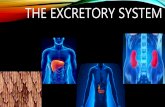
Human excretory system
-
Upload
shubham-agarwal -
Category
Science
-
view
42 -
download
1
Transcript of Human excretory system

NAME - SAKSHI AGARWALCLASS- Xth-CROLL NO. – 24

Excretory System The kidneys regulate the amount of water,
salts and other substances in the blood. The kidneys are fist-sized, bean shaped
structures that remove nitrogenous wastes (urine) and excess salts from the blood.
The ureters are tubes that carry urine from the pelvis of the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
The urinary bladder temporarily stores urine until it is released from the body.
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
The outer end of the urethra is controlled by a circular muscle called a sphincter.

Excretory System

The Kidney
Each kidney is composed of three sections: the outer (renal) cortex, the (renal) medulla
(middle part) and the hollow inner (renal) pelvis. The cortex is where the blood is filtered. The medulla contains the collecting ducts
which carry filtrate (filtered substances) to the pelvis.
The pelvis is a hollow cavity where urine accumulates and drains into the ureter.

The Parts of the Kidney

Function of the Kidney The principal function of the
kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body.
At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney.
If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the workload.

The kidney has other functions but it is usually associated with the excretion of cellular waste such as :
1) urea (a nitrogenous waste produced in the liver from the breakdown of protein. It is the main component of urine)
2) uric acid (usually produced from breakdown of DNA or RNA) and
3) creatinine (waste product of muscle action).

All of these compounds have nitrogen as a major component.
The kidneys are more than excretory organs.
They are one of the major homeostatic organs of the body.
They control water pH, secrete erythropoietin (a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production) and activate vitamin D production in the skin.
That is why a doctor can tell so much from a urine sample.

How blood is Filtered ?
The filtering units of the kidneys are the nephrons.
There are approximately one million nephrons in each kidney.
The nephrons are located within the cortex and medulla of each kidney.
The tubes of the nephron are surrounded by cells and a network of blood vessels spreads throughout the tissue. Therefore, material that leaves the nephron enters the surrounding cells and returns to the bloodstream by a network of vessels.

Parts of the Nephron
Each nephron consists of the following parts: 1) glomerulus ; 2) Bowman’s capsule ; 3) proximal tubule ; 4) loop of Henle ; 5) distal tubule ; 6) collecting duct.

A few disorders of the excretory system
Obstructive disorderskidney stones kidney cancer
Renal failure - (kidney failure)UTIs - urinary tract infections, often caused
by gram-negative bacteriacystitis-bladder infectionsurethritis-inflammation of the
urethrapyelonephritis- inflammation of the kidneys

kidney stones Cause - metabolic disorder involving
calcium, proteins and uric acid the build up of these substances into a large deposit (stone)
Symptoms - irritation of the urinary tract, bleeding in the urinary tract, in cases with large stones there can be extreme pain as
the stone(s) try to pass through the tract Treatments - removal by surgical means,
breakdown of stones by either physical (ultrasound) or chemical means, dietary changes to reduce chances of stones.

Renal (kidney) failure
Causes - infections, trauma,
diabetes, tumors
Symptoms - build up of toxins in the blood stream (urea), jaundice, fatigue
Treatments - dialysis, drug therapy, transplants

Ureters
ureters - In human, the ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle fibers that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually 25–30 cm long and 3–4 mm in diameter. Long narrow tubes with expanded upper end (renal pelvis) located inside each kidney. Function is to drain the renal pelvis to urinary bladder

ureter

Urinary bladder
urinary bladder- The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. Elastic muscular organ capable of great expansion. Function of urinary bladder is storage of urine.

Urinary bladder

Urethra
urethra – is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of fluids from the body . In male, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine.In female , the urethra is shorter and emerges at the female external urethral orifice above the vaginal opening.

urethra

THANKYOU