Human respiratory system powerpoint presentation
-
Upload
ritu-sharma -
Category
Education
-
view
173 -
download
2
Transcript of Human respiratory system powerpoint presentation


Respiration
Process which involves taking in oxygen into the cells, using it for releasing energy by burning food and then eliminating the waste products like carbon dioxide and water from the body
It is a catabolic process as the food is broken down into simpler form. In short, respiration is a biochemical activity taking place with in the protoplasm of the cell and results in the liberation of energy

Breathing and RespirationBREATHING
1. Mechanism by which organisms obtain oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide
2. It is a physical process
3. It involves lungs of the organism
RESPIRATION
1. It includes breathing and oxidation of food in the cells of the organism to release energy
2. It is a biochemical process
3. It involves the mitochondria in the cells where food is oxidized to release energy

Types of respiration Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration
1. Oxygen is required
2. Such organisms are called aerobes
3. Occurs in mitochondria
4. Involves the process of glycolysis where glucose is broken down to pyruvic acid
5. Pyruvate is converted to CO2, water and energy by Krebs cycle
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
6. 38 ATP is generated
7. Occurs in all higher organisms
1. Oxygen is not required
2. Process is called anaerobiosis
3. It invovles the process of glycolysis in the cytoplasm.
4. It is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate CH3COCOO− + H+.
1. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP and NADH .
2. Pyruvate then enters different pathways and forms different products
3. Generally found in micro organisms , yeast and parasitic worms (prokaryotes)


Fermentation - Anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates and other organic compounds into alcohol, organic acids, gases etc .
When alcohol is produced it is called alcoholic fermentation
e.g. Yeast
C6H12O6 fermentation 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + Energy
C2H5OH ( acetobacter aceti) CH3COOH + H2O
(Ethanol) (Acetic acid)
Acetobacter aceti is used in the production of vinegar by converting the ethanol in wine into acetic acid.

When lactic acid is produced as an end product then it is called lactic acid fermentation e.g. Bacteria and parasitic worms
e.g. C6H12O6 2CH3CHOHCOOH + energy
(glucose) (lactic acid)
( The anaerobic respiration in human muscle tissue produces lactic acid as an end product during vigorous physical exercise)

Types of aerobic respirationDirect respiration
1. It is the exchange of oxygen (of air) with CO2 of the body cells
2. Without special respiratory organs or blood e.g. aerobic bacteria, plants, sponges
1. In this type special respiratory organs like skin, buccopharyngeal lining, gills, and lungs are used
2. It also involves the blood
Indirect respiration

Cutaneous Respiration- Respiration in which skin is used
e.g. annelids, amphibians
Buccopharnygeal respiration- Respiration in which buccopharyngeal lining is involved e.g. Frog, toad
Branchial respiration- It is exhibited by many annelids, most crustaceans, molluscs and all fishes

Types of indirect respirationExternal respiration
1. A physical process in which an organism takes in oxygen and gives out CO2
2. May involve respiratory surface such as integument,gills,trachea or lungs
3. E.g. gas exchange between air in the alveoli and blood in pulmonary capillaries
Internal respiration1. Also called tissue
respiration
2. Food is broken down into simpler molecules within the cells and energy is produced
3. E.g. gas exchange between tissue cells and the blood in systemic capillaries

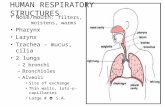
Human respiratory systemIt is chiefly divided into two components:
1. Respiratory tract
2. Respiratory organ
Respiratory Tract- A passage which allows movement of inspired and expired air in and out of the lungs. It consists of
1. Nostrils
2. Nasal chambers
3. Internal nares
4. Pharynx
5. Larynx
6. Trachea

Human Respiratory System

1. Nostrils-The two nostrils are the openings of the nasal cavity and lie above the mouth . They are separated by the septum
2. Nasal chambers- A pair of passages in the head above the palate. They are separated from each other by a septum.
Each nasal chamber is divided into three regions:
1. Vestibular region
2. Respiratory region
3. Olfactory region

• Vestibular region- Lies within the external naris, short and lined by hairy skin. Acts as a filter and prevents the entry of dust particles.
• Respiratory region- The middle region lined with respiratory epithelium. Ciliated and rich in mucous glands.
• Olfactory region- The upper region of the nasal chamber, lined with olfactory epithelium. Acts as an organ of smell.

3. Internal Nares-Openings of nasal chambers in the roof of nasopharynx and are closed by uvula during swallowing.
4. Pharynx-. The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat that is behind the mouth and nasal cavity and above the esophagus and the larynx ( the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs)
A short vertical approx. 12cm long tube behind the buccal cavity
It is divided into three parts:
1. Nasopharynx
2. Oropharynx
3. Larngyopharynx


Nasopharynx- Upper part of pharynx extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate
Oropharynx- Middle part of pharynx in front of the buccal cavityLaryngyopharynx- Lower part of pharynx, leads into two tubes the
trachea and the esophagus
5. Larynx- Often called Adam’s apple. More prominent in men than in women
A cartilaginous box helps in sound production hence called sound box . Enlarged upper end of the trachea situated in the neck on the level of the 4th to the 6th cervical vertebrae.Open into laryngopharynx by a slit like aperture called glottis
The glottis bears a leaf like cartilaginous flap called the epiglottis


6. Trachea- or windpipe is approx 4 inches long, extends from larynx to the middle of thoracic cavity where it divides into to bronchi (the right and left primary bronchi)
• One major branch enters each lung. The right primary bronchus
divides into the secondary bronchi, which extends into two lobes of the left lung.
• The secondary bronchi subdivides into smaller tertiary bronchi and further into still smaller bronchioles.
• The small terminal bronchioles give off the respiratory bronchioles which divide into alveolar ducts
This is called bronchial tree
The bronchial tree

The respiratory organs• The main respiratory organs are a pair of lungs
• The branching network of bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli comprise the lungs
• The lungs are two in number, fill the chest cavity lying one on each side separated in the middle by heart
• Lungs are covered by a double layered pleura with pleural fluid in between them
• This fluid acts as a lubricant permitting the lungs to move freely in the thoracic cavity during breathing

Mediastinum- It is the space in the thoracic cavity between the two lungs .It includes pleura of both the sides
The thoracic cavity- It is a hollow cavity and has two pleural cavities each enclosing a lung
It is barrel shaped bounded at the back by backbone andat the front by breast bone.
The sides are formed by the ribs
Diaphragm- A sheet of skeletal muscles, dome shaped muscular partition separating thorax from abdomen anteriorly at rest and attached to the lumber vertebrae and posteriorly to ribs performs an important role in respiration

External features of lungsLungs are soft spongy
elastic organs with smooth shiny surface
marked into numerous polyhedral areas
Conical in shape having a narrow apex at the upper end and broad concave base on lower end

Lungs are divided into lobes by fissures
The right lung has three lobes while the left lung has two lobes
Each of these lobes is composed of a number of lobules
Lungs consist of bronchioles and alveoli and an extensive network of blood vessels and the capillaries
The walls of the air sacs or alveoli are elastic and supplied with capillaries from the pulmonary artery and are kept moist by secretions to allow gases to diffuse.
It is done by the fluid produced by the walls of the alveoli
The surface tension of this fluid must be low else the alveoli may not expand when air is inhaled
The fluid therefore contains a surfactant ( a detergent like substance) to reduce surface tension

Pulmonary surfactantsPulmonary surfactant is a mixture of lipids and proteins which is
secreted into the alveolar space by epithelial type II cells. Themain function of surfactant is to lower the surface tension at theair/liquid boundary within the alveoli of the lung throughhydrophilic and hydrophobic forces.
Insufficient pulmonary surfactant in the alveoli can contribute tocollapse of part or all of the lung(atelectasis)

HUMAN LUNGS

In trachea and bronchi the goblet cells of the ciliated epitheliumproduce the mucus.
It is a slimy solution containing glycoprotein's
glycoprotein's are able to trap inhaled particles e.g. pathogensand dust
Chemical pollutants such as SO2 can dissolve in the mucus toform an acidic solution that irritates the airways
The nasal passages have tiny hairs lining them as well
macrophages, phagocytic WBC’s patrol the surface of the air waysremove particles such as bacteria

Mechanism of breathingWhen we breathe in and out the chest goes up and down
This happens when
• We inhale the ribs move upward and outward
• Chest becomes bigger
• When we exhale , the ribs move downwards and inwards
• Chest becomes smaller
Lungs are present in the chest cavity
The ribs surround this cavity on the sides
A large muscle called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity

During inhalation
• Ribs move out
• Diaphragm moves down
• Making the chest cavity bigger
• Air then rushes into the lungs and they inflate
During exhalation
• Ribs move downwards and inwards
• Diaphragm moves up
• Chest cavity is reduced
• Air rushes out of the lungs
• And the lungs grow smaller

THANK YOU
PREPARED BY
RITU.S