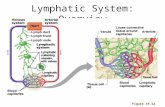
Immune System. 1 Constituents: Lymphocytes in blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and somewhere else,...
-
Upload
christian-josephs -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of Immune System. 1 Constituents: Lymphocytes in blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and somewhere else,...
Immune SystemImmune System1 Constituents: 1 Constituents: LymphocytesLymphocytes in blood vessels, in blood vessels,
lymphatic vessels and somewhere else, lymphatic vessels and somewhere else,
lymphatic tissueslymphatic tissues and and lymphatic organslymphatic organs..
2 Function: 2 Function: Destroy the invaders, such as Destroy the invaders, such as
pathogenic orgnisms and other antigens. pathogenic orgnisms and other antigens.
Destroy the useless or harmful cells inDestroy the useless or harmful cells in
human body, such as old RBC, cancer-human body, such as old RBC, cancer-
transformed cells, etc.transformed cells, etc.
LymphocyteLymphocyte
Functionally, lymphocytes can be divided intoFunctionally, lymphocytes can be divided into 3 3 types: types: T cell, B cell and NK cellT cell, B cell and NK cell..
1.T-lymphocyte: educated in thymus and involved in cell-mediated
immune response.
Helper T-lymphocyte----(cluster of the differentiation)CD4+T-lymphocyte.
it can upregulate both cell-mediated immune
response and humoral immune response;
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte----CD8+T-lymphocyte. a kind of effector cells
cytotoxic/suppressor T- lymphocyte can
downregulate or turn off immune response
HIV
2. B-lymphocyte 2. B-lymphocyte
B-lymphocyte plasma cell antibodyB-lymphocyte plasma cell antibody
neutralize antigen neutralize antigen
AgAg
B-lymphocyte: educated in the bone marrow and
involved in humoral immune response
3. Natural killer lymphocyte3. Natural killer lymphocyte
NK cell:NK cell: effector cell. effector cell.
It can kill abnormal cells directly.It can kill abnormal cells directly.
Lymphatic tissueLymphatic tissue1.defination:1.defination: the tissue which is mainly composed of the tissue which is mainly composed of lymphocytes.lymphocytes.2. classification:2. classification:(1) diffuse lymphatic tissue(1) diffuse lymphatic tissue (2) lymph nodule: lymph follicle(2) lymph nodule: lymph follicle
( 2 ) lymph nodule Also lymphoid follicle,mainly composed of B lymph
ocytes.
After stimulation of antigen , the germinal center wi
ll appear.
Classification : primary lymph nodule secondary lymph nodule
lymphatic nodule:lymphatic nodule: concentration of lymphocytes concentration of lymphocytes
contained in the meshwork of reticular cells.contained in the meshwork of reticular cells.
mainly containing B cells together with somemainly containing B cells together with some
plasma cells, macrophages,etc..plasma cells, macrophages,etc..
primary nodule:primary nodule: without germinal center; without germinal center;
Secondary nodule:Secondary nodule: with germinal center (B cells with germinal center (B cells
proliferates here rapidly). proliferates here rapidly).
Ag
lymphatic organslymphatic organs
Primary (central) lymphatic organsPrimary (central) lymphatic organs ---- thymus and bone marrow ---- thymus and bone marrow ----site that T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes ----site that T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes get educated respectively.get educated respectively.
Secondary (peripheral) lymphatic organsSecondary (peripheral) lymphatic organs ---- lymph node, spleen and tonsil---- lymph node, spleen and tonsil ---- sites that immune responses are initiated. ---- sites that immune responses are initiated.
Thymic cortexThymic cortex
Thymocytes:Thymocytes: developing T-lymphocytes.about developing T-lymphocytes.about 98% of them undergo apoptosis.98% of them undergo apoptosis.
Thymic cortex contains thymocytes (more ) and epithelioreticular cells (less).
Thymic cortexThymic cortex
There are There are 33 types of epithelioreticular cells in the cortex. types of epithelioreticular cells in the cortex.
TypeType I: I: Located at the boundary of the cortex and capsule.Located at the boundary of the cortex and capsule. involved in the formation of blood-thymus barrier.involved in the formation of blood-thymus barrier.
Type II: Type II: Located within the cortex .It is Located within the cortex .It is APC and involved and involved in thymic cell educationin thymic cell education..
Type III:Type III: Located at the boundary of the cortex and medulla.Located at the boundary of the cortex and medulla. A kinds of APCs to present Ag.A kinds of APCs to present Ag.
Blood-thymus barrierBlood-thymus barrier
It is the structure between thymocytes and blood , a physical barrier to protect developing T-lyphocytes from exposure to Ag.
Components: lining endotheium of capillary wall and
its basal lamina;
macrophages in the perivascular C.T.;
type I endothelioreticular cells with
their tight junctions.
Thymic medullaThymic medullaIt contains epithelioreticular cells (more) and T lymphocytes(less).
T lymphocytes here are mature ones.
There have another 3 types of epithelioreticular cells
Type IV: located between the medulla and cortex;
Type V: located throughout the medulla;
Type VI: form the thymic or Hassall’s corpuscles in medulla
Thymic corpuscleThymic corpuscleThymic corpuscle: a characteristic feature of the thymus.
It is a isolated mass of closely packed,
concentrically arranged type VI
epithelioreticular cells .
Found in the thymic medulla.
Function of the thymusFunction of the thymus
Site of T lymphocyte educationSite of T lymphocyte education stem cells maturation and stem cells maturation and differentiation into T lymphocytesdifferentiation into T lymphocytes
Cortex Cortex Cortex consists ofCortex consists of superficial cortex, paracortex and sinusessuperficial cortex, paracortex and sinuses 1. superfacial cortex1. superfacial cortex is organized into nodules, mainly is organized into nodules, mainly composed of composed of B-lymphocytesB-lymphocytes..
It is also bone marrow-dependent cortex.It is also bone marrow-dependent cortex. 2. Paracortex2. Paracortex is free of nodules, mainly composed of is free of nodules, mainly composed of T-lymphocytesT-lymphocytes.. It is also thymus-dependent cortex.It is also thymus-dependent cortex.
3.Sinuses3.Sinuses is divided into subcapsular sinuses and trabecular is divided into subcapsular sinuses and trabecular sinuses where filter the flowing lymph through it.sinuses where filter the flowing lymph through it.
Specialized high endothelial venulesSpecialized high endothelial venules (HEVs) (HEVs)
Location:Location: in the paracortex in the paracortex
Function:Function: entry of circulating lymphocytes into the entry of circulating lymphocytes into the
lymph node---enlarging immune responselymph node---enlarging immune response
recirculation of of lymphocytesrecirculation of of lymphocytes
blood vessels lymph nodes blood vessels lymph nodes
lymphatic vessels lymphatic vessels
HEVs
Bone marrow
thymus
MedullaMedulla
Medulla consists of medullary cords and sinuses.Medulla consists of medullary cords and sinuses.
Medullary cords:Medullary cords: cords of lymphatic tissue containing cords of lymphatic tissue containing
B cells,plasma cells and macrophagesB cells,plasma cells and macrophages
Medullary sinuses:Medullary sinuses: similar with the sinuses in the cortex similar with the sinuses in the cortex but with more macrophages.but with more macrophages.
Functions of lymph nodeFunctions of lymph node
(( 11 )) filtering lymphfiltering lymph ;;
(( 22 )) initiate immune responses. initiate immune responses.
phagocytosis of macrophage;phagocytosis of macrophage;
B cells proliferate and differentiate intoB cells proliferate and differentiate into
plasma cells and memory B cells.plasma cells and memory B cells.
3. spleen3. spleen the structure of the spleen:capsule,red pulp and white pulpthe structure of the spleen:capsule,red pulp and white pulp
Capsule of the spleenCapsule of the spleen
Capsule: Capsule: C.T. containing myofibroblasts, blood vessels,etc.C.T. containing myofibroblasts, blood vessels,etc.
spleen
Red pulp
White pulp
Periarterial lymphatic sheath(PALS)
Malpighian body ( splenic nodule )
Splenic cord
Splenic sinus
Paracortex in lymph node
Lymphatic nodule in lymph node
Cord of lymphatic tissue with lots of blood cells
White pulpWhite pulp
Malpighian body:
Periarterial lymphatic sheath:
A thick accumulation of lymphocytes surA thick accumulation of lymphocytes surrounding the artery.rounding the artery.
Red pulpRed pulp
It contains large number of blood cells that it filters It contains large number of blood cells that it filters and degrades.and degrades.
Splenic cord: a meshwork of reticular cells and fibers
containing lots of RBCs, macrophages,
plasma cells,etc.
Splenic sinus: special sinusoidal vessels lined by rod-
shaped epithelial cells. The processes
of macrophages extend into the sinuses.
Function of the spleenFunction of the spleen
It performs both immune and hemopoietic functionsIt performs both immune and hemopoietic functions
1. filtering blood: killing pathogenic Ag and destroying s1. filtering blood: killing pathogenic Ag and destroying senescent, abnormal RBC ,etc.;enescent, abnormal RBC ,etc.;
Splenectomy----increasing abnormal RBC in bloodSplenectomy----increasing abnormal RBC in blood Splenomegaly----malariaSplenomegaly----malaria
2. initiation of immune responses2. initiation of immune responses ;;
3. formation of blood cells during early fetal life3. formation of blood cells during early fetal life ;;
4. storage of blood.4. storage of blood.
Key pointsKey points
1.T-lymphocytes get mature in thymus while B-lymphocytes get mature 1.T-lymphocytes get mature in thymus while B-lymphocytes get mature in the bone marrow.B-lymphocytes can convert to plasma cells whicin the bone marrow.B-lymphocytes can convert to plasma cells which are responsible for producing Ab. h are responsible for producing Ab.
2. The structure and function of thymus: cortex and medulla . Hassall’s 2. The structure and function of thymus: cortex and medulla . Hassall’s corpuscle and blood-thymus barrier.corpuscle and blood-thymus barrier.
3.The structure and function of lymph node;the celular components of l3.The structure and function of lymph node;the celular components of lymphatic nodule and paracortex.ymphatic nodule and paracortex.
4.The structure and function of spleen:red pulp and white pulp ( malpig4.The structure and function of spleen:red pulp and white pulp ( malpighian body and ).hian body and ).
Thymic cortexThymic cortex
There are There are 33 types of epithelioreticular cells in thymic cortex. types of epithelioreticular cells in thymic cortex.
epithelioreticular cellsepithelioreticular cells
Type I Type II Type III
Located at the boundary of the cortex and capsule.Serve as a barrier that isolate thymocytes and C.T.
Located within the cortex .It is APC with MHC II molecules which are involved in thymic cell education.
Located at the boundary of the cortex and medulla.A kinds of APCs to present Ag.
antigen-presenting cell (APC)antigen-presenting cell (APC)
1. function1. function :: sequestering Ag and presentingsequestering Ag and presenting
it to helper CD4+T lymphocyte to it to helper CD4+T lymphocyte to facilitate immune responses.facilitate immune responses.
2. 2. componentscomponents :: macrophages,Kuffer cells of liver, macrophages,Kuffer cells of liver,
Langerhans’ cells in epidermis, Langerhans’ cells in epidermis, reticular dentritic cells of spleen reticular dentritic cells of spleen and lymph node,and lymph node, type II and type III epithelioreticular type II and type III epithelioreticular cell of the thymus and B lymphocytecell of the thymus and B lymphocyte
MHC MHC (major histocompatability gene complex)(major histocompatability gene complex)
MHC MHC I:I: expressed on the surface of all expressed on the surface of all
nucleated cells and platelets.nucleated cells and platelets.
MHC II:MHC II: expressed on the surface of all APCs. expressed on the surface of all APCs.
Circulation in the spleenCirculation in the spleen
Branches of splenic artery enter the white pulp froBranches of splenic artery enter the white pulp from trabeculae;m trabeculae;
Central artery :sends branches to white pulp Central artery :sends branches to white pulp itself and marginal sinuses;itself and marginal sinuses; continues to penicillar continues to penicillar arterioles in splenic cord ;arterioles in splenic cord ;
Penicillar arterioles continue with sheathed capillaPenicillar arterioles continue with sheathed capillaries which are empty the blood in the cord,then the ries which are empty the blood in the cord,then the blood cells enter the splenic sinuses.blood cells enter the splenic sinuses.