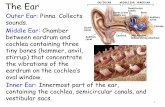
The Ear. 1. The outer ear collects sound waves. 2. The sound waves make the eardrum vibrate.
How do we hear? - · PDF file1. Sound waves are collected by the ear lobe or pinna. 2. The...
Transcript of How do we hear? - · PDF file1. Sound waves are collected by the ear lobe or pinna. 2. The...
Starter - recap
Which sound is:
The quietest
The loudest
The highest
The lowest
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
‘Ear’ ear Starter: Answer TRUE or FALSE Challenge: Answer why?
1) If your eardrum breaks you will be deaf forever 2) People use their ears in the same way bats do 3) Antibiotics can treat some hearing problems 4) The ear bones are in the middle of the ear
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
Objectives:
• Name the parts and positions of the ear
• Describe how sound is detected by the ear
• Explain some different types of hearing loss
‘Ear’ ear
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
1. Sound waves are collected by the ear lobe or pinna.
2. The waves travel along the ear canal.
3. The waves make the ear drum vibrate.
4. The small bones [ossicles] amplify the vibrations.
5. The cochlea turns the vibrations into electrical signals.
6. The auditory nerve takes the signals to the brain.
The Ear
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
Ears and hearing
Something vibrates to produce a sound. Sound travels through _____________ to the ear.
When the vibrations reach the eardrum they are transferred to the small _____________ called the hammer, anvil and stirrup. The bones pass the vibrations to the ____________.
This contains sense cells which change the vibrations to _____________ signals called impulses.
The auditory nerve takes the _____________ to the brain. We hear the sound when the message reaches the _____________ .
Ear canal
bones
cochlea
electrical
signals
brain © cgrahamphysics.com 2016
Sound key words
sound – A form of energy produced by vibrations, which is detected by the ear
cochlea – The part of the inner ear that changes vibrations into electrical signals which are then sent to the brain.
eardrum – The thin membrane in the ear which vibrates when sound reaches it.
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
Fun ear facts
Movie Sound - Lesson 4 - Ears All Shapes and Sizes.avi
Movie Sound - Lesson 4 - Human Body Ear - Hearing.avi
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
Use the questions and answers below to write sentences about the ear in your book.
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016
• Are 2 ears better than 1 for determining the direction of a sound?
• Could you devise an experiment to test this?
© cgrahamphysics.com 2016