CHAPTER 7 MARKETING STRATEGY. Growth Strategies Marketing Choices Guerrilla Marketing Marketing Mix.
I 7 marketing
-
Upload
reindy-gustyawan -
Category
Education
-
view
1.242 -
download
2
description
Transcript of I 7 marketing

Sesi 7Sesi 7Understanding Marketing Processes and Consumer Behavior
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.McGraw-Hill/Irwin

Key TopicsDefinition of marketing
The external marketing environment
Segmentation and target marketing
The consumer buying process
Organizational markets and buying behavior
Consumer and industrial products
Branding and packaging

What Is Marketing?
““Planning and executing the conception, pricing, Planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives”organizational objectives”
““Planning and executing the conception, pricing, Planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives”organizational objectives”
Finding a need and filling it!Finding a need and filling it!Finding a need and filling it!Finding a need and filling it!
OROR

Nature of Marketing
To create value by allowing people and organizations to obtain what they need and want

The Exchange Relationship
Exchange:The act of giving up something (money, credit, labor, goods) in return for something else (goods, services, or ideas)
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Exchange Process: Giving Up One Thing in Return for Another
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Marketing Creates Utility
Utility--a product’s ability to satisfy human needs and wants
Place
Time
Ownership
Form
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Functions of Marketing
Buying
Selling
Transporting
Storing
Grading
Financing
Marketing research
Risk taking
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Marketing Concept
The idea that an organization should try to satisfy customer’s needs through coordinated activities that allow it to achieve its own goals (profit)
Did You Know? Trying to determine a customer’s true needs is difficult because no one fully understands what motivates people to buy.
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Evolution of the Marketing Concept
The production orientationDuring the second half of the 19th century
The sales orientationBy the early part of the 20th century
The marketing orientationBy the 1950s
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Marketing Orientation
Requires organizations to:Gather information about customer needs
Share that information throughout the entire firm
Use that information to help build long-term relationships with customers
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Developing Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy: A plan of action for developing pricing, distributing and promoting products that meet the needs of specific customers
Two major components:Selecting a target market
Developing the appropriate marketing mix
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

12-13
Selecting a Target Market
Market A group of people who have a need, purchasing power, and the desire and authority to spend money on goods, services, and ideas
Target market A more specific group of consumers on whose needs and wants a company focuses its marketing effort
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Total-Market Approach
The marketer tries to appeal to everyone and assumes that all buyers have the same needs
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Target Market Strategies Total-Market Approach
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Market Segmentation
Market Segmentation:A strategy to divide the total market into groups of people who have relatively similar product needs
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Market Segment
A collection of individuals, groups, or organizations who share one or more characteristics and have similar product needs and desires
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Bases for Segmenting Markets
Demographic
Geographic
Psychographic
Behavioristic
Did You Know? During its first year of operation, sales of Coca-Cola averaged just nine drinks per day for total first-year sales of $50. Today, Coca-Cola products are consumed at the rate of one billion drinks per day.
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Keys to Successful Market Segmentation
1. Consumers’ product needs must be heterogeneous
2. Segments must be identifiable and divisible
3. The market must be divided so segment sales, cost, and profit can be compared
4. One segment must have enough profit potential to justify a special marketing strategy
5. The chosen segment must be reached by the firm with a particular marketing strategy
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

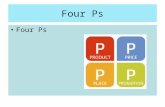
Marketing Mix: The “Four P’s”
(Distribution)(Distribution)
roductroductroductroduct ricingricingricingricing
romotionromotionromotionromotionlacelacelacelace

Developing the Marketing Mix
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Product
A good, service, or idea that has tangible and intangible attributes that provide satisfaction and benefit to consumers
Products should be sold at a profit
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Price
A value placed on a product or service that is exchanged between a buyer and seller
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Distribution
Making products available to consumers in the quantities and locations desired
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Promotion
A persuasive form of communication that attempts to expedite a marketing exchange by influencing individuals and organizations to accept goods, services, and ideas
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Promotional Mix
AdvertisingAdvertising
Personal Selling
Personal Selling
Sales Promotions
Sales Promotions
Public Relations
Public Relations

Marketing Research & Information Systems
Marketing researchA systematic, objective process of getting customer information to guide marketing decisions
Marketing information systemA framework for assessing information about customers from internal and external sources
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Collecting Data
Primary dataMarketing information that is observed, recorded, or collected directly from respondents
Secondary dataInformation that is compiled inside or outside an organization for some purpose other than changing the current situation
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Buying Behavior
The decision processes and actions of people who purchase and use products
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Psychological Variables of Buying Behavior
Perception
Motivation
Learning
Attitude
Personality
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Social Variables of Buying Behavior
Social roles
Reference groups
Social classes
Culture
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Marketing Environment
External forces that directly or indirectly influence the development of marketing strategies
PoliticalLegalRegulatorySocialCompetitiveEconomic, and technological
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Marketing Mix and the Marketing Environment
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

REVIEWJelaskan bagaimana supply dan demand dapat mempengaruhi jumlah produksi maupun distribusi
Sebutkan dan jelaskan mengenai “The Function of Management”
Apa yang dimaksud Competitive environtment dan Makro Environtment ?Jelaskan bagaimana lingkungan dapat berpengaruh terhadap bisnis
Sebutkan dan jelaskan bentuk-bentuk kepemilikan perusahaan
Jelaskan tantangan dan konsekuensi dari bisnis global
Faktor-faktor apa sajakah yang mempengaruhi pembentukan struktur organisasi? Sebutkan bentuk-bentuk struktur organisasi yang anda ketahui!
Apa yang dimaksud Marketing Mix ? Jelaskan!