Heel pain: Plantar Fasciitis
-
Upload
otto-faulkner -
Category
Documents
-
view
94 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Heel pain: Plantar Fasciitis

Dr Isstelle JoubertMay 2011

Presenting History:
Mr A, 39yo manbilateral painful feet
one year history
gradual onset
no history of trauma or recent surgery lower limbs
job: salesman
Previous history:Surgical: both ankles, knee and right arm fracture
Medical: gout, chronic sinusitis
Social: OH stop July 2010, non-smoker, 4L coke DAILY!
Family history: dad died age 48 - myocardial infarction

Clinical examination:BP - 130/90
BMI - 39.8 (W=138kg, H=184cm)
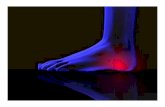
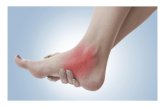
Examination of feet: localized tenderness plantar aspects, especially medial calcaneal tuberosities
Current chronic medication:Puricos 300 i od (raised u/a)
Glucophage 500mg i od (raised insulin)
Lorien 20mg i od (depressive mood)

Special investigations:X-ray of both feet - “heel spurs” seen on X-ray
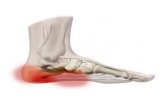
Heel spur

Management: Local infiltration of steroid (both heels)
Insoles in shoes
Weight loss advised
Follow-up: one foot - totally pain free
other one - some discomfort

Three stage assessment:
Biological
change his current health status drastically - diet, weight, level of exercise
Personal/Psychological impact
fear of loss of income if pain persists
stays at home when pain is unbearable
gets frustrated - conflict with clients
Social/contextual impact
expectations colleagues (not staying at home), family (activity, diet - better quality of life)

Problem list:
Active - bilateral painful feet
Passive
obesity
hyperinsulinaemia
family history - MI
increased blood levels of uric acid
unhealthy diet
no exercise

Differential diagnosis:
Plantar fasciitis
Tibialis posterior syndrome
Referred pain as a result of a S1-radiculopathy
Stress fracture - calcaneal or navicular
Fat pad injury
Peripheral neurogenic pain: tibial nerve related
Trigger point pain


Synonyms:
painful heel syndrome
heel spur syndrome
runner’s heel
subcalcaneal bursitis
periostitis
policeman’s heel (most of day-time on their feet)1

Definition:
musculoskeletal disorder
affecting the plantar aponeurosis or fascia
(inflammation)
mostly infero-medial aspect

Prevalence:
young and old
athletes and non-athletes
not gender specific2
United States3,4
600 000 outpatient visits annually
athletes, 5 - 14%5 of running injuries

Anatomy of the foot and plantar fascia:
arises: medial process of calcaneal tuberosity
attachment: distally to plantar aspect of the forefoot, medial and lateral intermuscular septa
mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical loading
noci-ceptors transmit info on pain and inflammation6

Pathophysiology:
not well understood
mechanical overload and excessive strain
microscopic tears in the fascia
triggering the inflammatory repair processes
entesal fibrocartilage - prone to degenerative change
increase cartilage cell clustering
formation of fissures within the fibrocartilage
ossification = spurs

Neurologic nerve entrapment
neuropathies
lumbar spine disorders
tarsal tunnel syndrome
Soft tissue achilles tendonitis
plantar fascia rupture
retrocalcaneal bursitis
fat pad atrophy
heel contusion
posterior tibial tendonitis
Skeletal calcaneal epiphysitis
inflammatory arthropathies
subtalar arthritis
calcaneal stress fracture
infections (osteomyelitis)
Other metabolic disorders:
osteomalacia, Paget’s
disease, sickle cell disease
tumors
vascular insufficiency
Differential diagnosis4,8,9:

Symptoms and signs:
pain inferior on heel
worse on weight bearing
worse: first few steps in the morning
persisting from months to years
character: throbbing or piercing
improves after resting - worsens again with continued activity throughout the day
limiting daily activities - walking barefoot, on toes or climbing stairs

tenderness localised to medial aspect of the calcaneal tuberosity

assessing gait: excessive supination or pronation

plantar fascia tight -stretching reproduce pain

Possible causes7:

Anatomical
•Pes planus (flat feet): strain - fascia try maintain stable arch during the propulsive phase of gait
•Pes cavus (high arch): strain - decreased eversion - absorb shock Activities
•running / dancing: max plantarflexion ankle + dorsiflexion MTP joints Elderly persons - non-supportive / inappropriate footwear10
Obesity / increased work-related weight bearing
study found NO association for BMI11
Possible causes7...

Special investigations:
•aim
confirm the diagnosis
•modalities available
ultrasound plain x-rays of feet bone-scan MRI nerve conduction studies blood tests

• Ultrasound
useful
non-invasive technique
increased thickness + hypo-echoic fascia
Special investigations:

• Plain x-rays of feet
generally unhelpful
rule out stress fractures of calcaneus
calcifications noticed + osteophytes (heel spurs)
study: osteophytes visible 50% with plantar fasciitis, 19% without plantar fasciitis12
Special investigations:

• Bone-scan
increased uptake at the calcaneus not very specific technique
very sensitive
potential malignant bony lesions
Special investigations:

• Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
thickening of the plantar fascia detecting tears or rupture of the fascia
Special investigations:

• Nerve conducting studies
no improvement in three months’ of conservative Rx
? other causes: nerve entrapment / tarsal tunnel syndrome
Special investigations:

• Blood tests
CRP - ? infection
HLA B27-genes - ? HLA-B27-spondyloarthropaties (psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis)
uric acid - gout
raised ALP, normal PO4 + Ca2+ - ? Paget’s disease
Special investigations:

Management:
•Avoidance of aggravating activities
•Cryotherapy
•NSAID
•Stretching
•Taping
•Foot orthoses
• Night splinting
• Soft tissue therapy
• Corticosteroid injection
• Iontophoresis16
• Extracorporeal shock wave therapy17,18
• Surgery

Management: • Avoidance of aggravating activities
• Cryotherapy8 ↓ pain by
↓ motor, sensory nerve conduction velocity
↓ swelling, cellular metabolism
methods
reusable cold packs / crushed ice bags
ice massage / endothermal cold packs
(towel between bag and skin - avoid nerve damage/ frostbite)
on area of pain - 5 - 30 minutes
• NSAID: orally / topically / injection (1st month of Rx)
↓ local inflammation

Management:
• Stretching7:
• Focus on calf and Achilles tendon or plantar fascia itself
• Key-component in Rx
• Short term benefits pain relief increased calf flexibility
• Long-term benefits decrease in pain and functional limitations high rate of satisfaction effective inexpensive easy to implement-tool

Management:
• Taping:
designed to provide inversion of the calcaneus
improving the biomechanical position and stability
limits the range of motion
increase proprioception
increase reduction of intensity of pain
• Biomechanical correction with foot orthoses:
↓ pain associated with plantar fasciitis14
prefabricated foot orthoses + stretching = ↓ pain
silicone heel pads / well supported arches and midsoles

Management: • Night splints or Strasbourg sock:
maintains ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension
constant mild stretch of fascia
allows heal at a functional length
indicated – no improvement after 6 months
wearing - 3 months

• Soft tissue therapy:
manual therapeutic techniques aim - restore normal muscle length + joints movement
Management:
• Corticosteroid injection15
advantages ↓ inflammatory processoutpatient basisfast recoverypain ↓
risk of rupture of the plantar
mixture: 4ml of local anaesthetic 1ml of corticosteroid

Management:
•Iontophoresis16
topically applied steroid
Dexamethasone 0.4% or acetic acid 5% delivered topically
propelled into the injured tissue with a small electric charge
short term pain relief (2 - 4 weeks)

Management: • Extracorporeal shock wave therapy17,18
what: • stimulation healing of the soft tissue• reduction of calcification• inhibition of pain receptors or denervation • to achieve pain relief
proposed responses due to• release of enzymes • hyperstimulation of axons• release of nitrous oxide and growth factors
Three devices • OssaTron • Epos Ultra • Sonorex

How?conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy
... Extracorporeal shock wave therapy17,18

Management:
... Extracorporeal shock wave therapy17,18
four main goals 50% improvement in pain from baseline ↓ pain on rising, walking in morning of at least 50% ↑ activity level + self-assessed ability to move pain free for time +
distance discontinuation of pain meds
Successful when: all criteria are met in 3 - 12 months after treatment

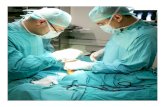
Management: • Surgery:
Options isolated, partial or complete release with or without the resection of the calcaneal spur excision of abnormal tissue or nerve decompression
Open or via endoscopic approach
Who? moderate to severe symptoms persistent resistant in spite of conservative management at least six months
Endoscopic procedures more rapid recovery return to pre-surgery activities

What is new / controversial in plantar fasciitis?
Shock waves
Elastography20
Botulinum toxin A21
Bipolar radiofrequency22
Acupunture23
Platelet rich plasma therapy24,25

• Shock waves:
• sound waves create vibrations
• cause controlled injury to tissue
• ↑ healing ability
• ↑ repair process
• Intracorporeal pneumatic shock19 therapy vs extracorporeal shock wave therapy
• energy generated inside / outside the body
• when extracorporeal shock devices are not available
• cheap, readily available, effective, safe
What is new / controversial in plantar fasciitis?

• Elastography20
new modality
measures tissue elasticity of plantar fascia
detect early stages of plantar fasciitis
ultrasonography (U/S):
• U/S: 65.8% sensitivity, 75% specificity
• elastography: 95% sensitivity, 100% specificity
• sono-elastography ↑ accuracy of dx from 68% to 96%
• staging of disease
What is new / controversial in plantar fasciitis?

• Botulinum toxin A21:
improve pain relief and overall foot function
ease severe muscle contractions
decrease inflammatory reactions
diminish wrinkles + tension headaches
Dr Brodsky, president of American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society
pain relief lasted at least one year
larger study under way
cost-effectiveness - $$
refractory patients
What is new / controversial in plantar fasciitis?

• Bipolar radiofrequency22:
minimally invasive technique
viable surgical treatment option
not improve on conservative measures
• Acupunture23:
enhances inhibitory processes
by stimulation of trigger points
muscles and peripheral nerves
increase the concentration of endorphins in the CNS
decreasing local inflammation
What is new / controversial in plantar fasciitis?

• Platelet rich plasma therapy24,25 (autologous growth factors)
new therapy
mid 1990’s for the discipline of maxillofacial surgery
pain relief
long lasting healing of musculoskeletal conditions
sample of patient’s blood - centrifuge
separates platelets from other components
concentrated platelet rich plasma injected into site of injury
initiates an increased healing response
lasting results
What is new / controversial in plantar fasciitis?

In conclusion...
think on your feet...
Be aware of many reasons for painful feet
Be aware of many management options
Plantar Fasciitis

References:
1.Akhtar A, Abbasie SH, Shami A et al. A comparative study of conventional versus interventional treatment in patients of plantar fasciitis. Ann Pak Inst Med Sci 2009; 5(2): 81-832.DiGiovanni BF, Nawoczenski DA, Lintal ME, et al. Tissue specific plantar fascia stretching exercise enhances outcomes in patients with chronic heel pain. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 2003;85A:1270-773.Riddle DL, Schappert SM. Volume of ambulatory care visits and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with plantar fasciitis: a national study of medical doctors. Foot Ankle Int 2004; 25:303-104.Cole C, Seto C, Gazewood J. Plantar Fasciitis: evidence-based review of diagnosis and therapy. Am Fam Physician 2005;72:2237-425.Noakes T. Lore of Running. Human Kinetics 20016.Wearing SC, Smeathers JE, Urry SR et al. The pathomechanics of plantar fasciitis. Sports Med 2006;36 (7):585-6117.Leaque AC. Current concepts Review: Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle international. 2008;29 (3) 358-366

References:
8.Brukner P, Khan K. Clinical Sports Medicine 3rd edition. McGraw Hill 2002.9.Murphy C. Plantar Fasiitis. Sportex.net10.Riddle DL, Pulisic M, Pidcoe P, et al. Risk factors for plantar fasciitis: a matched case-control study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85B (5): 872-711.Irving DB, Cook JL, Menz HB. Factors associated with chronic plantar heel pain: a systematic review. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2006;9:11-2212.DiMarcangelo MT, Yu TC. Diagnostic imaging of heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1997;14:281-301.13.Potter AJ. Investigating plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle online Journal. Nov 2009 2(11):4.14.Hume P, Hopkins W, Rome K et al. Effectiveness of Foot orthoses for treatment and prevention of lower limb injuries. Sports Med 2008; 38 (9): 759-779

References:
15.Wen-Chung T, Chih-Chin Hsu, Carl PC et al. Plantar fasciitis treated with local steroid injection: comparison between sonographic and palpation guidance. Journal of Clinical U/S Jan 2006 ; 34 (1) 12-1616.Foye PM, Lorenzo CT. Physical medicine and rehabilitation for plantar fasciitis treatment and management. Sep 2010.17.Kaltenborn JM. The Efficacy of Extracorporeal shock-wave treatment: a new perspective. Human Kinetics. 2005;6:50-5118.Moretti B, Garofalo R, Patella V et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in runners with a symptomatic heel spur. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrose 2006; 14:1029-103219.Dogramaci Y, Kalaci A, Emir A, Yanat AN, Gökce A. Intracorporeal pneumatic shock application for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a randomized, double blind prospective clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010 Apr; 130 (4): 541-6. Epub 2009 Aug 1120.Kapoor A, Sandhu HS, Sandhu PS et al. Realtime elastography in plantar fasciitis: comparison with ultrasonography and MRI. Current orthopaedic practice. Nov/Dec 2010; 21(6): 600-608

References:
21.Zablocki E. Botulinum toxin injection decreases plantar fascia pain. Medscape medical news. Nov 2005.22.Weil L Jnr, Glover JP, Weil LS Sr. A new minimally invasive technique for treating plantar fasciosis using bipolar radiofrequency: a prospective analysis. Foot Ankle Spec Feb 2008; 1 (1): 13-1823.Perez-Millan R, Foster L. Low frequency electro-acupuncture in the management of refractory plantar fasciitis: a case series. Medical Acupuncture: a Journal for physicians by physicians. 2001(13) nr 1.24.Creaney L, Hamilton B. Growth factor delivery methods in management of sports injuries: the state of play. Br. J. Sports Med. Nov 2007.25.Barrett SL, Erredge SE . Growth Factors for Chronic Plantar Fasciitis? Podiatry Today. Nov 2004.















![Plantar Fasciitis€¦ · Plantar Fasciitis [ 2 ] Heel bone (Calcaneus) Area of pain Plantar fascia. What causes Plantar Fasciitis? Suddenly increasing activity levels, or being overweight,](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f03fb297e708231d40bba04/plantar-fasciitis-plantar-fasciitis-2-heel-bone-calcaneus-area-of-pain-plantar.jpg)