of the injury
Migrated cells will differentiates and maturatesMigrated cells will differentiates and maturates
RepairRepair
Granulation tissue formation Granulation tissue formation Contraction of the tissueContraction of the tissue
Granulation tissueGranulation tissue
Slightly granular and pink appearance of the Slightly granular and pink appearance of the tissuetissue
Each granule is a new small blood vesselEach granule is a new small blood vessel there is thin covering of fibroblasts and young there is thin covering of fibroblasts and young collagencollagen
Granulation tissue formationGranulation tissue formation
1.1. Phase of inflammationPhase of inflammation
2.2. Phase of clearancePhase of clearance
3.3. Phase of in growth of granulation tissuePhase of in growth of granulation tissue