Hypertension
-
Upload
devansh-mehta -
Category
Presentations & Public Speaking
-
view
42 -
download
0
Transcript of Hypertension

HypertensionBy Devansh Mehta
M.PHARM.(PHARMACOLOGY)M.B.A.(Pharmaceutical Marketing and Hospital Administration)
B.PharmacyContact No.:+91-8171552727

Stages of Hypertension
• Blood pressure has two components:• Systolic pressure is the top number. It represents the pressure the
heart generates when it beats to pump blood to the rest of the body.• Diastolic pressure is the bottom number. It refers to the pressure in
the blood vessels between heartbeats.

• Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). So blood pressure would be expressed, for example, as 120/80 mmHg.
• High blood pressure is diagnosed when one or both of these numbers is too high. High blood pressure is also called hypertension.

• Blood pressure is categorized as follows:• Normal: Less than 120/80 mmHg• Prehypertension: 120/80 to 139/89 mmHg• Stage 1 hypertension: 140/90 to 159/99 mmHg• Stage 2 hypertension: 160/100 mmHg and above

• Usually, systolic pressure increases as we age. However, after age 60, diastolic pressure usually begins to decline.
• Prehypertension is not a disease—yet. But it does mean you are at increased risk for developing high blood pressure.
• Although high blood pressure can cause symptoms such as headache and pounding heartbeat, it often causes no symptoms at all.

• Even when high blood pressure is not causing any symptoms, it can silently damage many organs, including the:
• Brain• Eyes• Heart• Kidneys• Arteries throughout the body
• You may not recognize the damage that silent hypertension has been doing to your body until you suddenly are stricken with a major disease. For example, hypertension increases your risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney failure.


• SymptomsUsually, hypertension does not directly cause symptoms. When blood pressure is very high, it can cause:
• Headaches• Dizziness• Fatigue• Ringing in the ears

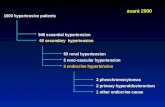
• Diagnosis• The diagnosis of hypertension depends on blood pressure readings.
Therefore, it's essential that blood pressure be measured carefully.

• To obtain an accurate blood pressure measurement:• Avoid the following for at least one hour before you have your blood
pressure taken:• Strenuous exercise• Smoking• Eating• Drinking caffeinated beverages
• Be seated for at least five minutes before the reading is taken.• Do not talk while your blood pressure is being measured.• Two readings should be recorded and averaged.

• If your blood pressure is high, your doctor should examine your eyes, heart and nervous system, to look for evidence of damage from hypertension.
• If there is no such evidence, you should return for at least two more blood pressure measurements. Only then should the doctor diagnose you with hypertension. That is because a single high reading can happen to anyone.
• Once you are diagnosed with hypertension, other tests will check for organ damage. These tests can include:
• Blood tests to check kidney function• An electrocardiogram (EKG) to look for:
• Thickening of the heart muscle• Reduced blood flow to your heart• Irregular heart rhythms

• Prevention• To prevent high blood pressure:• Get regular aerobic exercise• Limit your intake of salt and alcoholic beverages• Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in saturated fats• Avoid smoking• Maintain a desirable body weight• Hypertension increases your risk of heart attack and stroke. So it is important to modify your
risk factors for coronary artery disease. In addition to the above actions, you should:• Quit smoking• Reduce your high LDL (bad) cholesterol• You may be able to cure your hypertension with lifestyle changes alone.

http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/basics/tests-diagnosis/con-20019580
• Blood pressure measurements fall into four general categories:• Normal blood pressure. Your blood pressure is normal if it's below 120/80 mm Hg.
However, some doctors recommend 115/75 mm Hg as a better goal. Once blood pressure rises above 115/75 mm Hg, the risk of cardiovascular disease begins to increase.
• Prehypertension. Prehypertension is a systolic pressure ranging from 120 to 139 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure ranging from 80 to 89 mm Hg. Prehypertension tends to get worse over time.
• Stage 1 hypertension. Stage 1 hypertension is a systolic pressure ranging from 140 to 159 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure ranging from 90 to 99 mm Hg.
• Stage 2 hypertension. More severe hypertension, stage 2 hypertension is a systolic pressure of 160 mm Hg or higher or a diastolic pressure of 100 mm Hg or higher.

Diagnosis
• Hypertension is diagnosed on the basis of a persistently high blood pressure. Traditionally, theNational Institute of Clinical Excellence recommends three separate sphygmomanometer measurements at one monthly intervals.[48][49] The American Heart Association recommends at least three measurements on at least two separate health care visits.
• An exception to this is those with very high blood pressure readings especially when there is poor organ function.

Typical tests performed
Typical tests performedSystem Tests
Kidney Microscopic urinalysis, protein in the urine, BUN and/or creatinine
Endocrine Serum sodium, potassium, calcium, TSH
Metabolic Fasting blood glucose, HDL, LDL, and total cholesterol, triglycerides
Other Hematocrit, electrocardiogram, and chest radiographSources: Harrison's principles of internal medicines

Source:
• http://www.drugs.com/health-guide/high-blood-pressure-hypertension.html
• www.drugs.com

http://www.heart.org/
• The classes of blood pressure medications include:• Diuretics• Diuretics help the body get rid of excess sodium (salt) and water and
help control blood pressure. They are often used in combination with additional prescription therapies.

Generic name Common brand nameschlorthalidone Hygroton*chlorothiazide Diuril*furosemide Lasix*hydrochlorothiazide Esidrix*, Hydrodiuril*, Microzide*indapamide Lozol*metolazone Mykrox*, Zaroxolyn*

http://www.heart.org/
Potassium-sparing diureticsamiloride hydrochloride Midamar*spironolactone Aldactone*triamterene Dyrenium*
Loop diureticbumetanide Bumex*

Combination diureticsamiloride hydrochloride + hydrochlorothiazide Moduretic*spironolactone + hydrochlorothiazide Aldactazide*triamterene + hydrochlorothiazide Dyazide*, Maxzide*

Precautions while using Diuretics
Some noted possible side effects from diuretics:•Some of these drugs may decrease your body's supply of the mineral potassium. Symptoms such as weakness, leg cramps or being tired may result. Eating foods containing potassium may help prevent significant potassium loss. If your doctor recommends it, you could prevent potassium loss by taking a liquid or tablet that has potassium along with the diuretic. Diuretics such as amiloride (Midamar)*, spironolactone (Aldactone)* or triamterene (Dyrenium)* are called "potassium sparing" agents. They don't cause the body to lose potassium. They might be prescribed alone, but are usually used with another diuretic. Some of these combinations are Aldactazide*, Dyazide*, Maxzide* or Moduretic*.•Some people suffer from attacks of gout after prolonged treatment with diuretics. This side effect isn't common and can be managed by other treatment.•People with diabetes may find that diuretic drugs increase their blood sugar level. A change in medication, diet, insulin or oral anti-diabetic dosage corrects this in most cases.•Impotence may occur.

Beta blockers
Generic name Common brand names
acebutolol Sectral*
atenolol Tenormin*
betaxolol Kerlone*
bisoprolol fumarate Zebeta*
carteolol hydrochloride Cartrol*
metoprolol tartrate Lopressor*
metoprolol succinate Toprol-XL*
nadolol Corgard*
penbutolol sulfate Levatol*
pindolol* Visken*
propranolol hydrochloride* Inderal*
solotol hydrochloride Betapace*
timolol maleate* Blocadren*
Beta-blockers reduce the heart rate, the heart's workload and the heart's output of blood, which lowers blood pressure.

http://www.heart.org/
Combination beta-blocker/ diuretichydrochlorothiazide and bisoprolol Ziac*
Some noted possible side effects of beta-blockers:
•Insomnia•Cold hands and feet•Tiredness or depression•Slow heartbeat•Symptoms of asthma•Impotence may also occur•If you have diabetes and you're taking insulin, have your responses to therapy monitored closely.•If you have been prescribed beta-blockers, consult your healthcare provider prior to conception if you are considering pregnancy or if there is a chance you could become pregnant. If you discover that you are pregnant consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible to determine the safest medication for you at this time.

ACE inhibitors
• Angiotensin is a chemical that causes the arteries to become narrow, especially in the kidneys but also throughout the body. ACE stands for Angiotensin-converting enzyme. ACE inhibitors help the body produce less angiotensin, which helps the blood vessels relax and open up, which, in turn, lowers blood pressure.

Generic name Common brand namesbenazepril hydrochloride Lotensin*captopril Capoten*enalapril maleate Vasotec*fosinopril sodium Monopril*lisinopril Prinivel*, Zestril*moexipril Univasc*perindopril Aceon*quinapril hydrochloride Accupril*ramipril Altace*trandolapril Mavik*

• Some noted possible side effects of ACE inhibitors:
• Skin rash• Loss of taste• Chronic dry, hacking cough• In rare instances, kidney damage• Women who are taking ACE inhibitors or ARBs for high blood pressure should not
become pregnant while on this class of drugs. If you're taking an ACE inhibitor or an ARB and think you might be pregnant, see your doctor immediately. These drugs have been shown to be dangerous to both mother and baby during pregnancy. They can cause low blood pressure, severe kidney failure, excess potassium and even death of the newborn.

Angiotensin II receptor blockers
• These drugs block the effects of angiotensin, a chemical that causes the arteries to become narrow. Angiotensin needs a receptor- like a chemical "slot" to fit into or bind with- in order to constrict the blood vessel. ARBs block the receptors so the angiotensin fails to constrict the blood vessel. This means blood vessels stay open and blood pressure is reduced.

Generic name Common brand namescandesartan Atacand*eprosartan mesylate Teveten*irbesarten Avapro*losartan potassium Cozaar*telmisartan Micardis*valsartan Diovan*
Some noted possible side effects of Angiotensin II receptor blockers:
•May cause occasional dizziness.•ARBs should not be used during pregnancy. Medications that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury or even death to a developing fetus. When pregnancy is detected, consult your healthcare professional as soon as possible.

Calcium channel blockers
• This drug prevents calcium from entering the smooth muscle cells of the heart and arteries. When calcium enters these cells, it causes a stronger and harder contraction, so by decreasing the calcium, the hearts' contraction is not as forceful. Calcium channel blockers relax and open up narrowed blood vessels, reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure.

Generic name Common brand namesamlodipine besylate Norvasc*, Lotrel*bepridil Vasocor*diltiazem hydrochloride Cardizem CD*, Cardizem SR*, Dilacor XR*, Tiazac*felodipine Plendil*isradipine DynaCirc*, DynaCirc CR*nicardipine Cardene SR*nifedipine Adalat CC*, Procardia XL*nisoldipine Sular*verapamil hydrochloride Calan SR*, Covera HS*, Isoptin SR*, Verelan*

• Some noted possible side effects of calcium channel blockers:
• Palpitations• Swollen ankles• Constipation• Headache• Dizziness

Alpha blockers
Generic name Common brand namesdoxazosin mesylate Cardura*prazosin hydrochloride Minipress*terazosin hydrochloride Hytrin*
These drugs reduce the arteries' resistance, relaxing the muscle tone of the vascular walls.

Some noted possible side effects of alpha blockers:
•Fast heart rate•Dizziness•A drop in blood pressure when you stand up

Alpha 2 receptor agonist
Generic name Common brand namesmethyldopa
These drugs reduce blood pressure by decreasing the activity of the sympathetic (adrenaline-producing) portion of the involuntary nervous system. Methyldopa is considered a first line antihypertensive during pregnancy because adverse effects are infrequent for the pregnant woman or the developing fetus .
Some noted possible side effects of Alpha-2 Receptor Agonists:
•Methyldopa can cause drowsiness or dizziness

• Combined Alpha and Beta blockersCombined alpha and beta-blockers are used as an IV drip for those patients experiencing a hypertensive crisis. They may be prescribed for outpatient high blood pressure use if the patient is at risk for heart failure.
Generic name Common brand names
carvedilol Coreg*
labetolol hydrochloride Normodyne*, Trandate*
A noted possible side effect of combined alpha and beta-blockers:
•May cause a drop in blood pressure when you stand up

Central Agonist
• Central agonists also help decrease the blood vessels' ability to tense up or contract. The central agonists follow a different nerve pathway than the alpha and beta-blockers, but accomplish the same goal of blood pressure reduction.

Generic name Common brand namesalpha methyldopa Aldomet*clonidine hydrochloride Catapres*guanabenz acetate Wytensin*guanfacine hydrochloride Tenex*

Some noted possible side effects of central agonists:•Alpha methyldopa (Aldomet)* may produce a greater drop in blood pressure when you're in an upright position (standing or walking), and it may make you feel weak or faint if the pressure has been lowered too far. This drug may also cause drowsiness or sluggishness, dryness of the mouth, fever or anemia. Male patients may experience impotence. If this side effect persists, your doctor may have to change the drug dosage or use another medication.•Clonidine (Catapres)*, guanabenz (Wytensin)* or guanfacine (Tenex)* may produce severe dryness of the mouth, constipation or drowsiness. If you're taking any of these drugs, don't stop suddenly because your blood pressure may rise quickly to dangerously high levels.

Peripheral adrenergic blockers
• These medications reduce blood pressure by blocking neurotransmitters in the brain. This blocks the smooth muscles from getting the "message" to constrict. These drugs are rarely used unless other medications don't help.
Generic name Common brand namesguanadrel Hylorel*guanethidine monosulfate Ismelin*
reserpine Serpasil*

http://www.heart.org/
Some noted possible side effects of peripheral adrenergic inhibitors:•Reserpine may cause a stuffy nose, diarrhea or heartburn. These effects aren't severe, and no treatment is required other than to change the dosage. If you have nightmares or insomnia or get depressed, tell your doctor; you should stop using the drug.•Guanadrel (Hylorel)* or guanethidine (Ismelin)* may cause some diarrhea, which may persist in some people. This side effect usually becomes less of a problem if you continue treatment. These drugs reduce blood pressure more when you stand. Consequently, you may get dizzy and lightheaded and feel weak when you get out of bed in the morning or stand up suddenly. If you notice any of these reactions and if they persist for more than a minute or two, contact your doctor. He/she may instruct you to reduce or omit the next dose of the medication.•When taking guanethidine, don't stand in the hot sun or at a social gathering if you begin to feel faint or weak. These activities cause low blood pressure. Male patients may experience impotence. Contact your doctor if this occurs.

Blood vessel dilators (vasodilators)• Blood vessel dilators, or vasodilators, can cause the muscle in the
walls of the blood vessels (especially the arterioles) to relax, allowing the vessel to dilate (widen). This allows blood to flow through better.
Generic name Common brand nameshydralazine hydrocholoride Apresoline*minoxidil Loniten*†

Some noted possible side effects of vasodilators:
•Hydralzine (Apresoline)* may cause headaches, swelling around the eyes, heart palpitations or aches and pains in the joints. Usually none of these symptoms are severe, and most will go away after a few weeks of treatment. This drug isn't usually used by itself.•Minoxidil (Loniten)* is a potent drug that's usually used only in resistant cases of severe high blood pressure. It may cause fluid retention (marked weight gain) or excessive hair growth.
† Used in severe cases or when kidney failure is present.