hyperbolas
description
Transcript of hyperbolas

Hyperbolas translated away from the center

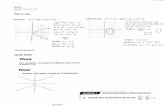
Example : Suppose the center is not at the origin (0, 0) but is at some other point such as (2, -1). To graph this hyperbola requires us to remember how graphs are moved horizontally and vertically by a change in the equation.
Using Example #1 above, we have
This will move the graph in our previous example 2 units right and 1 unit down. Both graphs are shown below.

Note that a = 3, b = 4,
In this graph the transverse axis is horizontal. Thus each focus is a distance of 5 horizontally from the center. One focus is at (7, -1) and one is at (-3, -1). Note that the graphing calculator does not do a good job of showing the top and bottom halves of the branches of the hyperbola joining at the vertices which are located at (-3, -1) and (5, -1).
Using this as a model, other equations describing hyperbolas with centers at (2, -1) can be written.
and the slope of the asymptotes is
If a = 3 and b = 2, and the transverse axis is horizontal, the equation is
The slope of the asymptotes is and the vertices are located at (-1, -1) and (5, -1).

The foci are located at
If a = 2 and b = 4, and the transverse axis is vertical, the equation is