Hip$Arthroscopy$$ · $Bony$Anatomy$ • Ball$and$Sockettype$ synovial$joint$ •...
Transcript of Hip$Arthroscopy$$ · $Bony$Anatomy$ • Ball$and$Sockettype$ synovial$joint$ •...

Hip Arthroscopy
Kennan Vance, DO

Problem
On average, Pa;ents with labral tears see an average of 4 physicians over a period of 2 years before the appropriate diagnosis is made
JBJS 2006; 88: 1448-‐57

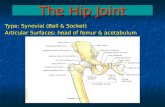
Bony Anatomy
• Ball and Socket type synovial joint
• Femoral Head and Neck • Acetabulum

Labrum
• Horseshoe shaped fibrocar;lage structure with aTachments inferiorly to the transverse acetabular ligament
• No intrinsic blood supply-‐comes from capsule and synovium
• Mul;ple nerve endings have been found within the labrum. (unlike the meniscus in the knee)

Labrum Cross Sec;on
• The Labrum and the Car;lage on the Acetabulum run together. Thus a tear in the labrum, usually disrupts the car;lage from the bone and causes a “delamina;on” injury.
• Watershed zone for blood supply
Labrum
Car;lage
Arthroscopy 2005; 21: 6

Labral Func;on
• Increases ar;cular surface area 22%
• Increases acetabular volume by 33%
• Contributes to joint stability in extremes of mo;on
• Provides a “seal” to the central compartment

Benefits of Labral Seal
• Resists distrac;on of femoral head from socket due to nega;ve intra-‐ar;cular pressure
• By maintaining fluid in central compartment, it allows more even distribu;on of compressive forces
• Provides nutri;on to the ar;cular car;lage and allows for a smooth gliding surface
• Allows for a low-‐fric;on environment by sealing fluid in central compartment
• With loss of “seal” it may increase joint compressive forces, increase joint fric;on, and lead to earlier OA

Labral Tear Mechanism
• Trauma;c (<50%) – External force to extended and ER hip
– Pivo;ng sports • Degenera;ve – 90% of atrauma;c labral tears have bony abnormali;es
– Femero-‐Acetabular Impingement (FAI)
– Dysplasia

FemoroAcetabular Impingement (FAI)
• Bony Mismatch of ball and socket joint
• Cam Lesion is an oval shaped femoral head
• Pincer is an overhang of the acetabulum
• Mixed lesion most common • With hip rota;on the ball
and socket have abnormal contact pinching and tearing the labrum
Cam lesion
Pincer

Consequences of FAI
• The abnormal contact leads to labral tears and car;lage lesions; which contributes to the breakdown of the joint and arthri;c changes

Treatment of FAI
• Tradi;onally done with an open surgical hip disloca;on with osteotomies performed.
• Arthroscopy has now replaced this method with less invasive approach, less damage to head blood supply, less infec;on, etc.

History
• Groin, Anterior, and Thigh Pain
• Pain with hip flexed and IR (impingement)
• Pain with sijng • Pain and catching with stairs or rising from a seated posi;on
• Back and SI joint pain
• Extra-‐ar;cular hip complaints – “hip dislocates” – “pops or snaps really loud”
– Pain on lateral side of hip; “can’t sleep on that side”

Physical Exam
• Difficult at best; an art in evolu;on
• Lots of overlap with SI joint, back, or extra-‐ar;cular problems
• Starts with inspec;on, palpa;on, ROM, and then special tests
• FADIR or Impingement test is workhorse

Physical Exam • Resisted SLR or “Ac;ve
Compression Test” • FABER for SI joint and
;ght Iliopsoas • Dynamic Internal
Rota;on Impingement Test (DIRIT)
• Dynamic External Rota;on Impingement Test (DEXTRIT)
• Intra-‐ar;cular injec;on – 87% sensi;ve and 100% specific for hip OA vs LSD

Imaging • Xrays • MRI with intra-‐ar;cular
contrast is the best imaging we currently have
• MRI can miss labral tears! • Not great for car;lage
lesions or “wave signs” • Arthroscopy is the gold
standard for diagnosing tears and other lesions

Arthroscopy • First performed in the 1970’s. • Slow to catch on due to several factors including difficulty and instrumenta;on
• Now more widely accepted and beTer understanding of hip pathology has progressed the art of hip arthroscopy
• Surgeons are con;nually pushing the spectrum of diseases that can be treated with arthroscopy. – Labral repairs and reconstruc;ons, FAI resec;on, Gluteus medius repairs, IT band releases, car;lage disorders, etc.

Who is a good candidate? • Non-‐arthri;c joint (>2mm
joint space) – 43% underwent THA within 3 yrs with <2mm. (10 ;mes more likely than if >2mm)
• No significant hip dysplasia
• BMI less than 35 ideally but more important is body morphology
• Non-‐osteoporo;c • Reasonable expecta;ons

How is it Performed?

Surgery Demo

Wave Sign

Results • Excision of labrum/car;lage
lesions without addressing bone yields 29-‐54% unsa;sfactory results
• Meta-‐analysis in 2010 indicates that addressing bony impingement was most convincing indica;on with good-‐excellent results from 69-‐89% of pts. – Labral debridement pts not as
good as repair
• Labral repair results are slightly beTer than debridement in short term results – We an;cipate with longer
follow up the results will be more convincing
– 15 studies showed good to excellent results ranging from 56-‐100%
CORR 2010;468:555-‐64

Complica;ons • Rate of 1.3-‐6.4% • Usually minor and transient
– Trac;on Neuropraxia to scia;c and pudental nerve
– Damage to LFC nerve • Intra-‐ar;cular damage from
surgery • Heterotopic Ossifica;on
– Naprosyn 500mg bid reduced incidence from 25% to 5.6%
– No prophylaxis aser mixed resec;ons were 16X’s more likely to develop HO
AJSM 2014;42(6) 1359-‐64

Factors Associated with Failure
• Older age • Presence of arthri;c changes
• Longer dura;on of symptoms
• Worse preopera;ve pain and func;onal scores

Other Hip Condi;ons Treated with Arthroscopy
• Synovial Disease • Loose Bodies • Iliopsoas release
– Internal Snapping hip • Adhesive Capsuli;s • Chondral Lesions • Joint Sepsis • Ruptured Lig Teres • External Snapping Hip • Greater Trochanteric Pain
Syndrome

Thanks