ICM Concept Map
-
Upload
ravenpiercey -
Category
Education
-
view
1.858 -
download
0
Transcript of ICM Concept Map

Concept Maps and Medical Interviewing
ICM I
April, 2011

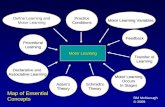
Concept Maps
• Concept mapping is a type of knowledge representation
• Representing knowledge in the visual format of a concept map allows one to gain an overview of a domain of knowledge
Adapted from John Pelley, PhD


Concept Maps
• Similar to an outline or a flowchart, a concept map is a way of representing or organizing knowledge.
• However, a concept map goes beyond the typical outline in that concept maps show relationships between concepts, including bi-directional relationships

Rotator Cuff

Rotator Cuff

The muscles of the rotator cuff

Concept Maps
• A concept map is a graphical representation where nodes (points or vertices) represent concepts, and links (arcs or lines) represent the relationships between concepts.
• The concepts, and sometimes the links, are labeled on the concept map.


Concept Maps
• The links between the concepts can be one-way, two-way, or non-directional.
• The concepts and the links may be categorized, and the concept map may show temporal or causal relationships between concepts.

Sample Concept Map
• An outline can be made more visual by spreading out information such as concepts, components, cause and effect relationships, characteristics, or definitions

12

13

Concept Mapping – Why?
• Concept maps create concrete experience!
• Visual organization of relationships– Visual structure aids long term memory
– “The magic isn’t in the map…”
• Active learning: requires decisions based on – Inspection – making a list
– Identification – finding terms that group
– Understanding – finding how things compare
14

Concept Mapping Applied to Communication and Interviewing

Complexity of Patient Interviews
• Much information may be gather in a clinical encounter with a patient.
• This information may be in the biomedical or psychosocial realms.

Complexity of Patient Interviews
• Organizing the information obtained in a interview will help the physician in making the proper diagnosis, know the patient as an individual, and develop a management plan tailored for the patient

Patient Interviews and Concept Maps
• One method to help organize the information obtained during the interview, its relationships, cause and effect, etc. may be through the use of concept maps

• “A consensus exits about the importance of effective communication between doctor and patient…
• Students may already possess good communication skills when they enter medical school…
• Before they have acquired much medical knowledge students tend to listen to what patients have to tell them, and are concerned about the emotional effects of illness and patients’ social difficulties.”
Kendrick and Freeling, 1993

The next slides review what will happen in yoursmall group interviewing
session…….

Exercise
• Interview SP
• Construct concept map as a group
• Present your concept maps to the whole group

Interview SP
• May use any method the group would like– One interviewer, ask the team for help
– Take turns, tag-team
– Ask questions as a group

Concept Map of Today’s Case
• The case may seem like a variety of separate components such as symptoms, problems, concerns, requests, etc, but actually all of these components are linked together in how the individual patient experiences his/her symptoms in the biological, psychological, and social perspectives.
Instructions presented to students

Concept Map of Today’s Case
• Constructing a “concept map” of the case will help you see the inter-relationships between these components.

Concept Map of Today’s Case
• We will use the concept map to utilize the information we gather from the patient not only to see the relationships between factors causing the patient’s symptoms, but also to begin to understand the patient as an individual in the context of his/her life.

How to make the concept map
• Begin by gathering the details of the case
• Identify the key “concepts” of this case: i.e. symptoms, problems, concerns, etc
• Write each “concept” on a post-it

How to make the concept map
• Begin to arrange the concepts into groups on the large piece of paper
• As you arrange the concepts into groups, name the group headings and make post-its with the group headings
• If these group heading can be combined under a larger heading make a post-it for this heading

How to make the concept map
• Begin to arrange the post-its • You need to decide if you are arrange a top
down, right to left, or center out concept map• For top down put the most generalized
concepts at the top, for right to left on the right, and for the center out put the most generalized concepts as the first “bubble” out from the middle

Top Down Concept Map

Central Design Concept Map

How to make the concept mapcontinued
• Begin to draw lines or arrows between the post-its. You may write what the relationship is above the lines if you wish.
• Modify your concept map according to group discussion
• Once you have decided on a map, copy it on the second piece of large paper



Your concept maps….
• What did you learn?
• How did your group function?
• Take home points
• Questions?
34